Forex trading managers: the high-stakes world of global currency markets isn’t just about algorithms and charts; it’s about the sharp minds orchestrating the trades. These individuals navigate the complexities of international finance, balancing risk and reward with precision. From discretionary traders making gut calls to systematic managers relying on data-driven strategies, the role demands a unique blend of financial acumen, technical proficiency, and nerves of steel. This deep dive explores the daily grind, the critical decision-making processes, and the ever-evolving landscape of this fascinating career path.
We’ll uncover the essential skills, the technological tools they wield, and the key performance indicators that determine success. We’ll also examine the crucial role of risk management, the impact of technological advancements, and the future trajectory of this high-impact profession. Get ready for a behind-the-scenes look at the world of forex trading managers—a world where fortunes are made and lost in the blink of an eye.
Defining Forex Trading Managers

Forex trading managers are the unsung heroes of the financial world, navigating the volatile waters of the foreign exchange market to maximize returns for their clients or firms. They’re the strategists, the risk assessors, and the ultimate decision-makers in the world of currency trading. Their role extends far beyond simply buying and selling currencies; it involves a deep understanding of global economics, market trends, and sophisticated trading techniques.
Forex trading managers are responsible for overseeing and managing various aspects of forex trading operations. This includes developing and implementing trading strategies, monitoring market conditions, managing risk, and analyzing trading performance. Their decisions directly impact the profitability and stability of their portfolios, whether they manage funds for institutional clients or individual investors.
Roles and Responsibilities of Forex Trading Managers
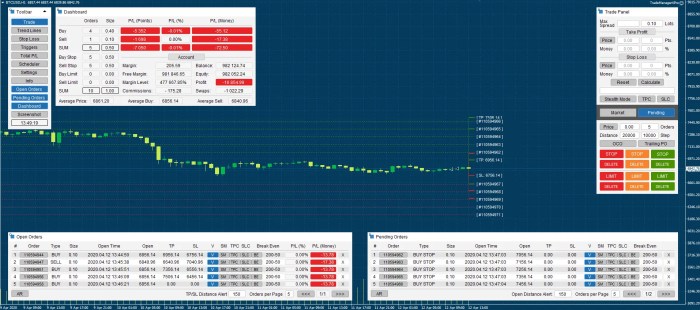
Forex trading managers wear many hats. Their core responsibilities include portfolio management (allocating capital across different currency pairs), risk management (setting stop-loss orders and hedging strategies to limit potential losses), trade execution (placing and monitoring trades), and performance analysis (tracking key metrics like Sharpe ratios and maximum drawdown to evaluate the effectiveness of trading strategies). They also often need to stay abreast of global economic news and political events that can significantly impact currency values, requiring constant monitoring and adjustment of trading strategies. Furthermore, communication with clients or superiors, providing regular updates on portfolio performance and market analysis, is crucial.
Types of Forex Trading Managers
Forex trading managers can be broadly categorized into discretionary and systematic managers. Discretionary managers utilize their experience, judgment, and market insights to make trading decisions, often relying on technical and fundamental analysis. Systematic managers, on the other hand, employ pre-programmed algorithms and automated trading systems based on quantitative models and historical data. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, with discretionary managers offering flexibility and adaptability, while systematic managers provide consistency and objectivity. The choice between these styles often depends on the firm’s investment philosophy and risk tolerance.
Skills and Qualifications Needed for Successful Forex Trading Managers
Success in this field demands a potent combination of skills. A strong understanding of financial markets, including economics, macroeconomics, and international finance, is essential. Proficiency in technical and fundamental analysis, coupled with a deep understanding of various trading strategies (e.g., scalping, swing trading, day trading), is crucial. Furthermore, strong analytical and problem-solving skills are needed to interpret complex data and make informed decisions. Excellent risk management skills are paramount, as is the ability to handle pressure and make quick, decisive decisions in volatile market conditions. Finally, effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for managing client relationships and working collaboratively within a team. A relevant degree (e.g., finance, economics) and professional certifications (e.g., Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)) are often preferred, although experience can sometimes substitute for formal qualifications.
