
The Basics of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios: Dive into the thrilling, yet risky, world of forex trading. We’re not just talking about making money; we’re talking about smart money management. Understanding risk-to-reward ratios isn’t just about minimizing losses—it’s about maximizing your potential profits while keeping your sanity intact. This guide breaks down the essentials, showing you how to calculate your ratios, incorporate them into your trading plan, and even level up your strategy with advanced techniques. Get ready to trade smarter, not harder.
Forex trading, with its inherent volatility, can be a rollercoaster. One wrong move, and your hard-earned cash can vanish faster than you can say “margin call.” But fear not! This isn’t a doom and gloom story. Mastering risk-to-reward ratios is your key to navigating this exciting market. We’ll explore various strategies, from simple calculations to advanced techniques, so you can confidently approach every trade with a clear understanding of your potential gains and losses. Prepare to transform your trading game.
Introduction to Forex Trading Risk

Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, carries significant inherent risks. Unlike investments in stocks or bonds, the forex market operates 24/5, with continuous price fluctuations influenced by a multitude of global factors. Understanding these risks is paramount before engaging in any forex trading activities. Ignoring them can lead to substantial financial losses.
Forex trading involves leveraging, meaning you can control a larger amount of currency than you actually own. While leverage magnifies profits, it equally magnifies losses. A small adverse price movement can quickly wipe out your trading capital if you’re not careful. This inherent risk necessitates a robust risk management strategy.
Factors Contributing to Forex Market Volatility
Several interconnected factors contribute to the forex market’s inherent volatility. These factors influence currency exchange rates and create opportunities and challenges for traders. Understanding these factors allows traders to anticipate potential market movements and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Geopolitical Events: International conflicts, political instability, and significant policy changes in major economies can trigger dramatic shifts in currency values. For example, unexpected political upheaval in a major country could cause its currency to depreciate sharply against other currencies.
- Economic Data Releases: The release of economic indicators like inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth can significantly impact currency values. A surprisingly strong inflation report, for instance, might cause a central bank to raise interest rates, strengthening the currency.
- Central Bank Actions: Decisions made by central banks regarding interest rates, monetary policy, and quantitative easing directly influence currency values. A surprise interest rate cut could weaken a currency as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
- Market Sentiment: Speculation and market sentiment play a crucial role. News reports, analyst opinions, and overall market confidence can drive significant price fluctuations, irrespective of underlying economic fundamentals.
- Unexpected Events: Unforeseen events like natural disasters, pandemics, or major technological disruptions can introduce significant volatility into the market, causing rapid and unpredictable currency movements.
Examples of Potential Losses in Forex Trading
The potential for losses in forex trading is substantial, and it’s crucial to understand the various ways losses can occur. Failure to manage risk effectively can lead to significant financial setbacks.
Let’s consider a scenario: A trader invests $1000 with a leverage of 1:100, effectively controlling $100,000. If the currency pair they traded moves against them by just 1%, their $1000 investment could be completely wiped out. This illustrates the power of leverage and the potential for rapid and substantial losses. Another example: A trader might fail to set stop-loss orders, resulting in unlimited losses if the market moves significantly against their position. Without proper risk management, even a small mistake can lead to significant financial consequences.
Understanding Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Successfully navigating this landscape requires a deep understanding of risk management, and a key component of that is the risk-to-reward ratio. This ratio is essentially the backbone of a sound trading strategy, helping you balance potential profits against potential losses. Ignoring it can lead to significant financial setbacks, even wiping out your trading account.
Understanding the risk-to-reward ratio allows you to make informed decisions, ensuring your trading plan is not only profitable but also sustainable in the long run. It’s not about avoiding risk entirely—that’s impossible in forex—but about intelligently managing it to maximize your chances of success.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio Definition
The risk-to-reward ratio in forex trading is a simple calculation that compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss. It’s expressed as a ratio, for example, 1:2, 1:3, or even 1:1. The first number represents the potential loss (risk), while the second represents the potential profit (reward). A 1:2 ratio, for instance, means that for every $1 you risk, you aim to make $2 in profit.
