What Is a Pip in Forex Trading? That’s the million-dollar question (or should we say, the million-pip question?) for anyone diving into the exciting – and sometimes terrifying – world of foreign exchange. Understanding pips is fundamental; it’s the bedrock upon which your forex profits (or losses) are built. Think of it as the smallest unit of currency movement, the tiny tick that makes or breaks your trade. Get ready to decode the secrets of these minuscule price shifts, because mastering pips is your key to forex fluency.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about pips, from their basic definition and calculation to their crucial role in risk management and strategy development. We’ll explore pipettes (those even tinier increments!), demonstrate how pip movements directly impact your profits and losses, and show you how leverage amplifies their effect. By the end, you’ll be able to confidently navigate the world of forex trading, armed with a deep understanding of these crucial price fluctuations.
Definition of a Pip in Forex
So, you’re diving into the exciting (and sometimes nerve-wracking!) world of forex trading? Understanding the basics is key, and one of the very first things you need to grasp is the concept of a “pip.” It might sound technical, but it’s actually pretty straightforward.
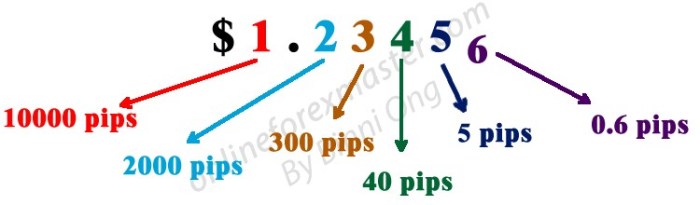
A pip, short for “point in percentage,” represents the smallest price movement in a currency pair. Think of it as the smallest increment you can see on the forex market’s price ticker. It’s the fundamental unit for measuring profit or loss in your forex trades. Most currency pairs are priced to four decimal places, with the last digit representing a pip.
Pip Value Calculation
Let’s say you’re trading the EUR/USD pair. If the price moves from 1.1000 to 1.1001, that 0.0001 increase is one pip. Now, the value of that pip depends on your trade size (the amount of base currency you’re trading). A larger trade size means a larger pip value. For example, a one-pip movement on a trade of 10,000 EUR would be worth more than a one-pip movement on a trade of 1,000 EUR. The exact value will also be influenced by the exchange rate between the base currency and your account currency. Forex brokers typically provide pip calculators to help you determine the value of a pip for your specific trade.
Numerical Example of Pip Change
Imagine you bought 10,000 units of EUR/USD at 1.1000. If the price rises to 1.1010, that’s a ten-pip movement (1.1010 – 1.1000 = 0.0010). Assuming a pip value of $10 per pip (this varies depending on your broker and trade size), your profit would be 10 pips x $10/pip = $100. Conversely, if the price dropped to 1.0990, you’d have a ten-pip loss of $100.
Beginner’s Definition of a Pip
In simple terms, a pip is the smallest price change you’ll see in a forex trade. It’s how you measure your profits and losses. Think of it as a tiny step up or down in the currency market.
Pip Value Calculation

Understanding pip value is crucial for effective forex trading. It directly impacts your profit or loss, so knowing how to calculate it is essential for managing risk and setting realistic trading goals. The value of a pip isn’t fixed; it fluctuates based on several key factors.
Pip value is determined primarily by two things: the lot size you’re trading and the specific currency pair involved. A lot size represents the number of base currency units you’re trading. For example, a standard lot is 100,000 units of the base currency. The currency pair itself influences pip value because it dictates the exchange rate between the base and quote currency.
Factors Influencing Pip Value
The value of a pip is influenced by the interplay between the lot size and the exchange rate of the currency pair. A larger lot size means a larger pip value, while the exchange rate determines the conversion of the pip value into your account’s base currency (usually USD). For instance, a pip in EUR/USD will have a different value than a pip in USD/JPY because of the differing exchange rates between the involved currencies. The base currency of your trading account also plays a role; if your account is in USD, pip values will be calculated in USD.
Calculating Pip Value for Different Currency Pairs
Let’s illustrate pip value calculation with examples. Remember, a pip is generally the fourth decimal place for most major pairs (except JPY pairs, where it’s the second decimal place).
Example 1: EUR/USD
Let’s say you’re trading a standard lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD, and the current exchange rate is 1.1000. A one-pip movement (0.0001) would be 100,000 units * 0.0001 = 10 units of EUR. To find the USD value, convert this to USD using the current exchange rate: 10 EUR * 1.1000 USD/EUR = $10. Therefore, the pip value is $10 for a standard lot of EUR/USD at this exchange rate.
