
CFD forex trading opens a world of high-octane financial possibilities, but it’s a double-edged sword. This isn’t your grandma’s savings account; we’re talking leveraged trades on global currency markets, where fortunes can be made (or lost) in the blink of an eye. Understanding the mechanics, risks, and strategies is crucial before diving in. This guide breaks down the complexities of CFD forex trading, helping you navigate this thrilling yet potentially perilous landscape.
We’ll dissect the core differences between CFDs and traditional forex trading, exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. We’ll then delve into the nitty-gritty of market analysis, covering technical indicators, fundamental analysis, and risk management strategies specifically tailored for CFD forex trading. Think of this as your survival manual for the forex jungle.
Introduction to CFD Forex Trading

Forex trading, the global exchange of currencies, has always been a thrilling yet complex arena for investors. Now, with the rise of Contracts for Difference (CFDs), a new layer of accessibility and leverage has been added to the mix. This introduction will unravel the mechanics of CFD forex trading, highlighting its distinctions from traditional forex trading and weighing its advantages and disadvantages.
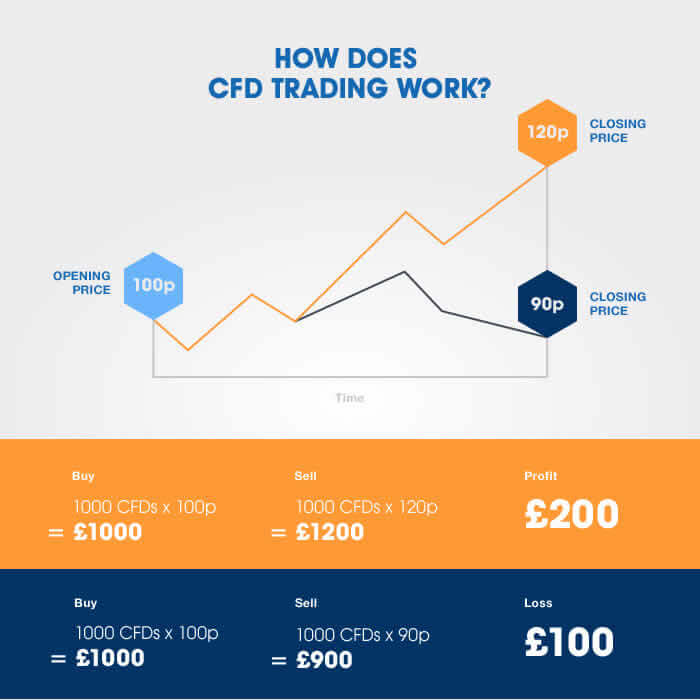
CFD forex trading allows you to speculate on the price movements of currency pairs without actually owning the underlying assets. You’re essentially betting on whether the price will go up or down. Instead of buying and selling currencies directly, you enter into a contract with a broker agreeing to exchange the difference between the opening and closing price of a currency pair, multiplied by the contract size. This difference, plus or minus any applicable fees, is your profit or loss.
CFD Forex Trading Mechanics
The process begins with opening a CFD trading account with a broker. You then select a currency pair (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/JPY) and specify the trade size (lots). You choose whether to go “long” (expecting the price to rise) or “short” (expecting the price to fall). The profit or loss is determined by the difference between the entry and exit price multiplied by the lot size and the leverage applied. For example, if you go long on 1 lot of EUR/USD and the price increases by 10 pips, you’ll make a profit (the exact amount depending on the broker’s specifications and leverage). Conversely, if the price decreases, you’ll incur a loss. The leverage provided by the broker magnifies both potential profits and losses.
Differences Between CFDs and Traditional Forex Trading
Traditional forex trading involves actually buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market. This requires owning the assets outright. With CFDs, you’re speculating on price movements without taking ownership. This key difference impacts several aspects, including capital requirements, risk exposure, and regulatory oversight. In traditional forex trading, you need sufficient capital to purchase the currency pair outright. With CFDs, leverage allows you to control larger positions with smaller capital investment, significantly amplifying potential returns but also increasing risk. Additionally, the regulatory environment for CFD trading can differ from that of traditional forex trading, depending on the jurisdiction.
Advantages of Using CFDs for Forex Trading
CFDs offer several advantages. The most prominent is leverage, enabling traders to control larger positions with less capital. This can amplify potential profits, though it also increases risk. Another advantage is the ability to go short, allowing traders to profit from falling prices. This flexibility is not always available in traditional forex trading. Furthermore, CFD trading offers relatively quick execution and accessibility through online trading platforms, making it convenient for many traders.
