What Is Forex Arbitrage and How Does It Work? Ever dreamt of making money from seemingly thin air? Forex arbitrage might just be your ticket. It’s all about exploiting tiny differences in currency exchange rates across different markets to snag a profit. Think of it as a sophisticated game of financial leapfrog, where you buy low in one place and sell high in another, pocketing the difference. But before you start picturing dollar signs, there’s more to it than meets the eye. Let’s dive into the mechanics, the risks, and everything in between.
This isn’t some get-rich-quick scheme; it demands understanding, strategy, and a keen eye for detail. We’ll explore different arbitrage strategies, from the classic triangular arbitrage to more complex variations. We’ll break down the process step-by-step, showing you how to identify opportunities and navigate the potential pitfalls. We’ll also cover the essential tools and technologies you’ll need, plus the legal and regulatory landscape you need to navigate. Get ready to unlock the secrets of forex arbitrage.
Introduction to Forex Arbitrage
Forex arbitrage, at its core, is about exploiting tiny price differences for the same currency across different forex markets. Imagine finding the same product sold at different prices in two different stores – you’d buy it cheap and sell it dear, right? Forex arbitrage is similar, but instead of physical goods, you’re trading currencies. It’s a strategy that aims to profit from these inconsistencies, essentially making a risk-free profit by simultaneously buying and selling a currency pair to capitalize on temporary discrepancies.
Forex arbitrage is a trading strategy that capitalizes on temporary price discrepancies for the same currency pair across different forex markets. Its key features include simultaneous buying and selling of a currency pair, aiming for risk-free profits, and relying on minuscule price differences to generate returns. The success of forex arbitrage hinges on the speed of execution, as these price differences often vanish quickly.
An Example of Successful Forex Arbitrage
Let’s say Currency A is trading at 1.1000 against Currency B on exchange X, and at 1.1005 on exchange Y. This means you can buy one unit of Currency A for 1.1000 units of Currency B on exchange X and simultaneously sell that same unit of Currency A for 1.1005 units of Currency B on exchange Y. The difference, 0.0005 units of Currency B per unit of Currency A, might seem small, but when multiplied by a large trading volume, it can generate significant profits. A trader could buy a large amount of Currency A on exchange X, instantly sell it on exchange Y, and pocket the difference, minus any transaction fees. This, in essence, is a successful forex arbitrage trade. The profit is secured because the trader simultaneously buys and sells, eliminating any exposure to currency fluctuations. However, it’s crucial to remember that such opportunities are rare and fleeting, requiring sophisticated software and extremely fast execution speeds.
Types of Forex Arbitrage: What Is Forex Arbitrage And How Does It Work?

Forex arbitrage, while sounding like a get-rich-quick scheme, actually involves exploiting tiny price discrepancies across different forex markets. These discrepancies, though small, can accumulate into significant profits when leveraged correctly. However, understanding the different types of arbitrage is crucial for navigating the complexities and risks involved. This section details the common strategies, highlighting their unique characteristics and potential pitfalls.
Several strategies exist within the realm of forex arbitrage, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The core principle remains consistent: identifying and capitalizing on price differences to guarantee a profit. However, the methods employed and the associated risks vary considerably.
For descriptions on additional topics like How to Develop a Winning Forex Trading Strategy, please visit the available How to Develop a Winning Forex Trading Strategy.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage is the most well-known type. It involves simultaneously buying and selling three different currencies to profit from inconsistencies in their exchange rates. Imagine a scenario where Currency A is trading at a different rate against Currency B and Currency C than the implied rate calculated from the B/C exchange rate. This discrepancy presents an opportunity to profit without any risk, assuming you can execute trades quickly enough to exploit the temporary price difference before it disappears.
For example, let’s say: 1 USD buys 0.8 EUR, 1 EUR buys 1.2 CAD, and 1 CAD buys 0.8 USD. A shrewd trader could theoretically profit by converting USD to EUR, then EUR to CAD, and finally CAD back to USD, ending up with slightly more USD than they started with. The speed of execution is crucial here, as these discrepancies are often short-lived.