Job Descriptions of Forex Trading Managers Across Various Financial Institutions
The specific responsibilities of a forex trading manager can vary depending on the size and type of financial institution. For instance, a forex trading manager at a large investment bank might focus primarily on institutional clients, managing large sums of money and executing complex trades. Their role might involve more interaction with clients and a higher level of strategic decision-making. In contrast, a forex trading manager at a smaller hedge fund might have a more hands-on approach, directly involved in the execution of trades and the development of trading algorithms. A prop trading firm might require a manager with a strong understanding of risk management and a proven track record of profitability. Regardless of the institution, however, the core responsibilities of portfolio management, risk management, and performance analysis remain central to the role.
The Forex Trading Manager’s Daily Tasks
A day in the life of a Forex trading manager is a whirlwind of market analysis, risk management, and strategic decision-making. It’s a high-pressure environment demanding constant vigilance and adaptability, requiring a unique blend of analytical skills, technical expertise, and nerves of steel. Let’s delve into the intricacies of their daily routine.
A Typical Day for a Forex Trading Manager
The daily schedule of a Forex trading manager is highly dynamic, influenced by global market events and the specific strategies employed. However, a typical day often unfolds as follows: The day begins before the market opens, reviewing overnight news and preparing for the trading day. This includes analyzing economic indicators, reviewing charts and technical analysis, and assessing potential market movements. During market hours, the manager actively monitors trades, adjusts positions based on market fluctuations, and communicates with traders and analysts. The afternoon is dedicated to portfolio analysis, risk assessment, and reporting. The day ends with a review of the day’s performance and planning for the next trading session. This process involves constant monitoring of various news sources, market data feeds, and trading platforms.
Challenges Faced by Forex Trading Managers
Forex trading managers encounter a myriad of challenges daily. Managing risk effectively is paramount, requiring constant monitoring of market volatility and implementing appropriate risk mitigation strategies. Staying ahead of the curve necessitates a deep understanding of global economic trends, geopolitical events, and their impact on currency pairs. The constant pressure of achieving performance targets and managing client expectations adds another layer of complexity. Furthermore, technological issues, data inaccuracies, and unexpected market shocks can significantly impact their work. For instance, a sudden geopolitical event could trigger significant market volatility, requiring rapid adjustments to trading strategies and risk management plans. Similarly, a technical failure of a trading platform could lead to missed opportunities or even losses.
Decision-Making Processes in Forex Trading Management
The decision-making process for a Forex trading manager is multifaceted and data-driven. It involves a careful assessment of market conditions, considering various factors such as economic indicators (e.g., inflation rates, interest rates, GDP growth), geopolitical events, and technical analysis (e.g., chart patterns, support and resistance levels). Risk tolerance and investment objectives are also crucial elements. For example, a manager might decide to increase exposure to a particular currency pair if the economic indicators suggest strong growth in that country’s economy, but reduce exposure if geopolitical instability arises in that region. This requires a deep understanding of both fundamental and technical analysis, as well as the ability to interpret and synthesize complex information.
Workflow Diagram and Daily Tasks Summary
The following table provides a simplified workflow diagram of a Forex trading manager’s daily tasks:
| Task | Tools Used | Time Allocation | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Analysis (Pre-Market) | Charting software, economic calendars, news websites | 1-2 hours | Information overload, conflicting signals |
| Trade Execution and Monitoring | Trading platform, order management systems | 4-6 hours | Market volatility, technical glitches |
| Risk Management and Portfolio Adjustment | Risk management software, portfolio tracking tools | 2-3 hours | Unexpected market events, inaccurate data |
| Reporting and Communication | Email, reporting software, client communication platforms | 1 hour | Client dissatisfaction, communication breakdowns |
Risk Management Strategies Employed
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Successful forex trading managers understand this and employ a robust suite of risk management strategies to protect their capital and ensure consistent profitability. These strategies aren’t just about limiting losses; they’re about optimizing returns while maintaining a sustainable trading approach.