Example 2: USD/JPY
Now consider a standard lot (100,000 units) of USD/JPY with an exchange rate of 110.00. A one-pip movement (0.01) is 100,000 units * 0.01 = 1000 units of JPY. To find the USD value, convert this using the exchange rate: 1000 JPY / 110 JPY/USD = approximately $9.09. Note the difference in pip value compared to the EUR/USD example.
Pip Value Table for Common Currency Pairs
The following table shows pip values for common currency pairs at different lot sizes, assuming a simplified exchange rate for illustrative purposes. Actual pip values will vary based on the current market exchange rate.
| Currency Pair | Lot Size | Pip Value (USD) | Pip Value (Base Currency) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.1 lot (10,000 units) | $1 | €0.91 (approx.) |
| EUR/USD | 1 lot (100,000 units) | $10 | €9.09 (approx.) |
| USD/JPY | 0.1 lot (10,000 units) | $0.91 (approx.) | ¥100 |
| USD/JPY | 1 lot (100,000 units) | $9.09 (approx.) | ¥1000 |
| GBP/USD | 0.1 lot (10,000 units) | $1.25 (approx.) | £1 (approx.) |
| GBP/USD | 1 lot (100,000 units) | $12.50 (approx.) | £10 (approx.) |
Pipettes in Forex Trading
Forex trading often involves minute price changes, and sometimes, even the smallest fraction of a pip matters. That’s where pipettes come in – they offer a level of precision that takes forex trading to the next level of detail. Understanding pipettes is crucial for traders aiming for maximum accuracy in their analysis and execution.
Pipettes represent a smaller increment of price movement than a pip. While a pip is typically the smallest price fluctuation displayed for a currency pair, a pipette represents a further subdivision of that pip. Think of it like centimeters versus millimeters – a centimeter is a pip, and a millimeter is a pipette. This added precision allows traders to observe even the tiniest price shifts, potentially influencing their trading strategies.
Pipette Value and its Relation to a Pip
A pipette is one-tenth of a pip (0.00001 for most currency pairs). Its value is directly tied to the pip value, simply being one-tenth of it. For example, if a pip’s value is $10, then a pipette’s value is $1. This means that the profit or loss generated by a pipette movement is ten times smaller than that of a pip. This increased precision allows for a more nuanced understanding of market movements and can be crucial for scalpers and those employing high-frequency trading strategies.
Pip and Pipette Display on Trading Platforms
The way pips and pipettes are displayed varies across different trading platforms. Some platforms might display the full five decimal places, explicitly showing the pipette value alongside the pip. For example, a price of 1.23456 might be displayed, where ‘6’ represents the pipette. Other platforms might only display four decimal places, effectively rounding off the pipette value. In such cases, the trader needs to be aware of the platform’s display settings to correctly interpret the price changes and calculate their potential profit or loss. Understanding the platform’s precision is vital to avoid misinterpretations and ensure accurate trade execution. Let’s imagine two scenarios:
Scenario 1: A platform displays EUR/USD as 1.12345. Here, the ‘5’ represents the pipette.
Scenario 2: Another platform displays the same EUR/USD pair as 1.1234. Here, the pipette value is not explicitly shown, implying rounding or a less precise display.
The trader must be aware of these differences to accurately calculate their profit and loss and avoid errors in their trading analysis.
Importance of Pips in Profit/Loss Calculation
Pips are the fundamental unit of measurement in forex trading, directly impacting a trader’s profit or loss. Understanding how pips translate into monetary value is crucial for effective risk management and successful trading. Essentially, every pip movement represents a change in the currency pair’s price, and the accumulation of these small changes determines your overall trading outcome.
Pips directly influence the financial results of your forex trades. Each pip movement, up or down, results in a corresponding change in your account balance. The magnitude of this change depends on the lot size you’ve traded. A small pip movement might seem insignificant on its own, but consistent movement in a favorable direction, across multiple trades, can lead to substantial gains. Conversely, adverse pip movements can quickly accumulate into significant losses.
Pip Movement and Profit/Loss Calculation
Let’s illustrate how pip movements affect your trading results with a scenario. Imagine you’ve opened a long position (buying) on EUR/USD with a standard lot size (100,000 units) at an exchange rate of 1.1000.
- Initial Entry: You buy EUR/USD at 1.1000.
- Pip Movement 1: The price moves up by 10 pips to 1.1010. This represents a profit.
- Pip Movement 2: The price continues to rise, adding another 15 pips, reaching 1.1025.
- Pip Movement 3: The market reverses, and the price drops by 5 pips to 1.1020.
- Closing Position: You decide to close your position at 1.1020.