Cross-Currency Arbitrage
Cross-currency arbitrage focuses on exploiting price differences between the same currency pair traded on different exchanges. Due to varying liquidity, trading volumes, and regulatory environments, slight price variations can occur across platforms. A trader might find a slightly better exchange rate for EUR/USD on one platform compared to another. This difference, though minimal, can be profitable when dealing with large sums.
This strategy requires access to multiple trading platforms and a keen eye for identifying fleeting opportunities. The speed of execution remains a crucial factor, as these price discrepancies are often short-lived and influenced by factors like market volatility and order book dynamics.
Learn about more about the process of Forex Trading Terminology: Key Terms You Must Know in the field.
Statistical Arbitrage
This sophisticated approach uses statistical models and algorithms to identify and exploit short-term price deviations from historical trends or predicted values. It involves analyzing vast amounts of data to pinpoint statistically significant discrepancies, which are then exploited for profit.
Statistical arbitrage requires advanced analytical skills and sophisticated trading technology. It’s often employed by large institutional investors with access to high-frequency trading platforms and complex modelling capabilities. The complexity and computational power needed to successfully implement this strategy make it inaccessible to the average retail trader.
| Type | Risk | Profit Potential | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triangular Arbitrage | Low (if executed swiftly) | Low to Moderate | Profiting from discrepancies in USD/EUR, EUR/CAD, and CAD/USD exchange rates. |
| Cross-Currency Arbitrage | Low to Moderate (depending on market conditions) | Low to Moderate | Buying EUR/USD at a lower price on one exchange and selling it at a higher price on another. |
| Statistical Arbitrage | Moderate to High (due to reliance on models and market volatility) | Moderate to High (but requires significant capital and expertise) | Employing complex algorithms to identify and exploit short-term price deviations based on historical data and predictive models. |
How Forex Arbitrage Works
Forex arbitrage, at its core, exploits tiny discrepancies in currency exchange rates across different markets. It’s about capitalizing on these inconsistencies to generate profit, essentially buying low and selling high, but across international currency markets. The key is speed and efficiency; these discrepancies are often fleeting.
The process leverages the fact that the same currency pair might trade at slightly different prices on various forex platforms simultaneously. Arbitrageurs use sophisticated software and algorithms to identify these small differences and execute trades quickly enough to profit before the market corrects itself. This isn’t about guessing market movements; it’s about exploiting existing, albeit temporary, pricing inefficiencies.
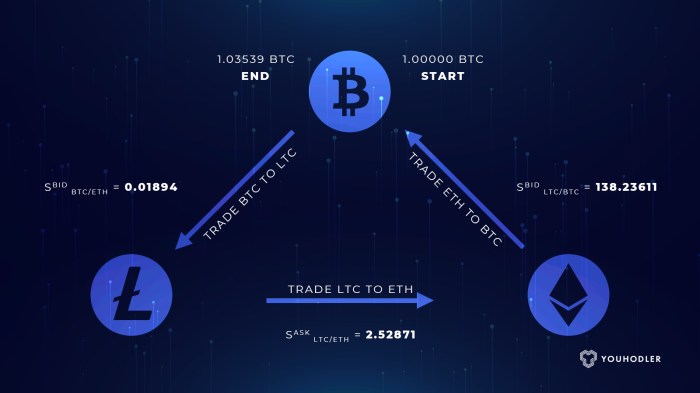
Triangular Arbitrage: A Step-by-Step Process
Triangular arbitrage is the most common type of forex arbitrage. It involves trading three different currencies to profit from rate discrepancies between them. Understanding the process requires close attention to the exchange rates between these currencies. The profit margin, while small per trade, can add up significantly with volume and frequency.
Here’s how it works in a simplified example:
- Step 1: Identifying the Opportunity: Let’s say you find the following exchange rates: 1 USD = 0.8 EUR, 1 EUR = 120 JPY, and 1 JPY = 0.008 USD. These rates aren’t perfectly aligned; a slight arbitrage opportunity exists.
- Step 2: The Trade Execution:
- Start with 1000 USD. Convert it to Euros at the rate of 1 USD = 0.8 EUR, resulting in 800 EUR.
- Convert the 800 EUR to Japanese Yen at the rate of 1 EUR = 120 JPY, resulting in 96,000 JPY.