Effective risk management is the cornerstone of any successful forex trading operation. It’s a multifaceted process that involves careful planning, diligent monitoring, and a deep understanding of market dynamics. Neglecting risk management can quickly lead to significant losses, even wiping out entire trading accounts. Therefore, a comprehensive approach is crucial.
Discover how forex trading mentors has transformed methods in this topic.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines the amount of capital allocated to each trade. It’s calculated based on factors like risk tolerance, account size, and the potential reward-to-risk ratio of a specific trade setup. A common approach is to risk a fixed percentage of the account balance on any single trade – for example, 1% to 2%. This ensures that even a losing trade won’t severely impact the overall account balance. Sophisticated algorithms and software are often used to automate position sizing calculations, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting potential losses on open positions. These orders automatically close a trade when the market price reaches a predetermined level. For example, a trader might set a stop-loss order at a point where a loss would be acceptable, preventing further losses if the market moves against their position. Properly placed stop-losses are a vital safeguard against substantial financial setbacks. The placement of these orders often involves technical analysis, identifying key support and resistance levels to determine optimal placement.
Take-Profit Orders
Take-profit orders are the counterpart to stop-loss orders. They automatically close a trade when the market price reaches a predetermined profit target. This helps to secure profits and prevents the erosion of gains if the market reverses unexpectedly. Combining stop-loss and take-profit orders creates a defined risk-reward profile for each trade, enabling better control over potential outcomes. Strategic placement of these orders can be crucial for maximizing returns.
Diversification
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across multiple currency pairs, trading strategies, or even asset classes. This reduces the impact of losses from any single trade or market event. For instance, instead of concentrating solely on EUR/USD, a forex trading manager might also trade GBP/JPY, USD/CHF, and AUD/USD. This approach reduces the overall risk exposure, as a downturn in one market may be offset by gains in another. It’s a key element of managing overall portfolio risk and enhancing long-term stability.
Risk Tolerance Levels and Their Implications
Understanding and managing risk tolerance is paramount. Different traders have different levels of comfort with risk. This influences their trading strategies and the level of risk they are willing to accept.
- Conservative Risk Tolerance: These traders prioritize capital preservation. They typically employ smaller position sizes, tighter stop-losses, and diversified portfolios. They aim for consistent, albeit smaller, profits. They might focus on lower-risk strategies with smaller potential rewards but lower potential losses.
- Moderate Risk Tolerance: These traders seek a balance between risk and reward. They might use moderate position sizes, wider stop-losses, and a moderately diversified portfolio. They aim for a balance between capital preservation and substantial profit generation.
- Aggressive Risk Tolerance: These traders are comfortable with higher risk for the potential of larger returns. They might use larger position sizes, wider stop-losses, and potentially less diversified portfolios. They are prepared to accept larger potential losses in pursuit of greater profits. This strategy often involves more advanced techniques and sophisticated risk management systems.
Monitoring and Controlling Risk Exposure
Continuous monitoring of risk exposure is essential. This involves regularly reviewing open positions, assessing market conditions, and adjusting risk parameters as needed. Sophisticated trading platforms often provide tools for real-time risk monitoring, allowing managers to quickly identify and address potential problems. Regular performance reviews and stress testing scenarios help identify potential weaknesses in the risk management framework. Moreover, maintaining detailed records of trades and their outcomes provides valuable data for refining future strategies and risk management approaches.
Technology and Tools Used: Forex Trading Managers
Forex trading managers rely on a sophisticated technological arsenal to navigate the complexities of the global currency market. Their success hinges on access to real-time data, powerful analytical tools, and efficient execution platforms. The right technology empowers them to make informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and ultimately, maximize profits.
Essential Software and Platforms
Forex trading managers utilize a range of software and platforms, each playing a crucial role in their daily operations. These tools provide access to market data, facilitate order execution, and enable backtesting and analysis. Popular choices include trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), known for their extensive charting capabilities and automated trading features. Bloomberg Terminal and Refinitiv Eikon are also frequently used, offering comprehensive market data, news, and analytics. Specialized charting software like TradingView provides advanced charting tools and technical analysis indicators. Finally, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software helps manage client communication and portfolio information.
