
Understanding the Role of Central Banks in Forex Trading? Think of it like this: central banks are the puppet masters, pulling the strings of global currency markets. Their decisions – from interest rate hikes to subtle comments in press releases – can send shockwaves through the forex world, impacting everything from your vacation budget to international trade deals. This isn’t just about dry economics; it’s about understanding the power dynamics that shape the global financial landscape and how savvy traders leverage this knowledge for profit (or, let’s be honest, sometimes painful losses).
We’ll delve into how monetary policies like interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing directly influence exchange rates, exploring the strategies central banks use to intervene in markets. We’ll also uncover how analysts predict currency movements based on central bank announcements and actions, and discuss the inherent risks involved in this complex game of global finance.
Introduction to Central Banks and Forex Markets
Central banks and forex markets are intrinsically linked, with the actions of the former significantly influencing the latter. Understanding this relationship is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of international finance. This section explores the fundamental roles of central banks in managing their national economies and how these actions impact the global foreign exchange market. We will also examine the structure and function of the forex market itself.
Central Banks: Guardians of the Economy
Central banks are the primary monetary authorities within a country. Their main responsibilities include maintaining price stability, managing inflation, and promoting full employment. They achieve this through various monetary policy tools, such as adjusting interest rates, managing the money supply, and influencing exchange rates. For example, raising interest rates can curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, but it can also strengthen a nation’s currency in the forex market. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic growth but may weaken the currency. These decisions are complex, requiring a delicate balancing act between economic growth and price stability.
The Structure and Function of Forex Markets
The foreign exchange (forex or FX) market is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. Unlike stock exchanges with physical locations, the forex market operates 24 hours a day, across multiple time zones. Major trading centers include London, New York, Tokyo, and Singapore, with transactions occurring electronically between banks, corporations, and individual traders. The market’s sheer size and constant activity make it highly liquid, allowing for relatively quick and easy conversion of currencies. However, this liquidity also contributes to its volatility, making it susceptible to rapid price swings driven by various factors, including central bank actions.
Interaction Between Central Bank Policies and Forex Market Fluctuations
Central bank policies directly impact forex markets. For instance, if a central bank unexpectedly raises interest rates, investors may be attracted to higher returns in that country, increasing demand for its currency and causing its value to appreciate against other currencies. This is because higher interest rates make it more attractive to deposit money in that country’s banks. Conversely, if a central bank lowers interest rates or engages in quantitative easing (injecting money into the economy), its currency may depreciate as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. The impact of these policies is not always immediate or predictable; various economic and geopolitical factors also influence currency movements. The European Central Bank’s (ECB) response to the 2008 financial crisis, for example, involved significant monetary easing, which initially weakened the Euro against other major currencies. However, subsequent recovery and other economic factors eventually influenced the Euro’s value.
Impact of Monetary Policy on Exchange Rates
Central banks wield significant power over their national currencies, influencing exchange rates through various monetary policy tools. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of the forex market. These policies, primarily focused on maintaining price stability and fostering economic growth, have direct and often predictable effects on currency valuations.
Interest Rate Adjustments and Currency Values
Interest rate adjustments are a cornerstone of monetary policy. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and causing its value to appreciate. Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less attractive, leading to depreciation as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. This is because higher interest rates offer greater returns on investments denominated in that currency, making it more appealing to international investors. For instance, if the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates, investors might shift funds from lower-yielding assets in other countries into US dollar-denominated assets, thereby increasing demand for the US dollar and strengthening it against other currencies. The magnitude of the effect depends on several factors, including the size of the rate change, the overall economic health of the country, and market expectations.
Effects of Quantitative Easing (QE) and Other Unconventional Monetary Policies
Quantitative easing (QE), an unconventional monetary policy involving a central bank injecting liquidity into the market by purchasing assets, often has a depreciating effect on the currency. This is because the increased money supply can lead to inflation, reducing the purchasing power of the currency. Other unconventional policies, such as negative interest rates or forward guidance (explicit communication of future policy intentions), also impact exchange rates, though their effects are often more complex and less predictable than those of interest rate adjustments. For example, the European Central Bank’s extensive QE program following the 2008 financial crisis contributed to a weakening of the euro against other major currencies. The market’s reaction to these unconventional policies is often highly sensitive to the specifics of the program, its perceived effectiveness, and market sentiment.
