
How to Analyze Forex Market Trends? Think of it like reading tea leaves, but instead of mystical brews, you’re deciphering the cryptic whispers of global economies. This isn’t just about charts and graphs; it’s about understanding the heartbeat of international finance, predicting the ebb and flow of currencies, and potentially, making some serious bank. We’ll unravel the secrets of technical analysis, fundamental indicators, and risk management, turning you from a forex novice into a trend-savvy trader.
From understanding basic currency pairs and their valuations to mastering technical indicators like moving averages and RSI, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complex world of forex trading. We’ll explore how global events, economic data, and even political shifts can dramatically influence exchange rates, giving you a holistic view of market dynamics. Get ready to decode the forex market’s hidden language and learn how to predict its next move.
Understanding Basic Forex Market Mechanics

The forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market, is the largest and most liquid financial market globally. Understanding its mechanics is crucial for anyone looking to navigate this complex world. This section will break down the fundamental concepts, enabling you to grasp the core principles of forex trading.
Currency Pairs and Valuation
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another. These exchanges are represented as currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). The first currency listed is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. For example, an EUR/USD rate of 1.10 means that 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.10 US Dollars. The value of these pairs fluctuates constantly based on a multitude of factors.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates, How to Analyze Forex Market Trends
Several interconnected factors influence exchange rates, creating the dynamic nature of the forex market. Interest rate differentials between countries play a significant role. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for that currency and pushing its value up. Economic data releases, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment figures, also significantly impact currency values. Positive economic news tends to strengthen a currency, while negative news weakens it. Political events, such as elections or geopolitical instability, can cause dramatic shifts in exchange rates as market sentiment changes rapidly. Unexpected events, like natural disasters or significant policy changes, can also have a considerable impact.
Types of Forex Orders
Forex traders utilize various order types to execute trades according to their strategies and risk tolerance. A market order is executed immediately at the best available price. This is suitable for traders who want to enter a position quickly, but it may not always be at the most favorable price. A limit order allows traders to specify the price at which they want to buy or sell a currency pair. The order will only be executed if the market reaches that price. This offers better price control but carries the risk that the order may not be filled if the market doesn’t reach the specified price. A stop order, also known as a stop-loss order, is used to limit potential losses. It automatically sells a currency pair if it falls below a specified price (for long positions) or buys it if it rises above a specified price (for short positions). This helps protect against significant losses but does not guarantee the best exit price.
Major, Minor, and Exotic Currency Pairs
The forex market categorizes currency pairs into three main types based on their liquidity, volatility, and trading hours.
| Currency Pair | Volatility | Liquidity | Trading Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, USD/CAD | Generally Moderate | Very High | 24/5 (Except weekends) |
| EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, GBP/JPY, AUD/USD, NZD/USD | Moderately High | High | 24/5 (Except weekends) |
| USD/MXN, USD/TRY, USD/ZAR, EUR/TRY, GBP/PLN | High | Lower | 24/5 (Except weekends, potentially shorter hours for some pairs) |
Identifying Forex Market Trends
Navigating the forex market successfully hinges on your ability to accurately identify and interpret market trends. Understanding whether the market is trending upwards, downwards, or sideways is crucial for making informed trading decisions. This section will equip you with the tools and knowledge to decipher these trends effectively.
Uptrends, Downtrends, and Sideways Trends
Forex market trends are broadly categorized into three types: uptrends, downtrends, and sideways (or ranging) trends. An uptrend is characterized by a series of higher highs and higher lows, indicating a sustained upward price movement. Conversely, a downtrend displays lower highs and lower lows, signaling a consistent decline in price. A sideways trend, also known as a range-bound market, shows price fluctuations within a defined high and low, lacking a clear directional bias. Identifying these trends forms the bedrock of any successful trading strategy. Consistent identification allows traders to align their trades with the prevailing market sentiment, increasing the probability of profitable outcomes.