The Role of Data Analytics in Forex Trading Management
Data analytics is the backbone of effective forex trading management. Managers leverage historical price data, economic indicators, news sentiment, and other relevant information to identify trends, predict market movements, and optimize trading strategies. This involves using statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and other quantitative techniques to analyze large datasets and extract actionable insights. For instance, a manager might use regression analysis to model the relationship between interest rate changes and currency pair movements, or employ sentiment analysis to gauge market sentiment towards a specific currency. The ability to effectively process and interpret this data is crucial for making well-informed trading decisions.
Algorithmic Trading and Automated Systems
Algorithmic trading, or automated trading, plays an increasingly significant role in forex trading management. These systems use pre-programmed rules and algorithms to execute trades automatically, based on predefined criteria. This allows for faster execution speeds, reduced emotional bias, and the ability to manage a large number of trades simultaneously. Common types of algorithmic trading strategies include trend following, mean reversion, and arbitrage. For example, a mean reversion algorithm might automatically buy a currency pair when it falls below a certain moving average, and sell when it rises above another. While algorithmic trading offers significant advantages, it’s crucial to carefully design and test algorithms to ensure their robustness and effectiveness. Risk management remains paramount, even with automated systems.
Useful Resources for Forex Trading Managers
A constant pursuit of knowledge is vital for success in forex trading management. Staying updated on market trends, new technologies, and best practices requires dedicated effort. The following resources can provide valuable insights and support:
- Books: “Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas, “Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques” by Steve Nison, “How to Make Money in Stocks” by William J. O’Neil.
- Articles: Publications from reputable financial news sources like the Financial Times, Bloomberg, and Reuters, along with academic journals specializing in finance and economics.
- Websites: Investopedia, Forex Factory, Babypips (for beginners), and official websites of central banks and regulatory bodies.
Performance Measurement and Evaluation
Forex trading managers, the unsung heroes (or villains, depending on the month!) of the financial world, need a robust system to measure their performance. Without clear metrics, assessing success or failure becomes a blurry guessing game. This section dives into the crucial KPIs, reporting methods, and review processes used to evaluate these high-stakes professionals.
Evaluating a forex trading manager isn’t just about the bottom line; it’s a multi-faceted assessment considering risk management, consistency, and overall strategy effectiveness. The right KPIs, reporting structures, and review processes are essential for ensuring accountability and driving continuous improvement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Forex Trading Managers
Several key performance indicators are used to gauge the effectiveness of a forex trading manager. These aren’t just numbers on a spreadsheet; they’re vital signals reflecting the manager’s skill, strategy, and risk management prowess. A balanced approach, considering both profitability and risk, is crucial.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The most straightforward measure, calculating the percentage return on invested capital. A consistently high ROI indicates strong performance.
- Sharpe Ratio: This risk-adjusted return metric measures excess return per unit of risk. A higher Sharpe ratio suggests better risk-adjusted performance.
- Sortino Ratio: Similar to the Sharpe Ratio, but it only considers downside deviation, focusing on negative returns. This provides a more nuanced view of risk management.
- Maximum Drawdown: This metric identifies the largest peak-to-trough decline in portfolio value. Lower maximum drawdown indicates better risk control.
- Calmar Ratio: The ratio of average annual rate of return to maximum drawdown. A higher Calmar ratio suggests better risk-adjusted returns.
- Win Rate: The percentage of winning trades compared to the total number of trades. A high win rate, coupled with a favorable average win/loss ratio, points to a successful trading strategy.
Portfolio Performance Tracking and Reporting
Tracking and reporting portfolio performance is an ongoing process, demanding meticulous record-keeping and the use of specialized software. Regular updates ensure transparency and facilitate timely adjustments to the trading strategy.
Methods include daily/weekly/monthly performance summaries, detailed trade logs, and the use of portfolio management software that automatically calculates KPIs and generates reports. Visualizations, such as charts and graphs, are crucial for effective communication and identification of trends.