Importance of Managing Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Effective risk-to-reward management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. A consistent approach to this ratio helps you control your losses and protect your capital. By setting a minimum acceptable risk-to-reward ratio, you filter out trades that are too risky relative to their potential profit. This disciplined approach helps you avoid emotional trading decisions and stick to your trading plan, even during periods of market volatility. Think of it as a safety net, protecting you from significant drawdowns. For example, a trader with a 1:3 risk-to-reward ratio would need only win one out of every three trades to break even, assuming consistent risk amounts.
Examples of Different Risk-to-Reward Ratio Strategies
Different traders employ various risk-to-reward strategies depending on their risk tolerance and trading style. Some prefer conservative ratios like 1:1 or 1:1.5, prioritizing capital preservation. Others, with higher risk tolerance, might employ ratios of 1:2 or even 1:3, aiming for larger profits from fewer winning trades. The choice depends on individual circumstances and market conditions. A scalper, for instance, might prefer a 1:1 ratio due to the short-term nature of their trades, while a swing trader might target a 1:2 or 1:3 ratio, holding positions for longer periods.
Comparison of Different Risk-to-Reward Ratios
The following table illustrates the implications of different risk-to-reward ratios:
| Ratio | Risk Amount ($) | Potential Reward ($) | Overall Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 100 | 100 | Conservative; needs a high win rate to be profitable. |
| 1:1.5 | 100 | 150 | Moderately conservative; allows for some losses while still aiming for profit. |
| 1:2 | 100 | 200 | Moderate risk; a good balance between risk and reward. |
| 1:3 | 100 | 300 | Higher risk; requires fewer winning trades to be profitable but carries greater potential for losses. |
Calculating Risk-to-Reward Ratios

Understanding risk-to-reward ratios is crucial for successful forex trading. It’s not just about making profits; it’s about managing risk effectively and ensuring your potential gains outweigh your potential losses. This section will walk you through the process of calculating these ratios and setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Calculating your risk-to-reward ratio involves determining the potential profit relative to the potential loss on a trade. A higher ratio generally indicates a more favorable trade setup, though context is key – a high ratio doesn’t guarantee success. The calculation itself is straightforward, but understanding its implications within your overall trading strategy is paramount.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Level Determination
Defining your stop-loss and take-profit levels is the first step in calculating your risk-to-reward ratio. Your stop-loss order protects you from significant losses if the trade moves against you, while your take-profit order secures your profits when the trade reaches your target price. Accurate placement of these orders is vital for managing risk and maximizing potential returns. These levels are usually set based on technical analysis, support and resistance levels, or other relevant market indicators.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio Calculation
The risk-to-reward ratio is calculated by dividing the potential profit (take-profit price minus entry price) by the potential loss (entry price minus stop-loss price).
Risk-to-Reward Ratio = (Take-Profit Price – Entry Price) / (Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price)
This formula gives you a numerical representation of your risk versus reward. For example, a ratio of 1:2 means that for every $1 you risk, you stand to gain $2. A ratio of 1:1 means your potential profit and loss are equal.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you’re trading EUR/USD. You enter a long position (buying) at 1.1000. You place your stop-loss order at 1.0970, and your take-profit order at 1.1050.
Your potential profit is 1.1050 – 1.1000 = 0.0050.
Your potential loss is 1.1000 – 1.0970 = 0.0030.
Therefore, your risk-to-reward ratio is 0.0050 / 0.0030 = 1.67, or approximately 1:1.67. This indicates that for every $1 you risk, you stand to gain approximately $1.67. Remember that this is a simplified example and doesn’t account for spreads or commissions, which will slightly alter the final ratio. Furthermore, the actual outcome of a trade can differ significantly from the calculated ratio due to market volatility and unforeseen events.
Applying Risk-to-Reward Ratios in Practice
So, you’ve grasped the theory behind risk-to-reward ratios. Now, the real challenge begins: putting it into action. Successfully integrating these ratios into your trading strategy isn’t just about numbers; it’s about building a disciplined and sustainable approach to forex trading. This section will guide you through practical application, common pitfalls, and best practices.