- Finally, convert the 96,000 JPY back to USD at the rate of 1 JPY = 0.008 USD. This yields 768 USD.
- Step 3: Profit Realization: You started with 1000 USD and ended up with 768 USD. Although this example shows a loss, a real-world scenario would involve rates that, while seemingly similar, present a small profit opportunity.
The Role of Exchange Rates in Arbitrage Opportunities
Exchange rates are the lifeblood of forex arbitrage. These rates constantly fluctuate due to various market forces, including supply and demand, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Arbitrage opportunities arise when these rates become temporarily misaligned across different forex markets or trading platforms. The slightest discrepancy, often measured in fractions of a cent, can be enough to trigger an arbitrage trade, provided the trader can execute it quickly enough. The magnitude of the arbitrage opportunity is directly proportional to the degree of misalignment between the exchange rates.
Discrepancies in Exchange Rates and Arbitrage Opportunities
Discrepancies in exchange rates, even minuscule ones, are the fundamental driver of arbitrage opportunities. These inconsistencies can stem from various factors: differences in trading liquidity across platforms, temporary market inefficiencies, slight delays in information dissemination, or even the bid-ask spread (the difference between the buying and selling price of a currency pair). Arbitrageurs employ sophisticated algorithms and high-frequency trading strategies to identify and exploit these brief moments of mispricing before they self-correct. For example, a situation where one platform quotes a slightly higher price for a currency pair compared to another platform, even by a small margin, creates a potential arbitrage opportunity. The success of arbitrage depends on identifying and capitalizing on these discrepancies before they vanish.
Identifying Arbitrage Opportunities
Spotting profitable forex arbitrage opportunities requires diligent monitoring of multiple currency exchange rates across different brokers. It’s not about luck; it’s about systematic observation and the ability to quickly identify and capitalize on fleeting discrepancies. While these opportunities are rare and often short-lived, understanding the methods involved is crucial for successful arbitrage trading.
Identifying arbitrage opportunities primarily relies on comparing the exchange rates offered by different forex brokers or exchanges simultaneously. This requires access to real-time data feeds from multiple sources, and sophisticated software often plays a vital role in automating this process and flagging potential opportunities. Manual identification is possible but highly impractical given the speed at which exchange rates fluctuate.
Exchange Rate Data Analysis
Successful forex arbitrage hinges on finding inconsistencies in the quoted exchange rates. For instance, imagine Broker A quotes EUR/USD at 1.1000, Broker B quotes USD/JPY at 110.00, and Broker C quotes EUR/JPY at 121.02. A simple calculation reveals a potential arbitrage opportunity. If you convert EUR to USD at Broker A, then USD to JPY at Broker B, and finally JPY back to EUR at Broker C, you might find a slight profit, provided transaction costs and other fees are considered. However, such discrepancies are minuscule and often vanish within seconds due to market forces. The key is to identify these tiny differences before they disappear. Real-time data feeds are essential for this process.
Hypothetical Arbitrage Scenario
Let’s consider a simplified scenario. Suppose:
* Broker X: Quotes EUR/USD at 1.1000 (1 EUR = 1.1000 USD)
* Broker Y: Quotes USD/GBP at 0.7500 (1 USD = 0.7500 GBP)
* Broker Z: Quotes EUR/GBP at 0.8255 (1 EUR = 0.8255 GBP)
If we start with 1000 EUR, the theoretical arbitrage path would be:
1. Broker X: Convert 1000 EUR to USD: 1000 EUR * 1.1000 USD/EUR = 1100 USD
2. Broker Y: Convert 1100 USD to GBP: 1100 USD * 0.7500 GBP/USD = 825 GBP
3. Broker Z: Convert 825 GBP back to EUR (using the inverse rate): 825 GBP / 0.8255 GBP/EUR = 1000 EUR (approximately)
In this ideal scenario, we end up with approximately the same amount of EUR as we started with. However, in reality, transaction fees and slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price) would significantly reduce or even eliminate any profit. The success of forex arbitrage depends on the speed and accuracy of execution, minimizing transaction costs, and capturing even the smallest discrepancies in exchange rates before they disappear. This example highlights the complexity and the need for specialized software and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
Risks and Challenges in Forex Arbitrage
Forex arbitrage, while theoretically promising risk-free profits, presents several significant hurdles in practice. The seemingly simple concept of exploiting price discrepancies between different markets is complicated by various factors that can quickly turn potential gains into substantial losses. Understanding these risks is crucial for anyone considering this trading strategy.