Disadvantages of Using CFDs for Forex Trading
Despite the advantages, CFDs also come with significant drawbacks. The high leverage inherent in CFD trading can lead to substantial losses if the market moves against the trader’s position. Moreover, CFD trading often involves overnight fees (rollover charges) which can erode profits or add to losses. The complexity of leverage and margin calls can also lead to unforeseen financial difficulties for inexperienced traders. Finally, the regulatory landscape for CFDs can vary significantly, and traders should carefully research the broker’s regulatory status and compliance to mitigate risks.
Find out about how best forex trading system can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Market Analysis for CFD Forex Trading

Navigating the forex market, especially with CFDs (Contracts for Difference), requires a keen understanding of market forces. Successful CFD forex trading hinges on accurately predicting price movements, and this is where market analysis comes into play. Whether you lean towards the technical or fundamental approach, or a blend of both, a robust analytical strategy is crucial for mitigating risk and maximizing potential profits.
Market analysis in CFD forex trading involves assessing various factors that influence currency prices. This assessment helps traders make informed decisions about buying or selling currency pairs. The two primary approaches are fundamental and technical analysis, each offering a unique perspective on market dynamics.
Technical Indicators in CFD Forex Trading
Technical analysis utilizes price charts and various indicators to identify trends and predict future price movements. These indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data, volume, and open interest. Several popular technical indicators used by CFD forex traders include:
- Moving Averages (MA): Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, highlighting the underlying trend. Simple Moving Averages (SMA) and Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) are commonly used. A bullish crossover occurs when a shorter-term MA crosses above a longer-term MA, suggesting a potential uptrend. Conversely, a bearish crossover signals a potential downtrend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. Readings above 70 generally suggest an overbought market, while readings below 30 indicate an oversold market. These levels are not absolute signals but rather suggest potential reversal points.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. MACD crossovers (above or below the signal line) and divergence between the MACD and price action can signal potential trend changes.
Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis in CFD Forex Trading
Fundamental analysis focuses on macroeconomic factors that influence currency values. This includes economic data releases (GDP, inflation, unemployment), political events, central bank policies, and geopolitical risks. Technical analysis, on the other hand, relies solely on price charts and indicators, disregarding fundamental factors.
A comparison reveals their distinct strengths and weaknesses. Fundamental analysis provides a long-term perspective, identifying underlying forces driving currency values. However, it can be less precise in predicting short-term price fluctuations. Technical analysis excels at identifying short-term trends and potential entry/exit points, but it might miss the bigger picture shaped by fundamental factors. Many successful traders employ a combination of both approaches, leveraging the strengths of each to gain a more comprehensive market outlook. For example, a trader might use fundamental analysis to identify a currency likely to appreciate over the long term due to strong economic fundamentals, and then use technical analysis to pinpoint optimal entry and exit points within that longer-term trend.
Risk Management Strategies for CFD Forex Trading
CFD trading involves significant risk due to leverage. Effective risk management is paramount to prevent substantial losses. Key strategies include:
- Position Sizing: Never risk more than a small percentage (e.g., 1-2%) of your trading capital on any single trade. This limits potential losses even if a trade goes against you.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to automatically exit a trade if the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. This prevents unlimited losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Set take-profit orders to automatically lock in profits when a trade reaches a target price. This helps secure gains and avoid giving them back.
- Diversification: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio across different currency pairs to reduce overall risk. A diversified portfolio is less susceptible to large losses from a single unfavorable market movement.
Trading Platforms and Tools
Navigating the world of CFD forex trading effectively hinges on choosing the right platform and mastering its tools. The platform you select will significantly impact your trading experience, from order execution speed to the availability of analytical resources. Understanding the features and capabilities of different platforms is crucial for successful trading.
The right platform empowers you with the tools to analyze markets, execute trades efficiently, and manage your risk effectively. A well-designed platform provides intuitive navigation, robust charting capabilities, and access to real-time market data, all essential components for informed decision-making.