Incorporating risk-to-reward ratios effectively requires a meticulously planned trading strategy. It’s not a one-size-fits-all approach; the optimal ratio will depend on your individual risk tolerance, trading style, and market conditions. The key is consistency and self-awareness.
Incorporating Risk-to-Reward Ratios into a Trading Plan
A robust trading plan should explicitly define your risk-to-reward targets. For example, a conservative trader might aim for a 1:2 ratio (risking $100 to potentially gain $200), while a more aggressive trader might opt for a 1:3 or even 1:4 ratio. This ratio should be consistent across all your trades to maintain a structured approach to risk management. Remember to factor in trading costs like spreads and commissions when calculating potential profits. The plan should also Artikel your stop-loss and take-profit levels, directly linked to your chosen risk-to-reward ratio. For instance, if your risk-to-reward is 1:2, and you’re risking 1% of your account ($100 on a $10,000 account), your stop-loss would be placed to limit your loss to $100, while your take-profit would be set to secure a $200 profit.
Common Mistakes in Risk-to-Reward Management
Many traders fall into common traps when managing risk-to-reward. One frequent error is ignoring the ratio altogether, leading to inconsistent and potentially disastrous outcomes. Another mistake is chasing larger rewards without adequately considering the associated risk. This often manifests as widening stop-losses or failing to set them at all, hoping for a market reversal that may never materialize. Over-leveraging is another significant issue, as it magnifies both profits and losses, making even a small loss disproportionately damaging. Finally, emotional trading – reacting to market fluctuations without adhering to your predetermined plan – frequently leads to deviations from the established risk-to-reward ratio.
Different Risk Management Techniques
Various risk management techniques can be combined with risk-to-reward ratios to enhance effectiveness. Position sizing, for example, is crucial. By limiting the amount of capital risked per trade, you control potential losses, even if the trade goes against you. Diversification, spreading your investments across different currency pairs or asset classes, reduces the impact of any single losing trade. Furthermore, employing trailing stop-losses, which adjust automatically as the price moves in your favor, can help lock in profits while minimizing potential losses. These strategies work best when integrated with a clearly defined risk-to-reward framework.
Best Practices for Applying Risk-to-Reward Ratios
To maximize the effectiveness of risk-to-reward ratios, follow these best practices. First, rigorously backtest your strategy using historical data to assess its performance under various market conditions. Second, maintain a detailed trading journal to track your trades, identify patterns, and refine your approach. Third, consistently review and adjust your risk-to-reward ratio as needed, based on your performance and market dynamics. Fourth, avoid emotional decision-making; stick to your pre-defined plan, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. Fifth, continuously educate yourself on forex trading and risk management techniques to improve your understanding and decision-making capabilities. Finally, always remember that forex trading involves inherent risk, and no strategy guarantees profit.
Risk-to-Reward Ratios and Position Sizing
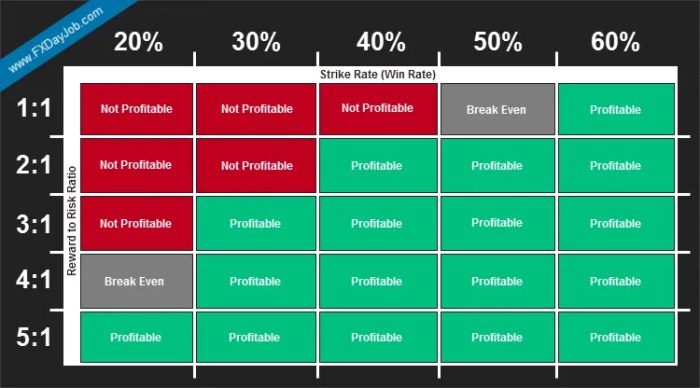
Understanding risk-to-reward ratios is only half the battle in forex trading. The other crucial element is position sizing – determining how much capital to allocate to each trade. Getting this right ensures your trading strategy aligns with your risk tolerance and maximizes potential profits while minimizing potential losses. Ignoring position sizing can negate even the best risk-to-reward calculations, leading to significant account drawdown.