Comparative Impact of Monetary Policy Approaches Across Countries
Different countries employ different monetary policy approaches, leading to varying impacts on their currencies. Countries with strong economic fundamentals and stable political environments tend to see their currencies appreciate, even if their central banks adopt expansionary policies. Conversely, countries with weaker economic conditions may experience currency depreciation, regardless of their monetary policy stance. The interplay between domestic and global economic factors significantly influences the final outcome. For instance, a country with a large current account deficit might see its currency depreciate even if its central bank raises interest rates, as the underlying economic weakness outweighs the positive effects of higher rates.
Comparison of Monetary Policies and Currency Effects
The following table compares the monetary policies of three major central banks and their effects on their respective currencies. Note that these are simplified representations and the actual impacts are much more nuanced and depend on a multitude of factors.
| Central Bank | Recent Monetary Policy Stance | Effect on Currency | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Reserve (US) | Interest rate hikes to combat inflation | US Dollar appreciation | Strong US economy, global demand for USD |
| European Central Bank (ECB) | Gradual interest rate increases, ending QE | Euro fluctuating, generally strengthening | Economic recovery in Europe, geopolitical events |
| Bank of Japan (BOJ) | Maintaining ultra-low interest rates, yield curve control | Japanese Yen depreciation | Low inflation, divergence from other central banks’ policies |
Central Bank Interventions in Forex Markets

Central banks, the guardians of a nation’s monetary policy, sometimes directly intervene in the foreign exchange (forex) market. These interventions are not commonplace, but they can significantly impact exchange rates and the overall economy. Understanding the “why,” “how,” and “consequences” of these interventions is crucial to grasping the complexities of the global financial system.
Central bank interventions typically occur when exchange rates deviate significantly from the central bank’s target or perceived equilibrium, threatening price stability or economic growth. Such deviations might stem from speculative attacks, large capital flows, or imbalances in the current account. The scale and frequency of these interventions vary considerably depending on the country’s economic structure, its exchange rate regime, and the central bank’s overall policy goals.
Situations Leading to Central Bank Intervention
Central banks might intervene directly in the forex market under several circumstances. For instance, a rapid and sharp depreciation of the domestic currency, potentially fueling inflation, might prompt intervention. Conversely, an excessively strong currency could harm export competitiveness and stifle economic growth, prompting intervention to weaken it. Furthermore, significant volatility in exchange rates, even without substantial directional movement, can create uncertainty and disrupt economic activity, leading central banks to stabilize the market. Finally, central banks may intervene to manage the country’s foreign exchange reserves, smoothing out fluctuations and ensuring sufficient liquidity. The specific triggers and thresholds for intervention vary from country to country and are often kept confidential for strategic reasons.
Direct Intervention Strategies
Central banks employ several strategies for direct intervention. The most common is buying or selling the domestic currency in the forex market. For example, to appreciate the domestic currency, a central bank will sell foreign currency reserves (e.g., US dollars) and buy its own currency. This increases demand for the domestic currency, pushing its value upward. Conversely, to depreciate the domestic currency, the central bank would sell its own currency and buy foreign currency. Other strategies include coordinated interventions with other central banks, where multiple nations work together to influence exchange rates. These coordinated efforts often aim to address global imbalances or respond to systemic risks.
Consequences of Central Bank Intervention
Central bank interventions, while potentially effective in the short term, can have both positive and negative consequences. Positive outcomes can include stabilizing exchange rates, mitigating volatility, and supporting economic growth by influencing export competitiveness. However, interventions can also distort market mechanisms, leading to unintended consequences. For example, large-scale interventions can deplete foreign exchange reserves, impacting a country’s ability to respond to future economic shocks. Moreover, repeated interventions might undermine market confidence in the central bank’s ability to manage the exchange rate sustainably, leading to further volatility. Furthermore, interventions can create moral hazard, encouraging excessive risk-taking by market participants who anticipate future interventions to bail them out.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Central Bank Intervention
The decision to intervene in forex markets is complex and involves weighing potential benefits against potential drawbacks.