Identifying Potential Trend Reversals Using Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns provide valuable visual clues about potential trend reversals. These patterns, formed by the opening, closing, high, and low prices of a currency pair over a specific period, can signal shifts in market momentum. For instance, a “hammer” candlestick, characterized by a small body with a long lower wick, often suggests a potential bottom in a downtrend. Conversely, a “shooting star,” with a small body and a long upper wick, might indicate a potential top in an uptrend. Other important reversal patterns include the engulfing pattern (where a candle completely engulfs the previous candle) and the double top/double bottom patterns. Recognizing these patterns requires practice and experience, but mastering them significantly enhances your ability to anticipate trend changes.
Technical Indicators for Trend Confirmation
Technical indicators offer quantitative support for trend identification. Moving averages, for example, smooth out price fluctuations and highlight the overall trend direction. A simple moving average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific period, while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions, potentially signaling trend reversals. The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) compares two moving averages to identify momentum shifts and potential trend changes. By combining these indicators, traders can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market’s direction and strength. For example, a bullish MACD crossing above its signal line, coupled with an RSI above 50 and a price above its 20-day SMA, strongly suggests an uptrend.
Using Support and Resistance Levels to Predict Price Movements
Support and resistance levels are crucial for predicting price movements. Support levels represent price points where buying pressure is expected to overcome selling pressure, preventing further price declines. Resistance levels, conversely, mark price points where selling pressure is likely to outweigh buying pressure, hindering further price increases. These levels are often formed by previous highs and lows, psychological round numbers, or significant chart patterns. A breakout above a resistance level often signals a bullish continuation, while a break below a support level can indicate a bearish continuation. However, it’s crucial to remember that support and resistance levels are not absolute barriers; they can be broken, leading to significant price movements. A step-by-step approach involves identifying historical highs and lows, drawing horizontal lines at these levels, and monitoring price action around these lines. Once a breakout occurs, traders can use this information to adjust their strategies and potentially capitalize on the resulting trend. For example, if the EUR/USD consistently finds support at 1.1000, a break above this level could signal a potential move towards 1.1100 or higher.
Analyzing Technical Indicators for Trend Analysis
Technical indicators offer a powerful lens through which to view forex market trends, supplementing price action analysis. By understanding how these indicators work and interpreting their signals, traders can improve their ability to identify potential trend reversals and capitalize on market momentum. This section will explore three key indicators: moving averages, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
Moving Average Comparison
Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, revealing underlying trends. Different types of moving averages offer unique perspectives. Simple Moving Averages (SMAs) calculate the average price over a specified period, while Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) give more weight to recent prices, making them more responsive to changes. Weighted Moving Averages (WMAs) allow for custom weighting schemes, prioritizing certain periods as more significant.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Strengths: Simple to calculate and understand. Weaknesses: Lags behind price movements, susceptible to noise from short-term fluctuations.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Strengths: More responsive to recent price changes than SMA, better for identifying trend shifts. Weaknesses: Can be more volatile than SMA, potentially generating false signals.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA): Strengths: Customizable weighting allows traders to emphasize specific price periods. Weaknesses: More complex to calculate and interpret than SMA or EMA, requires careful selection of weights.
RSI Indicator Interpretation and Divergence
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. It oscillates between 0 and 100. Readings above 70 generally suggest an overbought market, while readings below 30 indicate an oversold market. Divergence occurs when price and RSI move in opposite directions.
RSI values above 70 often signal potential trend reversals, while values below 30 may suggest buying opportunities. Bullish divergence occurs when the price makes lower lows, but the RSI makes higher lows. This divergence can signal a potential upward trend reversal. Conversely, bearish divergence, where the price makes higher highs but the RSI makes lower highs, may precede a downward trend reversal. For example, if the EUR/USD price makes a series of lower lows, but the RSI forms higher lows, this bullish divergence could indicate a weakening of the downtrend and a potential buying opportunity.
MACD Indicator and Momentum Changes
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator identifies momentum changes and potential trend shifts by comparing two moving averages. It consists of a MACD line (difference between two EMAs), a signal line (EMA of the MACD line), and a histogram (difference between the MACD and signal lines).