Comparison of Popular CFD Forex Trading Platforms
Choosing a trading platform is a personal decision, depending on your individual needs and trading style. Below is a comparison of some popular platforms, highlighting key features. Note that fees and features can change, so always verify the latest information on the provider’s website.
| Platform Name | Features | Fees (Example – Check Provider’s Website) | Mobile App Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetaTrader 4 (MT4) | Widely used, extensive charting tools, automated trading (Expert Advisors), large community support, custom indicators. | Spreads vary by broker; commissions may apply. | Yes, iOS and Android |
| MetaTrader 5 (MT5) | Improved version of MT4, offers more advanced charting tools, economic calendar, and enhanced order types. | Spreads vary by broker; commissions may apply. | Yes, iOS and Android |
| cTrader | Known for its speed and low latency, advanced charting tools, and algorithmic trading capabilities. | Spreads vary by broker; commissions may apply. | Yes, iOS and Android |
| TradingView | Powerful charting platform with a vast range of indicators and drawing tools, social trading features, and access to various brokers. | Subscription fees for advanced features; brokerage fees apply separately. | Yes, iOS and Android |
Charting Tools and Their Impact on Trading Decisions
Charting tools are indispensable for analyzing price movements and identifying potential trading opportunities. These tools allow traders to visualize price action, identify trends, and spot patterns that can inform their trading decisions. Different chart types (candlestick, bar, line) offer varying perspectives on price data. Technical indicators, such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD, provide additional insights into market momentum and potential reversals. Drawing tools, such as trend lines, Fibonacci retracements, and support/resistance levels, help traders identify key price levels and potential turning points. For example, identifying a clear upward trend using moving averages and a candlestick chart might encourage a trader to take a long position, while a bearish divergence between price and an indicator like RSI could signal a potential price reversal and prompt a trader to consider a short position or exit an existing long position.
Essential Features of a Robust Trading Platform for CFD Forex Trading
A robust trading platform should offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to support effective trading. These include: real-time market data feeds providing up-to-the-minute price quotes; advanced charting capabilities with a wide range of technical indicators and drawing tools; various order types (market, limit, stop-loss, take-profit) to manage risk and execute trades precisely; automated trading capabilities (for experienced traders); secure and reliable platform infrastructure ensuring stable performance; a user-friendly interface allowing for intuitive navigation and easy trade execution; access to educational resources and customer support. The platform should also integrate seamlessly with mobile devices, enabling traders to monitor and manage their positions on the go.
Strategies and Techniques: Cfd Forex Trading
Conquering the forex market with CFDs requires a strategic approach. Understanding different trading styles and mastering the execution process is crucial for consistent profitability. This section delves into various strategies, providing a step-by-step guide to trading and analyzing both successful and unsuccessful examples.
Trading Strategies
Choosing the right trading strategy depends on your risk tolerance, time commitment, and trading goals. Three popular approaches are scalping, day trading, and swing trading. Each demands a different level of attention and expertise.
Scalping involves making numerous trades throughout the day, aiming for small profits on minute price fluctuations. This strategy requires intense focus and quick reflexes. Day trading, on the other hand, focuses on holding positions for a single trading day, capitalizing on intraday price movements. Swing trading, conversely, involves holding positions for several days or even weeks, profiting from larger price swings.
Executing a CFD Forex Trade: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully executing a CFD forex trade involves a methodical approach. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Market Analysis: Begin by analyzing the market using technical and fundamental indicators to identify potential trading opportunities. This might involve examining charts for patterns, assessing economic news releases, or evaluating geopolitical events.
2. Order Placement: Once a potential opportunity is identified, place your trade using your chosen trading platform. Specify the currency pair, trade size (lot size), and the type of order (e.g., market order, limit order, stop-loss order). A market order executes immediately at the current market price, while a limit order only executes when the price reaches a specified level. A stop-loss order automatically closes your position when the price moves against you, limiting potential losses.
3. Position Monitoring: Continuously monitor your position, keeping an eye on price movements and any news that could impact your trade.
4. Order Management: Adjust your stop-loss and take-profit orders as needed to manage risk and secure profits. This dynamic approach ensures that you adapt to changing market conditions.
5. Trade Closure: Close your position when your trading goals are met or when your risk management parameters are triggered. This could involve manually closing the position or letting your stop-loss or take-profit orders automatically close it.
Successful and Unsuccessful CFD Forex Trades
Analyzing successful and unsuccessful trades offers invaluable lessons.
Successful Trade Example: A trader identified a bullish trend in EUR/USD based on a combination of technical analysis (e.g., upward-trending moving averages) and fundamental analysis (e.g., positive economic data from the Eurozone). They placed a buy order at 1.1000, setting a stop-loss at 1.0980 and a take-profit at 1.1050. The price rose to 1.1060, resulting in a profitable trade. The success stemmed from a well-defined trading plan, proper risk management, and accurate market analysis.
Unsuccessful Trade Example: A trader entered a short position in GBP/USD based solely on a hunch, without proper analysis. They failed to set a stop-loss order. The price moved against their position, resulting in significant losses. The failure resulted from a lack of proper market analysis, inadequate risk management (no stop-loss), and impulsive trading decisions.