To calculate your profit, we need to consider the total pip movement and the value of one pip for a standard lot. Assuming a pip value of $10 (this can vary depending on the currency pair and leverage), let’s break down the calculation:
- Total Pip Movement: The price moved from 1.1000 to 1.1020, resulting in a net positive movement of 20 pips (10 + 15 – 5).
- Profit Calculation: 20 pips * $10/pip = $200 profit.
Profit/Loss = (Closing Price – Opening Price) * Number of Pips * Pip Value per Lot
This simple example demonstrates how seemingly small pip movements can cumulatively affect your overall trading outcome. Consistent monitoring of pip movements and understanding their impact on your trades is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Remember, this calculation is simplified. Real-world scenarios involve spreads, commissions, and other factors influencing the final profit or loss.
Pips and Trading Strategies: What Is A Pip In Forex Trading?
Understanding pip value isn’t just about calculating profits; it’s the cornerstone of effective risk management in forex trading. Knowing the monetary value of a pip allows traders to accurately assess potential losses and set appropriate stop-loss orders, preventing significant capital erosion. This understanding directly informs the strategies traders employ and the targets they set.
Pip value directly influences the choice and effectiveness of trading strategies. Conservative strategies, for example, might focus on smaller pip targets and tighter stop-losses to minimize risk, while more aggressive strategies might aim for larger gains, accepting a higher risk tolerance. The volatility of the currency pair also plays a crucial role; higher volatility often necessitates adjustments to pip targets and stop-losses.
Risk Management and Pip Value
Accurate pip value calculation is paramount for effective risk management. Let’s say a trader has a $10,000 account and is trading a EUR/USD pair with a pip value of $10. If they place a trade with a stop-loss of 20 pips, their maximum potential loss is calculated as 20 pips * $10/pip = $200. This clear understanding allows for informed decisions about position sizing and risk exposure. Without this precision, risk assessment becomes a guess, potentially leading to significant losses. A trader might mistakenly underestimate their risk, leading to an unexpectedly large loss that wipes out a significant portion of their trading capital.
Trading Strategies Based on Pip Targets and Stop-Losses
Several trading strategies are directly built around pip targets and stop-loss levels. Scalping, for instance, often involves aiming for small, consistent profits of a few pips per trade, relying on high frequency and volume to generate overall gains. Conversely, swing trading might target larger pip movements, holding positions for days or even weeks to capture significant price swings. The selection of a strategy hinges on the trader’s risk tolerance, time commitment, and market analysis. A conservative trader might employ a strategy focusing on small, consistent gains with tight stop-losses, while a more aggressive trader might opt for a strategy with larger pip targets and wider stop-losses, accepting a higher risk of larger losses in exchange for the potential of larger profits.
Pip Movement and Strategy Selection
The movement of pips, or the volatility of a currency pair, significantly influences the selection of appropriate trading strategies. During periods of high volatility, wider stop-losses are often employed to protect against sudden, large price swings. Conversely, during periods of low volatility, traders might opt for tighter stop-losses and smaller pip targets, aiming for smaller, more consistent gains. For example, during a period of geopolitical uncertainty, a trader might choose a strategy with wider stop-losses to accommodate potentially large and rapid price movements. In contrast, during a period of relative market stability, a trader might employ a scalping strategy, aiming for smaller, more frequent gains with tighter stop-losses.
Visual Representation of Pip Movement
Understanding pip movement visually is crucial for forex traders. A price chart acts as a visual representation of currency pair price fluctuations over time, with each tiny tick often representing a pip or fraction thereof. Let’s explore how these movements are depicted.
Imagine a typical candlestick chart displaying the EUR/USD pair. The vertical axis represents the price, and the horizontal axis represents time. Each candlestick represents a specific time period (e.g., one hour, four hours, or one day). The body of the candlestick shows the opening and closing prices, while the wicks (or shadows) extend to show the high and low prices during that period. A single pip’s movement would be a very small, almost imperceptible, change in the price displayed on the chart’s vertical axis. For example, if the EUR/USD is trading at 1.1000, a one-pip increase would move the price to 1.1001. This tiny movement might be barely visible without zooming in, especially on charts covering longer timeframes. The visual impact is magnified when considering multiple pips movements which would create a more noticeable price change, resulting in a clear change in candlestick lengths and positions.