- Benefits:
- Stabilizing exchange rates and reducing volatility.
- Supporting economic growth by influencing export competitiveness.
- Managing foreign exchange reserves effectively.
- Countering speculative attacks on the currency.
- Drawbacks:
- Depletion of foreign exchange reserves.
- Potential for market distortion and unintended consequences.
- Risk of undermining market confidence and creating further volatility.
- Creation of moral hazard.
- Limited effectiveness in the long run if underlying economic imbalances are not addressed.
Forecasting Exchange Rates Based on Central Bank Actions
Central bank actions are a cornerstone of forex market analysis. Understanding how these actions influence exchange rates is crucial for anyone aiming to predict future movements. Analysts meticulously dissect central bank statements, policy decisions, and economic data releases to anticipate shifts in currency values. This involves more than just reading press releases; it requires a deep understanding of the economic context and the nuances of central bank communication.
Analysts use central bank statements and actions to predict future exchange rate movements by identifying shifts in monetary policy. These shifts, whether subtle hints or overt pronouncements, signal the central bank’s intentions regarding inflation, interest rates, and economic growth. These intentions, in turn, directly influence investor sentiment and capital flows, leading to changes in exchange rates. The process isn’t always straightforward, as central banks often employ carefully worded statements, leaving room for interpretation. However, experienced analysts are skilled at deciphering these messages and predicting their impact on the forex market.
Key Indicators and Data Points Used in Forecasting Exchange Rates Based on Central Bank Policies
Forecasting exchange rates based on central bank policies relies on a range of key indicators and data points. These are not merely numbers; they are pieces of a complex puzzle that analysts assemble to build a comprehensive picture of the likely future direction of a currency. The accuracy of the forecast depends heavily on the analyst’s ability to correctly interpret these indicators within the broader economic context.
- Interest Rate Decisions: Changes in interest rates are a powerful driver of exchange rates. Higher rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and pushing its value up. Conversely, lower rates can weaken a currency.
- Inflation Data: Central banks closely monitor inflation. High inflation often leads to interest rate hikes to cool down the economy, influencing currency values. Conversely, low or negative inflation might signal a need for easing monetary policy, potentially weakening the currency.
- Central Bank Statements and Press Conferences: The tone and content of central bank communications provide invaluable insights into their future intentions. Words like “gradual,” “hawkish,” or “dovish” can significantly impact market sentiment and exchange rate expectations.
- Economic Growth Forecasts: Strong economic growth prospects often attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency. Conversely, weak growth forecasts can lead to a weakening of the currency.
- Balance of Payments Data: The balance of payments reflects a country’s overall economic transactions with the rest of the world. A consistent trade deficit, for example, can put downward pressure on a currency.
Hypothetical Scenario: Impact of a Change in Central Bank Policy on a Currency Pair
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving the EUR/USD currency pair. Suppose the European Central Bank (ECB) unexpectedly announces a more hawkish stance than anticipated, signaling a faster-than-expected increase in interest rates to combat rising inflation. This could lead to several immediate effects:
First, the announcement would likely cause a surge in demand for the euro (EUR) as investors seek higher returns on their investments. Capital would flow into the Eurozone, pushing the EUR/USD exchange rate upwards. Second, the increased interest rates would make borrowing more expensive in the Eurozone, potentially slowing down economic growth, but this effect might be offset by the initial influx of capital. Third, the impact on the US dollar (USD) would likely be relatively muted unless the Federal Reserve (Fed) simultaneously adjusted its monetary policy in response. If the Fed maintained its existing policy, the contrast between the two central banks’ approaches would further strengthen the euro relative to the dollar. The net result would be a significant appreciation of the euro against the dollar in the short to medium term. This hypothetical scenario illustrates how a change in central bank policy, even a relatively small one, can significantly impact exchange rate movements. The extent of the impact would, of course, depend on various factors including the market’s reaction to the announcement, prevailing economic conditions, and the actions of other central banks.
The Role of Central Bank Communication in Forex Markets
Central bank communication isn’t just about releasing numbers; it’s a high-stakes game of influencing market expectations and, consequently, forex trading decisions. The words and actions of central bankers can send ripples through global currency markets, impacting everything from investment strategies to international trade. Understanding this communication is key to navigating the complexities of forex.