Risk Management and Capital Preservation
CFD forex trading offers incredible potential for profit, but it’s a double-edged sword. The high leverage available can amplify gains, but equally, it can magnify losses. Effective risk management isn’t just about protecting your profits; it’s about preserving your capital and ensuring you can continue trading even after experiencing setbacks. This section explores crucial risk management techniques to help you navigate the volatile forex market.
Leverage, Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders, and Position Sizing are essential elements in a robust risk management strategy. Understanding and implementing these will significantly reduce your risk and increase your chances of long-term success.
Leverage and its Implications for Risk
Leverage in CFD forex trading allows you to control a larger position than your actual capital would normally permit. For example, a 1:100 leverage means you can control $100,000 worth of currency with only $1,000 of your own money. While this amplifies potential profits, it also significantly increases losses. A small market movement against your position can quickly wipe out your entire account. Therefore, understanding and carefully managing leverage is paramount. Using high leverage should only be considered by experienced traders with a robust risk management plan in place. Conservative leverage levels, such as 1:10 or 1:20, are generally recommended for beginners.
Stop-Loss Orders and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss orders automatically close your position when the market moves against you by a predetermined amount, limiting potential losses. Take-profit orders automatically close your position when the market moves in your favor by a specified amount, securing your profits. These orders are crucial for managing risk, as they prevent emotional trading decisions and protect your capital from significant losses. For example, if you’re trading EUR/USD and anticipate a price increase, you might set a stop-loss order at a level slightly below your entry price to limit potential losses if the price moves against you. Simultaneously, you would set a take-profit order at a level reflecting your desired profit target.
Methods for Calculating Position Sizing and Risk Tolerance, Cfd forex trading
Determining your position size and risk tolerance is critical for successful risk management. One common method is to risk a fixed percentage of your account balance on each trade. For instance, a trader might decide to risk only 1% or 2% of their account balance per trade. This means if you have a $10,000 account and risk 1%, your maximum loss per trade would be $100. This approach ensures that a series of losing trades won’t quickly deplete your account. Another method involves calculating the position size based on a predetermined stop-loss level. For example, if you want to risk $100 on a trade and your stop-loss is 20 pips away from your entry price, you can calculate the appropriate position size based on the pip value of your currency pair. This ensures you never exceed your predetermined risk level, irrespective of the currency pair or leverage used.
Risk only what you can afford to lose. This is the golden rule of risk management.
Regulations and Legal Aspects
Navigating the world of CFD forex trading requires a solid understanding of the legal framework governing this market. Regulations vary significantly across jurisdictions, impacting everything from the licensing of brokers to the level of protection afforded to traders. Ignoring these legal aspects can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions.
The regulatory landscape for CFD forex trading is complex and constantly evolving. Different countries have different rules and oversight bodies. Some jurisdictions have robust regulatory frameworks designed to protect investors, while others have less stringent rules or even no specific regulations for CFDs. This lack of uniformity presents both opportunities and challenges for traders, necessitating careful due diligence before engaging with any broker.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in maintaining market integrity and protecting traders. These bodies establish rules and regulations, monitor market activity, and take enforcement actions against those who violate the rules. Examples include the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the US, and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia. Each body has its own specific rules and regulations, impacting the level of protection offered to traders and the types of brokers operating within their jurisdiction. Understanding the specific regulations of the jurisdiction where your chosen broker operates is paramount.
Legal Implications of Using CFDs for Forex Trading
Using CFDs for forex trading carries inherent legal implications. Traders need to be aware of the tax implications in their respective jurisdictions, as profits from CFD trading are generally considered taxable income. Additionally, understanding the contract specifications and terms is crucial to avoid disputes or legal issues. The legal framework surrounding CFDs also dictates aspects like margin requirements, leverage limits, and the potential for losses exceeding initial investment. It is vital to understand these aspects fully before engaging in CFD forex trading.
Traders’ Responsibilities Regarding Compliance and Responsible Trading
Traders bear the responsibility for understanding and complying with all applicable regulations and laws. This includes selecting regulated brokers, thoroughly reviewing contract terms, and maintaining accurate records of transactions. Responsible trading practices, such as risk management and avoiding excessive leverage, are also crucial. Failing to comply with regulations can result in penalties, including fines or legal action. Furthermore, irresponsible trading practices can lead to significant financial losses. Educating oneself on responsible trading strategies and adhering to legal requirements are essential for mitigating risks and protecting one’s capital.