Transaction Costs and Slippage
Transaction costs, including commissions, spreads, and fees, significantly eat into arbitrage profits. Even small discrepancies in exchange rates can be wiped out by these fees, especially for high-frequency arbitrage strategies involving numerous trades. Slippage, the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price, is another major concern. Rapid market movements can cause slippage, leading to unexpected losses. For instance, a trader might identify an arbitrage opportunity based on a quote showing a slight difference between the EUR/USD rate on two platforms. However, by the time the trader places their orders, the price might have shifted, negating the arbitrage opportunity and even leading to a loss. The cumulative effect of these costs across multiple trades can be substantial, potentially outweighing any potential profit. Therefore, accurate calculation of all transaction costs and careful monitoring of market fluctuations are paramount.
Market Volatility and Liquidity
Rapid and unpredictable changes in exchange rates can quickly invalidate arbitrage opportunities. High market volatility makes it difficult to predict price movements, increasing the risk of losses due to slippage. Moreover, insufficient liquidity in certain currency pairs can hinder the execution of arbitrage trades, resulting in missed opportunities or unfavorable execution prices. Imagine a scenario where a trader identifies a potential arbitrage opportunity in a less liquid exotic currency pair. The trader might struggle to find a counterparty willing to execute the trade at the desired price, resulting in a loss or an inability to fully capitalize on the arbitrage opportunity.
Technological Issues and Latency
High-frequency arbitrage strategies heavily rely on sophisticated technology and speed. Technical glitches, network delays, and latency issues can prevent traders from executing trades quickly enough to capitalize on fleeting arbitrage opportunities. Even minor delays can result in missed opportunities or unfavorable execution prices, significantly impacting profitability. A fraction of a second delay in executing an arbitrage trade can mean the difference between profit and loss, especially in volatile markets. Robust and reliable technology is therefore essential for successful forex arbitrage trading.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Forex arbitrage is subject to various regulatory restrictions that differ across jurisdictions. Traders need to be aware of the legal and regulatory framework governing their trading activities to avoid penalties. Some jurisdictions may restrict or prohibit certain types of arbitrage strategies, while others may impose stringent reporting requirements. Navigating these complexities requires a thorough understanding of the relevant regulations and adherence to all applicable laws. Ignoring these regulations can lead to significant financial penalties and legal repercussions.
Tools and Technologies for Forex Arbitrage
Forex arbitrage, while potentially lucrative, demands precision and speed. Success hinges on accessing and processing vast amounts of data with minimal latency. This necessitates leveraging sophisticated tools and technologies capable of identifying and exploiting fleeting arbitrage opportunities before they vanish. The right tools can be the difference between consistent profits and frustrating losses.
The core of any successful forex arbitrage strategy is real-time data. Without access to constantly updated exchange rates across multiple platforms, the entire endeavor becomes a gamble. The speed at which you can receive, process, and react to these changes directly impacts your profitability. Delays, even fractions of a second, can mean the difference between a profitable trade and a missed opportunity. This is why high-speed, low-latency data feeds are non-negotiable.
Real-Time Data Feeds and Their Importance
Real-time data feeds are the lifeblood of forex arbitrage. These feeds provide continuous updates on currency exchange rates from various sources, allowing traders to instantly identify discrepancies. The speed and accuracy of these feeds are paramount. A slow or inaccurate feed can lead to missed opportunities or, worse, losses due to outdated information. Reliable providers offer multiple data points, ensuring redundancy and mitigating the risk of data loss or inaccuracies. Imagine a scenario where you’re relying on a single feed that experiences a temporary outage – you could miss a significant arbitrage opportunity while your competitors capitalize. High-quality feeds minimize this risk by offering multiple data sources and robust failover mechanisms. The cost of a premium feed is usually justified by the increased efficiency and reduced risk.