Crossovers of the MACD line above the signal line often indicate a bullish signal, suggesting upward momentum and a potential trend continuation or initiation. Conversely, crossovers below the signal line are often considered bearish signals, suggesting downward momentum. The histogram’s height amplifies the strength of the signal; larger bars indicate stronger momentum. For example, a strong upward trend in GBP/USD might be confirmed by a MACD line crossing above its signal line accompanied by tall histogram bars.
Incorporating Fundamental Analysis into Trend Forecasting: How To Analyze Forex Market Trends
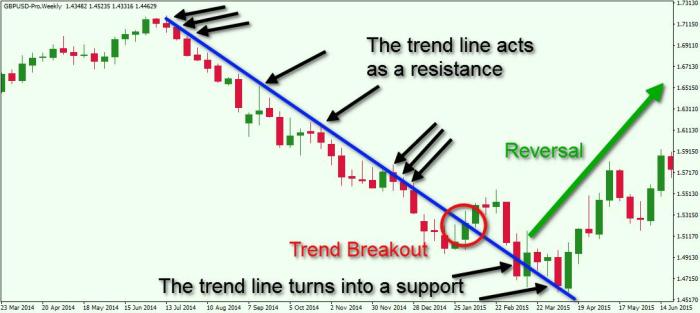
Fundamental analysis is the bedrock of successful long-term forex trading. While technical analysis charts price movements, fundamental analysis delves into the economic and political factors driving those movements. Understanding these underlying forces allows traders to anticipate shifts in currency values, enhancing their ability to predict trends and make informed trading decisions. Ignoring fundamental analysis is like navigating a ship without a map – you might get lucky, but you’re more likely to get lost.
Economic news and data releases act as powerful catalysts, often triggering immediate and significant price swings in the forex market. These events provide insights into a country’s economic health and future prospects, directly influencing investor sentiment and, consequently, currency demand. A positive surprise, such as unexpectedly strong GDP growth, can boost a currency’s value, while negative news can send it plummeting.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Influence on Currency Values
Several key economic indicators provide crucial information about a nation’s economic strength. Understanding their impact is paramount for effective fundamental analysis. A strong economy generally attracts foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and driving its value higher. Conversely, a weak economy often leads to capital flight and a depreciating currency.
Let’s look at three major indicators: Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, and unemployment. GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country. Higher GDP growth usually indicates a healthy economy and a stronger currency. Inflation, the rate at which prices rise, erodes purchasing power. High inflation generally weakens a currency as its value decreases relative to others. Unemployment reflects the percentage of the workforce without jobs. High unemployment often signals a struggling economy and can negatively impact currency value.
Obtain access to How to Use Moving Averages in Forex Trading to private resources that are additional.
Geopolitical Events and Central Bank Policies
Beyond economic data, geopolitical events and central bank policies significantly shape currency trends. Political instability, wars, or trade disputes can create uncertainty and volatility in the forex market, leading to sharp currency fluctuations. Central banks, through monetary policy decisions like interest rate adjustments, directly influence their national currencies. Raising interest rates typically attracts foreign investment, strengthening the currency, while lowering rates can weaken it. For example, the unexpected announcement of a new trade agreement between two major economies might send their respective currencies soaring, while the outbreak of a conflict in a region could cause a regional currency to plummet.
Impact of Economic Events on EUR/USD
The following table illustrates how different economic events might affect the EUR/USD currency pair. Remember that these are potential impacts, and the actual effect can vary based on market sentiment and other factors.