Browse the implementation of How to Trade Forex on a Budget in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Candlestick Chart and Pip Changes
The candlestick chart effectively visualizes pip changes through its structure. A rise in price, indicating a positive pip movement, is represented by a taller candlestick body, often green or white, with a higher closing price than the opening price. Conversely, a fall in price, showing a negative pip movement, is displayed as a taller red or black candlestick body, where the closing price is lower than the opening price. The length of the candlestick body directly corresponds to the magnitude of the pip movement within that time period. Longer bodies indicate larger pip changes, while shorter bodies signify smaller movements. The wicks, or shadows, extending above and below the body, further illustrate the price range during the period. A long upper wick might suggest that the price briefly reached a high before retracting, indicating a temporary increase of pips, whereas a long lower wick might signify a temporary price dip. By analyzing the candlestick’s body length and wick positions, traders can quickly gauge the extent and direction of pip movements within the specific timeframe.
Pips and Leverage

Leverage in forex trading is a double-edged sword. It magnifies both profits and losses, making even small pip movements significantly impact your account balance. Understanding how leverage interacts with pips is crucial for managing risk and maximizing potential returns. This section will explore the relationship between pips and leverage, illustrating how different leverage levels affect your trading outcomes.
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions than their account balance would normally permit. For instance, a 1:100 leverage means you can control a $100,000 position with only $1,000 in your trading account. This amplification, while offering the potential for substantial profits, also increases the risk of significant losses. A small adverse pip movement can quickly erode your capital if you’re using high leverage.
Leverage’s Effect on Pip Movement Impact, What Is a Pip in Forex Trading?
The impact of a pip movement on your account is directly proportional to the leverage used. With higher leverage, the same pip movement translates to a larger gain or loss in your account balance. Consider two scenarios: one with 1:100 leverage and another with 1:500 leverage, both trading the same currency pair with a lot size of 1 standard lot (100,000 units). A 10-pip move in the favorable direction would result in a $100 profit (10 pips x $1 per pip) with 1:100 leverage. However, with 1:500 leverage, the same 10-pip movement would yield a $500 profit (10 pips x $5 per pip). Conversely, a 10-pip move against your position would result in a $100 loss with 1:100 leverage and a $500 loss with 1:500 leverage.
Profit/Loss Calculation with Leverage and Pip Movement
Let’s illustrate the calculation with a concrete example. Suppose you open a long position on EUR/USD with a lot size of 0.1 lot (10,000 units) and a leverage of 1:200. The current price is 1.1000. If the price moves to 1.1010 (a 10-pip increase), your profit calculation would be:
Profit = (Pip Movement x Pip Value x Lot Size)
First, we determine the pip value. Assuming a pip value of $10 per 0.1 lot, the calculation is as follows:
Profit = (10 pips x $10/pip x 1) = $100
However, with a leverage of 1:200, the effective profit is amplified. The initial profit of $100 is multiplied by the leverage ratio, resulting in a profit of $20,000. This, of course, assumes the leverage is calculated correctly by the broker. However, it’s important to note that your broker’s margin requirements will dictate your actual profit or loss. This example illustrates how leverage can dramatically increase the potential returns (or losses) from even small pip movements. Remember that the opposite is also true – a 10-pip decrease would result in a substantial loss.
Comparing Leverage Levels
The table below compares the profit/loss for different leverage levels with a 10-pip movement (favorable and unfavorable) on a 0.1 lot trade where the pip value is $10:
| Leverage | 10-Pip Gain | 10-Pip Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 1:100 | $100 | -$100 |
| 1:200 | $200 | -$200 |
| 1:500 | $500 | -$500 |
This table clearly demonstrates that higher leverage significantly magnifies both profits and losses. While this can lead to faster account growth, it also carries a substantially higher risk. Therefore, responsible leverage management is paramount in forex trading.
Last Point
So, there you have it – a deep dive into the often-overlooked yet critically important world of pips in forex trading. From the basic definition and calculation to the strategic implications and visual representation on price charts, we’ve covered the essentials. Remember, understanding pips isn’t just about calculating profits; it’s about mastering risk management, fine-tuning your trading strategies, and ultimately, increasing your chances of success in the dynamic forex market. Now go forth and conquer those pips!
Questions and Answers
What happens if my trade doesn’t hit my pip target?
That’s where stop-loss orders come in handy! They help you limit potential losses by automatically closing your trade if the price moves against you by a predetermined number of pips.
How do I convert pip values between different currencies?
You’ll need the current exchange rates between the involved currencies. Use a currency converter to determine the equivalent value in your desired currency.
Are pip values always the same for a given currency pair?
No, they can vary slightly due to fluctuations in exchange rates, especially for pairs not quoted in USD.
Can I make money trading only a few pips at a time?
Absolutely! Scalping strategies, for example, focus on profiting from small, frequent pip movements. However, this requires discipline and quick reactions.
Browse the multiple elements of How to Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders in Forex to gain a more broad understanding.