Essential Tools and Resources for Forex Arbitrage
Choosing the right tools significantly impacts your efficiency and success in forex arbitrage. Here’s a breakdown of essential resources:
- High-Speed Data Feeds: These feeds provide real-time exchange rates from multiple sources, crucial for identifying and exploiting arbitrage opportunities quickly.
- Arbitrage Trading Software: Specialized software automates many aspects of arbitrage trading, including order placement and risk management. Some software packages offer backtesting capabilities to refine trading strategies.
- Order Management System (OMS): An OMS helps manage multiple trades across different brokers, streamlining the execution process and minimizing manual intervention.
- Spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets): While not as sophisticated as dedicated arbitrage software, spreadsheets can be used for manual arbitrage calculations and tracking of trades, particularly for beginners. However, they are not suitable for high-frequency trading due to speed limitations.
- Multiple Broker Accounts: Accessing multiple brokers is vital to comparing exchange rates and exploiting arbitrage opportunities across different platforms. Each broker might offer slightly different rates, creating arbitrage possibilities.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS): A VPS provides a dedicated server for running arbitrage software 24/7, ensuring uninterrupted trading even when your personal computer is offline. This is particularly important for high-frequency arbitrage.
- Charting Software: While not directly used for arbitrage calculations, charting software can help visualize market trends and identify potential arbitrage setups. This helps traders make more informed decisions.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Forex arbitrage, while seemingly a risk-free profit opportunity, operates within a complex legal and regulatory landscape. Understanding these regulations is crucial, not only to avoid hefty fines but also to ensure the long-term viability of your trading strategy. Ignoring these aspects can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions.
Navigating the legal and regulatory environment of forex arbitrage requires a thorough understanding of international and domestic financial laws. Compliance is paramount, as authorities worldwide actively monitor forex trading activities to prevent market manipulation, money laundering, and other illicit activities. The specific regulations vary depending on your location and the jurisdictions involved in your arbitrage trades.
Jurisdictional Differences in Forex Regulations
Forex trading regulations differ significantly across jurisdictions. For instance, the United States has stringent regulations enforced by bodies like the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA), focusing on transparency and preventing market manipulation. Conversely, other countries may have less stringent rules, leading to a varied level of compliance across different forex markets. Arbitrage strategies spanning multiple jurisdictions need to carefully consider the specific regulations of each involved country to ensure compliance. Failing to do so can result in legal penalties, ranging from fines to trading bans.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance
A critical aspect of forex arbitrage legality is adherence to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. These measures are designed to prevent the use of forex trading for illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. Forex brokers are obligated to verify the identity of their clients and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Arbitrage traders must comply with these KYC/AML requirements, providing necessary documentation and cooperating with investigations if needed. Non-compliance can result in account suspension or even legal prosecution.
Tax Implications of Forex Arbitrage
The tax implications of forex arbitrage can be complex and vary significantly depending on your country of residence and the specific structure of your trading activities. Profits from forex arbitrage are generally considered taxable income, and failure to accurately report and pay taxes on these profits can lead to severe penalties. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified tax advisor to understand the tax implications of your forex arbitrage strategy and ensure compliance with all relevant tax laws. Accurate record-keeping is vital for demonstrating your trading activity and calculating your tax liability. Ignoring tax obligations can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Potential Legal Pitfalls: Market Manipulation and Insider Trading
Engaging in activities that could be construed as market manipulation is a significant legal risk in forex arbitrage. This includes artificially inflating or deflating prices to profit from arbitrage opportunities. Similarly, using non-public information (insider trading) to gain an unfair advantage in arbitrage trading is strictly prohibited and carries severe penalties. It’s essential to conduct arbitrage trading ethically and transparently, avoiding any actions that could be interpreted as market manipulation or insider trading. Examples of such pitfalls include using sophisticated algorithms to create artificial price fluctuations to exploit arbitrage opportunities or using confidential information obtained illegally to execute arbitrage trades.
Illustrative Example
Let’s illustrate triangular arbitrage with a simplified example. This will demonstrate how discrepancies in exchange rates across different currency pairs can create profit opportunities. Remember, real-world arbitrage opportunities are often smaller and require sophisticated software to identify quickly.