Central bank communication significantly shapes market expectations by providing insights into future monetary policy. This guidance allows traders to anticipate potential shifts in interest rates, inflation targets, and overall economic outlook, enabling them to adjust their trading strategies accordingly. Transparency and clarity in communication are paramount, fostering market stability and reducing uncertainty. Conversely, ambiguous or inconsistent messaging can create volatility and confusion.
Central Bank Press Conferences and Publications Influence Forex Trading
Central bank press conferences and publications, such as monetary policy reports, are pivotal moments in forex trading. These events often trigger significant market reactions, as traders scrutinize every word and nuance for clues about the central bank’s future policy direction. For instance, a subtle shift in language regarding inflation or economic growth can signal a change in monetary policy stance, leading to immediate adjustments in currency valuations. The timing of these releases is also crucial, with unexpected announcements or deviations from market expectations often leading to sharp price swings. The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) press conferences, for example, are closely followed globally, and even minor changes in tone can cause significant volatility in the US dollar.
Comparison of Central Bank Communication Styles and Their Impact on Market Volatility
Different central banks adopt varying communication styles, significantly impacting market volatility. Some central banks, like the European Central Bank (ECB), favor a more cautious and data-dependent approach, communicating gradually and avoiding abrupt shifts in policy. This often results in lower market volatility. Others, like the Bank of England (BOE), may adopt a more proactive communication strategy, explicitly outlining future policy intentions. While this approach can offer greater clarity, it can also increase market volatility if unexpected changes are announced. The contrast in communication styles highlights the diverse approaches central banks employ in managing market expectations and maintaining financial stability. The impact of these differences can be seen in the differing levels of volatility experienced in the Euro and the British Pound, respectively.
Illustrative Example: An Unexpectedly Hawkish Statement
Imagine the following scenario: The European Central Bank (ECB), known for its relatively dovish stance, unexpectedly announces a more hawkish monetary policy in its press conference. The statement includes a commitment to faster interest rate hikes than previously anticipated, citing rising inflation concerns. This unexpected shift in rhetoric immediately sends shockwaves through the forex market.
Traders, initially expecting a continuation of the ECB’s accommodative policy, are surprised by the hawkish turn. This leads to a rapid reassessment of the Euro’s outlook. The sentiment shifts dramatically; traders anticipate higher interest rates, making the Euro more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Consequently, we witness a surge in demand for the Euro, causing its value to appreciate significantly against other currencies. This illustrative example highlights the immediate and substantial impact a single, unexpected statement can have on trader sentiment and subsequent currency trading activity. The magnitude of the Euro’s appreciation would depend on the specifics of the statement, the market’s initial expectations, and the overall global economic climate. However, a significant and rapid appreciation is highly likely in such a scenario.
Risks and Uncertainties Associated with Central Bank Actions: Understanding The Role Of Central Banks In Forex Trading
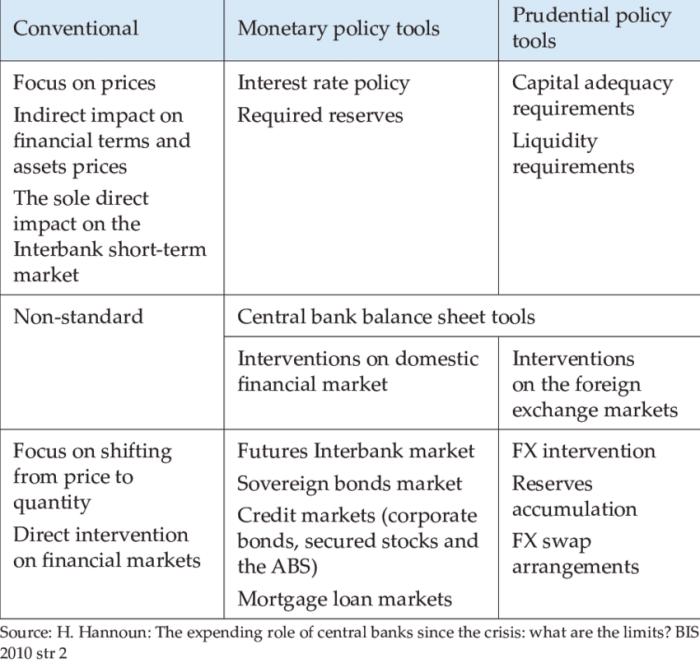
Relying solely on central bank actions for forex trading strategies is a risky game. While central banks wield significant influence over exchange rates, their actions are not always predictable, and their effectiveness can be significantly impacted by unforeseen circumstances. Understanding these inherent risks is crucial for any trader aiming to incorporate central bank policy into their strategies.