Position sizing is directly linked to your risk-to-reward ratio. A higher risk-to-reward ratio (e.g., 1:3) allows you to take smaller positions for the same level of risk, while a lower ratio (e.g., 1:1) necessitates larger positions to achieve the same risk exposure. This intricate dance between risk, reward, and position size is fundamental to sustainable forex trading. Properly sizing your positions protects your capital and lets you stay in the game long enough to profit from winning trades.
Position Size Calculation Based on Risk-to-Reward Ratio
Calculating the appropriate position size involves several factors, including your account balance, the risk percentage per trade, and the stop-loss distance. The goal is to determine the number of units (lots) to trade such that a stop-loss trigger results in a loss equal to your predetermined risk percentage. Let’s assume a trader has a $10,000 account, aims for a 1% risk per trade, and has identified a trade with a stop-loss of 50 pips.
To determine the position size, we can use the following formula:
Position Size = (Account Balance * Risk Percentage) / (Stop Loss in Pips * Pip Value)
In this case, the pip value depends on the currency pair and the lot size. Assuming a pip value of $10 per standard lot (100,000 units) for the EUR/USD pair:
Position Size = ($10,000 * 0.01) / (50 pips * $10/pip) = 0.2 lots
This means the trader should place a trade of 0.2 standard lots (or 20,000 units) to ensure a maximum loss of $50 (1% of their account). This calculation remains consistent regardless of the risk-to-reward ratio; the ratio influences the potential profit, not the initial risk calculation.
Impact of Different Position Sizes on Profit and Loss
Consider two scenarios with the same risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2, but different position sizes. In both cases, the stop-loss is 50 pips.
Scenario 1: Trader uses a 0.2 lot position (as calculated above). A stop-loss hit results in a $50 loss. If the trade hits the take-profit target (100 pips), the profit will be $100.
Scenario 2: Trader uses a 0.5 lot position. A stop-loss hit results in a $125 loss. If the trade hits the take-profit target (100 pips), the profit will be $250.
As we can see, increasing the position size amplifies both potential profits and potential losses proportionally. While larger positions offer greater profit potential, they also carry a higher risk. The key is to find a balance that aligns with your risk tolerance and trading strategy, informed by your chosen risk-to-reward ratio. This balance is what allows for consistent profitability over the long term. Remember, consistent small wins are often better than occasional large wins coupled with significant losses.
Advanced Risk-to-Reward Strategies
Mastering basic risk-to-reward ratios is just the first step in becoming a successful Forex trader. This section dives into more sophisticated techniques and strategies that seasoned traders employ to fine-tune their risk management and maximize their potential profits. We’ll explore how these advanced methods adapt to different trading styles and market conditions.
Advanced risk management isn’t about rigidly adhering to a single ratio; it’s about flexibility and adaptability. The best approach depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and market context. Understanding these nuances is crucial for consistent profitability.
Explore the different advantages of The Most Important Forex Trading Indicators You Should Know that can change the way you view this issue.
Trailing Stop-Losses, The Basics of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Trailing stop-losses are a dynamic risk management tool that protects profits while allowing trades to continue benefiting from favorable price movements. Unlike fixed stop-losses, which are set at a predetermined price level, trailing stop-losses adjust automatically as the price moves in your favor. This allows you to lock in profits while minimizing potential losses. For example, if you’ve bought EUR/USD at 1.1000 and set a trailing stop-loss of 50 pips, the stop-loss will move up to 1.1050 as the price rises to 1.1050, and then to 1.1100 as the price moves to 1.1100. This strategy ensures that even if the price experiences a slight reversal, you’ll still capture a significant portion of the gains.
Risk-to-Reward Ratios in Different Trading Styles
The optimal risk-to-reward ratio varies considerably depending on your chosen trading style. Scalpers, who aim for small, quick profits, might employ ratios like 1:1 or even 1:0.5, focusing on high win rates to compensate for smaller individual gains. Swing traders, on the other hand, might favor ratios of 1:2 or even higher, aiming for fewer but larger winning trades. The inherent volatility and timeframe of each style dictate the appropriate risk management approach. A scalper’s strategy might involve multiple trades daily, each with a tight stop-loss, while a swing trader might hold positions for days or weeks, employing wider stop-losses.