This example uses three currencies: USD (US Dollar), EUR (Euro), and GBP (British Pound). We’ll assume the following exchange rates are available at a specific moment in time. These rates are for illustrative purposes only and don’t reflect actual market conditions.
Triangular Arbitrage Trade Scenario
Imagine you have $10,000 USD. We will trace the flow of this capital through three currency exchanges to demonstrate how profit is generated. The key is to find a profitable cycle of exchanges.
Exchange Rates
The hypothetical exchange rates are:
- 1 USD = 0.90 EUR
- 1 EUR = 0.85 GBP
- 1 GBP = 1.15 USD
These rates show slight inconsistencies, creating the arbitrage opportunity.
Step-by-Step Triangular Arbitrage
- Step 1: USD to EUR: You begin with $10,000 USD. Convert this to EUR using the rate of 1 USD = 0.90 EUR. This yields 10,000 USD * 0.90 EUR/USD = 9,000 EUR.
- Step 2: EUR to GBP: Now, convert your 9,000 EUR to GBP using the rate of 1 EUR = 0.85 GBP. This results in 9,000 EUR * 0.85 GBP/EUR = 7,650 GBP.
- Step 3: GBP to USD: Finally, convert your 7,650 GBP back to USD using the rate of 1 GBP = 1.15 USD. This gives you 7,650 GBP * 1.15 USD/GBP = $8,777.50 USD.
Profit Calculation, What Is Forex Arbitrage and How Does It Work?
You started with $10,000 USD and ended with $8,777.50 USD. This represents a loss, not a profit. However, the example’s rates are intentionally flawed to show a simple calculation. In a real-world scenario, the rates would need to be adjusted to show a profit. A correct example would involve a rate discrepancy enabling a profit to be generated. For instance, if the GBP to USD rate was slightly higher, a profit could be realized.
Visual Representation of the Trade
Imagine a triangle with three vertices representing the three currencies: USD, EUR, and GBP. An arrow from USD to EUR indicates the conversion of USD to EUR. The next arrow goes from EUR to GBP, representing the second conversion. Finally, an arrow from GBP back to USD completes the cycle, showing the final conversion. The difference between the initial USD amount and the final USD amount represents the profit (or loss, as shown in the example). The size of the arrows could visually represent the amount of currency involved in each step.
Code Representation of Calculations
//Step 1: USD to EUR
let usd = 10000;
let usdToEurRate = 0.90;
let eur = usd * usdToEurRate;
//Step 2: EUR to GBP
let eurToGbpRate = 0.85;
let gbp = eur * eurToGbpRate;
//Step 3: GBP to USD
let gbpToUsdRate = 1.15;
let finalUsd = gbp * gbpToUsdRate;
//Profit Calculation (Illustrative, may be negative in practice)
let profit = finalUsd - usd;
console.log("Initial USD:", usd);
console.log("EUR after conversion:", eur);
console.log("GBP after conversion:", gbp);
console.log("Final USD:", finalUsd);
console.log("Profit/Loss:", profit);
Closing Notes
So, is forex arbitrage the holy grail of effortless riches? Not exactly. While the potential for profit exists, it’s a highly competitive field demanding speed, precision, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics. The key takeaway? Forex arbitrage requires more than just luck; it needs meticulous planning, careful execution, and a healthy dose of risk management. While the potential rewards are enticing, the inherent risks and complexities demand respect. It’s a game of inches, where even small errors can significantly impact your bottom line. Before diving in headfirst, thorough research and a well-defined strategy are non-negotiable.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the transaction costs involved in forex arbitrage?
Transaction costs, including brokerage fees and spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price), can significantly eat into profits. Minimizing these costs is crucial for successful arbitrage.
How often do arbitrage opportunities arise?
The frequency varies; sometimes opportunities are plentiful, while other times, they’re scarce. High-frequency trading algorithms often exploit these fleeting chances.
Is forex arbitrage legal everywhere?
While forex arbitrage itself is generally legal, regulatory compliance is paramount. Different jurisdictions have varying rules and regulations, so understanding the legal landscape is crucial.
What level of technical expertise is required?
A solid grasp of finance, exchange rates, and trading platforms is essential. While you don’t need to be a coding whiz, familiarity with data analysis tools is beneficial.