Central bank policy decisions are complex, influenced by a multitude of interacting economic factors, making accurate prediction challenging. Even the most sophisticated econometric models can fall short, particularly when facing unexpected economic shocks or shifts in global sentiment. This uncertainty translates directly into potential losses for traders who base their decisions on assumptions about central bank behavior.
Limitations of Predicting Central Bank Policy Decisions
Predicting central bank policy is notoriously difficult. Central banks often operate with a degree of opacity, deliberately avoiding clear signals to maintain flexibility in their responses to changing economic conditions. Furthermore, the interplay between various economic indicators – inflation, unemployment, GDP growth – makes it challenging to accurately gauge the direction of future policy. For example, a central bank might prioritize combating inflation over stimulating growth, even if unemployment is high, leading to outcomes that contradict simple forecasts. This inherent complexity makes relying solely on anticipated policy changes a risky proposition for forex traders.
Impact of Unexpected Events on Central Bank Policy Effectiveness
Unexpected events, such as geopolitical crises, natural disasters, or sudden shifts in global commodity prices, can significantly undermine the effectiveness of central bank policies. A planned interest rate hike, for instance, might be rendered ineffective if a major global event triggers a flight to safety, pushing investors towards the US dollar regardless of interest rate differentials. The 2008 financial crisis serves as a stark reminder of how unforeseen circumstances can overwhelm even the most well-intentioned central bank interventions. The effectiveness of quantitative easing programs, for example, was significantly hampered by the depth and speed of the economic downturn.
Risks Associated with Forex Trading Strategies Based on Central Bank Actions, Understanding the Role of Central Banks in Forex Trading
Several specific risks are associated with basing forex trading strategies solely on anticipated central bank actions. These include:
- Misinterpretation of Signals: Central bank communication is often nuanced and open to multiple interpretations, leading traders to misjudge the actual policy direction.
- Delayed Market Reaction: The market’s reaction to a central bank announcement may be delayed or muted, rendering a trading strategy based on immediate impact ineffective.
- Overreliance on Past Performance: Past central bank actions are not always indicative of future behavior, as economic conditions and priorities change over time.
- Unforeseen Economic Shocks: Unexpected economic events can nullify the effects of central bank interventions, leading to significant losses for traders who bet on their effectiveness.
Final Conclusion

So, the next time you see a news headline about a central bank’s move, remember: it’s not just economic jargon; it’s a direct line to understanding the forces that shape the forex market. Mastering the nuances of central bank influence isn’t just about predicting short-term fluctuations; it’s about developing a deeper understanding of the global financial ecosystem and how interconnected everything truly is. While predicting the market is never a sure thing, understanding the role of central banks is a crucial first step in navigating this thrilling, often chaotic, world of forex trading.
FAQ Guide
What are some examples of unconventional monetary policies?
Unconventional monetary policies include quantitative easing (QE), negative interest rates, and forward guidance. QE involves a central bank injecting liquidity into the market by purchasing assets. Negative interest rates incentivize banks to lend money, stimulating economic activity. Forward guidance involves communicating the central bank’s future intentions to influence market expectations.
How can I stay updated on central bank announcements?
Central banks typically publish calendars of upcoming meetings and announcements on their websites. Reputable financial news sources also provide real-time coverage of these events. Following key economic indicators and subscribing to relevant financial news alerts are also helpful.
Is forex trading based solely on central bank actions?
No, forex trading is influenced by many factors beyond central bank actions, including geopolitical events, economic data releases (like GDP and inflation), and market sentiment. Central bank policies are a significant factor, but not the only one.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of How to Analyze Forex Market Trends.
Discover the crucial elements that make The Benefits of Automated Forex Trading the top choice.