Comparison of Risk Management Strategies
Several risk management strategies exist beyond simple risk-to-reward ratios. These include strategies like position sizing, diversification, and money management rules. Position sizing determines the amount of capital allocated to each trade, limiting potential losses even with unfavorable risk-to-reward ratios. Diversification involves spreading investments across multiple currency pairs or asset classes, reducing the impact of losses in any single position. Money management rules, such as the “never risk more than X% of your account on a single trade” rule, provide an overarching framework for managing risk across all trades. While risk-to-reward ratios focus on individual trade outcomes, these broader strategies offer a more holistic approach to managing overall portfolio risk. A trader might use a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio while simultaneously adhering to a rule of never risking more than 2% of their account balance on any given trade. This combined approach offers a robust risk management system.
Visualizing Risk and Reward
Understanding risk-to-reward ratios in forex trading is crucial, but seeing it visually can solidify the concept and improve decision-making. Charts and graphs offer a powerful way to represent the potential profit and loss associated with each trade, making the abstract concept of risk and reward much more tangible.
Visualizing your risk and reward allows you to quickly assess the potential payoff against the potential downside of a trade. This visual representation helps you make more informed decisions, particularly when considering position sizing and overall trading strategy. By clearly seeing the potential outcomes, you can better manage your emotions and stick to your trading plan.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels on a Forex Chart
Imagine a forex chart depicting the EUR/USD pair. Let’s say you’ve identified a potential long position (buying EUR/USD) based on your technical and fundamental analysis. You anticipate the price will rise. To visually represent your risk and reward, you’d plot two key levels: a stop-loss order and a take-profit order. The stop-loss order, placed below the entry price, limits your potential loss if the trade moves against you. The take-profit order, placed above the entry price, secures your profit when the price reaches your target.
Let’s say you enter a long position at 1.1000. Your stop-loss order is placed at 1.0950, representing a 50-pip stop-loss (a pip is a unit of price movement in forex). Your take-profit order is placed at 1.1075, representing a 75-pip take-profit. Visually, you’d see a horizontal line at 1.0950 (stop-loss) and another at 1.1075 (take-profit) on your chart. The distance between your entry price and the stop-loss represents your risk, while the distance between your entry price and the take-profit represents your reward. In this example, the risk-to-reward ratio is 50 pips (risk) : 75 pips (reward), or 2:3. This means for every $50 risked, you stand to gain $75. The chart visually demonstrates this relationship clearly; the vertical distance from entry to stop-loss is smaller than the vertical distance from entry to take-profit, visually confirming the favorable 2:3 ratio. This visual representation makes the trade’s risk profile immediately apparent. A trader aiming for a 1:2 or higher risk-to-reward ratio would immediately see this trade meets their criteria.
Epilogue: The Basics Of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios
So, there you have it – the lowdown on forex trading risk-to-reward ratios. It’s not a magic bullet, but a powerful tool to refine your trading approach. By understanding your risk tolerance and calculating your ratios effectively, you can significantly improve your chances of success in the forex market. Remember, consistent application and discipline are key. Don’t just jump in; strategize, analyze, and conquer the forex world one calculated trade at a time. Happy trading!
Helpful Answers
What’s the ideal risk-to-reward ratio?
There’s no universally “ideal” ratio. Many traders aim for a 1:2 or 1:3 ratio (meaning for every $1 risked, they aim for a $2 or $3 profit), but it depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Experiment to find what works best for you.
How often should I adjust my risk-to-reward ratio?
Market conditions change constantly. Regularly review your ratio and adjust it as needed based on current volatility and your trading strategy. Flexibility is key.
Can I use risk-to-reward ratios for all trading styles?
Yes, the principle applies across various styles (scalping, swing trading, day trading), but the specific application and ratio may differ depending on your timeframe and strategy.
What if my trade doesn’t hit my take-profit level?
That’s the inherent risk. Even with calculated ratios, losses are possible. Focus on consistent application of your strategy and risk management to improve your overall win rate over time.
Obtain recommendations related to The Top Forex Trading Strategies for 2025 that can assist you today.