For descriptions on additional topics like How to Choose the Best Forex Trading Platform, please visit the available How to Choose the Best Forex Trading Platform.
| Event Type | Expected Impact on EUR | Expected Impact on USD | Overall Impact on EUR/USD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stronger-than-expected Eurozone GDP growth | Positive (EUR appreciates) | Neutral to slightly negative | EUR/USD rises |
| Increased US inflation | Neutral | Negative (USD depreciates) | EUR/USD rises |
| Unexpected rise in US unemployment | Neutral to slightly positive | Negative (USD depreciates) | EUR/USD rises |
| European Central Bank raises interest rates | Positive (EUR appreciates) | Neutral to slightly negative | EUR/USD rises |
| Geopolitical crisis in Europe | Negative (EUR depreciates) | Positive (USD appreciates as a safe haven) | EUR/USD falls |
Risk Management and Position Sizing in Trend Following
Successfully navigating the forex market isn’t just about identifying trends; it’s about protecting your capital while riding those trends. Risk management and proper position sizing are the cornerstones of consistent profitability in forex trading, acting as a safety net against inevitable losses and ensuring your trading journey is sustainable. Without a solid risk management plan, even the most accurate predictions can lead to devastating results.
Ignoring risk management is like sailing a ship without a rudder – you might get lucky for a while, but eventually, you’ll be at the mercy of the waves. The forex market is volatile, and unexpected events are common. A well-defined risk management strategy mitigates these risks, allowing you to trade confidently and consistently, even during periods of market uncertainty. This involves understanding your risk tolerance, setting appropriate stop-loss orders, and determining suitable position sizes.
Stop-Loss Orders: Your Safety Net
Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting potential losses. They are pre-set orders that automatically sell your currency pair when the price reaches a specified level, preventing further losses if the market moves against your position. Setting a stop-loss order is not optional; it’s a fundamental aspect of responsible trading. The placement of your stop-loss should be based on your analysis of the market and your risk tolerance, but it should always be in place before entering a trade. For example, if you’re trading EUR/USD, you might place a stop-loss order a few pips below your entry point to limit losses should the price suddenly reverse.
Risk Management Strategies: Different Approaches
Several risk management strategies help traders control their exposure. One popular method is fixed fractional position sizing. This involves risking a fixed percentage of your account balance on each trade, regardless of the potential reward. For example, a trader might risk only 1% or 2% of their account balance on each trade. This consistent approach prevents any single loss from significantly impacting the overall account balance. Another strategy is the use of trailing stop-losses, which move the stop-loss order in tandem with the price movement, locking in profits as the price goes in your favor. This allows you to take advantage of trends while minimizing risk as the trend progresses.
Determining Appropriate Position Sizes
Calculating appropriate position sizes requires understanding your risk tolerance and account balance. Let’s say you have a $10,000 account and you’re willing to risk 1% per trade ($100). If your stop-loss is set at 20 pips, you can calculate your position size using the following formula:
Position Size = (Risk Amount / Stop Loss in Pips) * Lot Size
In this example: Position Size = ($100 / 20 pips) * 10,000 units/lot = 5,000 units/lot (approximately 0.05 lots).
This means you should trade 0.05 lots of the currency pair to ensure your maximum loss per trade is limited to $100. Remember to adjust this calculation for your specific risk tolerance, account balance, and stop-loss placement. Different brokers may have different lot sizing, so always check your broker’s specifications.
Scenario: Improper Risk Management Leading to Losses
Imagine a trader with a $5,000 account who enters a trade without a stop-loss, risking their entire account balance on a single position. The market moves against them, and they lose everything. This is a stark illustration of the devastating consequences of ignoring risk management. Even with a well-defined strategy, it’s crucial to maintain discipline and consistently follow your risk management plan. The temptation to override your stop-loss or increase your position size beyond your risk tolerance can lead to significant losses, eroding your capital and potentially ending your trading career prematurely. Careful planning and strict adherence to your risk management strategy are essential for long-term success.
Chart Pattern Recognition for Trend Prediction

Chart patterns offer valuable insights into potential price movements in the forex market. By recognizing these recurring formations, traders can anticipate shifts in momentum and make informed trading decisions. While not foolproof, combining pattern recognition with technical indicators significantly enhances predictive accuracy. Understanding these patterns is a crucial skill for any serious forex trader.