Educational Resources and Further Learning
Navigating the world of CFD forex trading requires continuous learning. The market is dynamic, strategies evolve, and staying informed is crucial for success. This section explores various educational resources and learning methods, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages to help you choose the best path for your learning journey. Remember, consistent learning is key to long-term profitability and risk management.
Choosing the right learning method depends heavily on your learning style, available time, and budget. Some learners thrive in structured environments, while others prefer self-directed learning. Understanding these nuances will help you maximize your learning efficiency and ultimately, your trading success.
Reputable Websites and Educational Resources
Several reputable websites and platforms offer valuable educational resources for CFD forex traders, catering to both beginners and experienced individuals. Accessing these resources can significantly enhance your understanding of market dynamics, trading strategies, and risk management techniques.
- Babypips: Known for its beginner-friendly approach, Babypips offers a comprehensive curriculum covering forex basics, technical analysis, and trading psychology. Its free resources are excellent for building a solid foundation.
- Investopedia: A vast online encyclopedia of financial terms and concepts, Investopedia provides detailed explanations of forex trading, CFDs, and related topics. Its articles and tutorials are suitable for all skill levels.
- Myfxbook: This platform offers educational resources alongside tools for portfolio management and social trading. It allows you to analyze trading strategies and learn from experienced traders.
- DailyFX: Provides market analysis, educational content, and trading tools. Their educational materials cover a wide range of topics and skill levels.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Learning Methods
Different learning methods offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these trade-offs allows you to choose a learning path that best suits your individual needs and preferences. This informed choice will significantly influence your learning efficiency and overall success in CFD forex trading.
Find out about how forex trading seminar can deliver the best answers for your issues.
- Online Courses: Structured learning, expert guidance, often include interactive elements and assessments. Drawbacks can include cost and time commitment. Examples include Coursera and Udemy courses on financial markets.
- Books: Offer in-depth knowledge, often cheaper than online courses, and can be revisited repeatedly. However, they may lack interactive elements and updated information compared to online resources.
- Webinars: Provide real-time interaction with experts, often focused on specific topics. However, they are usually time-sensitive and may not offer the same depth as books or courses. Many brokerage firms offer free webinars for their clients.
- Mentorship Programs: Offer personalized guidance from experienced traders, leading to faster skill development. However, these programs can be expensive and require a significant time commitment.
Illustrative Examples (No image links)
Understanding CFD forex trading requires seeing it in action. Let’s examine both successful and unsuccessful trades to highlight key decision-making points and the impact of market conditions. These examples are simplified for illustrative purposes and don’t represent a guaranteed outcome in real trading.
Successful CFD Forex Trade: EUR/USD Long Position
This scenario involves a long position (buying) on the EUR/USD currency pair. The trader observed a period of sustained low volatility followed by a clear upward trend in the EUR/USD exchange rate, supported by positive economic news releases from the Eurozone, indicating increased strength of the Euro relative to the US dollar. The trader entered a long position at 1.1000. Technical indicators, such as a bullish crossover on a moving average, further confirmed the upward trend. Over the next few days, the EUR/USD rate rose steadily, reaching 1.1150. The trader closed their position at this price, realizing a profit of 150 pips (1 pip = 0.0001). This equates to a 1.5% return on investment, depending on the leverage used. The profit was secured before any potential reversal in the trend.
Unsuccessful CFD Forex Trade: GBP/USD Short Position
In this example, the trader took a short position (selling) on the GBP/USD currency pair. The trader believed the British Pound was overvalued based on recent economic data suggesting weakening economic growth in the UK. They entered a short position at 1.3000. However, unexpected positive news regarding Brexit negotiations caused a surge in demand for the Pound. The GBP/USD rate moved against the trader’s position, reaching 1.3150. The trader held onto the position hoping for a reversal, but the upward trend continued. Finally, the trader closed the position at 1.3200, incurring a loss of 200 pips (2%). This loss could have been mitigated by using a stop-loss order at a predetermined level (e.g., 1.3050), limiting potential losses. Furthermore, a more thorough analysis of geopolitical factors and news events influencing the GBP could have led to a different trading decision or a more effective risk management strategy.
Final Summary
Mastering CFD forex trading requires a blend of knowledge, discipline, and a healthy dose of risk management. While the potential rewards are undeniably enticing, remember that losses are just as possible. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge to navigate this dynamic market. However, continuous learning, practical application, and a realistic understanding of your risk tolerance are key to long-term success. Remember, it’s a marathon, not a sprint. So, buckle up, and trade responsibly!