Head and Shoulders Pattern
The head and shoulders pattern is a classic reversal pattern indicating a potential shift from an uptrend to a downtrend (or vice-versa for an inverse head and shoulders).
- Characteristics: A clear “head” forms, followed by two smaller “shoulders” on either side. A neckline connects the lows of the two shoulders. The head’s high is significantly higher than the shoulders’ highs.
- Confirmation Signals: A break below the neckline, confirmed by increased trading volume, is a strong bearish signal. Conversely, for an inverse head and shoulders, a break above the neckline with increased volume confirms a bullish reversal.
- Potential Outcomes: A successful head and shoulders pattern often leads to a price decline approximately equal to the height of the head from the neckline. The inverse head and shoulders pattern suggests a similar price increase.
Double Top/Bottom Pattern
Double tops and bottoms are powerful reversal patterns. A double top signals a potential shift from an uptrend to a downtrend, while a double bottom suggests a shift from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Characteristics: Two relatively equal highs (double top) or lows (double bottom) form, followed by a break below the neckline (double top) or above the neckline (double bottom).
- Confirmation Signals: A decisive break below the neckline of a double top or above the neckline of a double bottom, ideally with increased volume, confirms the pattern. Failure to break the neckline suggests the pattern might be invalid.
- Potential Outcomes: The price target for a double top is typically calculated by subtracting the distance between the neckline and the highest high from the neckline’s level. For a double bottom, add the distance between the neckline and the lowest low to the neckline’s level.
Triangles
Triangle patterns are continuation patterns, suggesting a period of consolidation before a potential breakout. There are several types of triangles, including symmetrical, ascending, and descending triangles.
- Characteristics: Triangles are characterized by converging trendlines forming a triangular shape. Symmetrical triangles show equal highs and lows converging. Ascending triangles have a flat bottom trendline and an upward sloping top trendline. Descending triangles have a flat top trendline and a downward sloping bottom trendline.
- Confirmation Signals: A breakout above the upper trendline of a triangle usually signals a continuation of the uptrend, while a breakout below the lower trendline signals a continuation of the downtrend. Increased volume during the breakout confirms the pattern’s validity.
- Potential Outcomes: The potential price movement after a breakout from a triangle is often equal to the triangle’s height (vertical distance between the widest points of the triangle). For example, if a symmetrical triangle has a height of 100 pips, the post-breakout move could be approximately 100 pips in the direction of the breakout.
Combining Chart Patterns with Technical Indicators
Using chart patterns alone can be risky. Combining them with technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, or MACD enhances accuracy and helps filter false signals. For example, a bullish divergence between the price and RSI, alongside a breakout from a double bottom pattern, significantly strengthens the bullish signal. Conversely, a bearish crossover of moving averages coupled with a head and shoulders pattern strengthens a bearish signal. This combined approach helps to minimize risk and improve trading success.
Concluding Remarks
Mastering forex trend analysis isn’t about getting rich quick; it’s about developing a keen understanding of market forces and making informed, calculated decisions. By combining technical analysis with fundamental insights and a robust risk management strategy, you can significantly improve your chances of success. Remember, the forex market is a dynamic beast, constantly evolving. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead of the curve. So, sharpen your analytical skills, embrace the challenge, and prepare to conquer the forex frontier.
Key Questions Answered
What’s the difference between a scalper and a swing trader in forex?
Scalpers aim for small profits on very short-term trades, often holding positions for only minutes. Swing traders, on the other hand, hold positions for days or weeks, capitalizing on larger price swings.
How can I stay updated on real-time forex market news?
Reliable financial news websites, dedicated forex trading platforms, and reputable economic calendars provide real-time updates on market-moving events.
What are some common mistakes beginner forex traders make?
Common mistakes include neglecting risk management, overtrading, emotional decision-making, and failing to develop a solid trading plan.
Are there any free resources available for learning forex analysis?
Many websites and online courses offer free introductory materials on forex trading and analysis. However, always be cautious of promises of guaranteed profits.