Get the entire information you require about best ai for forex trading on this page.
Performance Review Process for Forex Trading Managers
Performance reviews are not merely annual formalities; they are vital opportunities for feedback, strategy refinement, and identifying areas for improvement. A structured approach ensures objectivity and fosters a culture of continuous learning.
The process typically involves a formal meeting between the manager and their supervisor, where the manager presents their performance report, discussing both successes and shortcomings. The discussion should include an analysis of the KPIs, a review of individual trades, and a look at overall market conditions. The review concludes with setting new goals and developing action plans for the next period.
Sample Performance Report
A clear and concise performance report is essential for effective evaluation. The following table provides a sample structure, highlighting key metrics, actual results, and target goals.
| Key Metric | Actual Result | Target Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Return on Investment (ROI) | 15% | 10% |
| Sharpe Ratio | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Maximum Drawdown | -5% | -7% |
| Win Rate | 65% | 60% |
| Average Trade Profit | $500 | $400 |
The Future of Forex Trading Management

The forex market is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving market dynamics. Forex trading managers will need to adapt and embrace these changes to remain competitive and effective. The future of this profession is inextricably linked to the ability to leverage technology, understand emerging trends, and develop a future-proof skillset.
The impact of technological advancements on forex trading management is profound and multifaceted. Increased automation, sophisticated analytical tools, and the rise of artificial intelligence are reshaping the landscape. This is not just about faster execution speeds; it’s about deeper market insights, more efficient risk management, and the potential for entirely new trading strategies.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Algorithmic trading is becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing for the execution of complex trading strategies at speeds and scales previously unimaginable. Machine learning algorithms are being used to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and predict market movements with increasing accuracy. This necessitates a shift in the forex trading manager’s role from primarily manual execution to overseeing and optimizing these automated systems. For example, a manager might focus on backtesting algorithms, refining parameters, and integrating new data sources to improve predictive accuracy, rather than manually placing trades throughout the day. Furthermore, blockchain technology promises increased transparency and security in transactions, streamlining processes and reducing the risk of fraud.
Emerging Trends in Forex Trading Management
Several key trends are shaping the future of forex trading management. The increasing importance of data analytics and the use of AI-powered tools for predictive modeling is one significant development. Another is the growing demand for specialized expertise in areas like algorithmic trading, risk management, and regulatory compliance. The rise of fintech companies is also impacting the field, providing innovative solutions for trading execution, risk management, and portfolio optimization. For instance, we’re seeing a surge in robo-advisors for forex trading, requiring managers to understand and integrate these technologies into their workflows.
Future Skills and Knowledge Required
To thrive in this evolving environment, forex trading managers will need a robust skillset encompassing both technical and soft skills. Proficiency in data analytics, programming languages (like Python), and machine learning algorithms will be crucial. A deep understanding of financial markets, risk management principles, and regulatory compliance is also non-negotiable. Furthermore, strong communication, leadership, and problem-solving skills will be essential for managing teams and navigating complex market situations. Managers who can effectively bridge the gap between technological advancements and human expertise will be in high demand.
Predicted Evolution of the Forex Trading Manager’s Role (5-10 Years)
Imagine a visual representation: The current forex trading manager, depicted as a person meticulously analyzing charts and placing trades, gradually transitions over the next 5-10 years. This transition is represented by a morphing image where the person is increasingly surrounded by sophisticated technological interfaces. They are no longer solely focused on manual execution but are actively overseeing and optimizing AI-driven trading systems. The visual then shifts to show the manager collaborating with data scientists and engineers, leveraging their expertise to develop and refine advanced trading algorithms and risk management strategies. The final image shows the manager leading a team, effectively communicating market insights and risk assessments to stakeholders, demonstrating a strategic leadership role rather than a purely operational one. This evolution highlights the shift from a primarily operational role to a strategic, technology-focused leadership position.
Last Word
So, there you have it—a glimpse into the exhilarating and demanding world of forex trading managers. From meticulously managing risk to leveraging cutting-edge technology, these professionals are the architects of financial success in the dynamic forex market. The future of this field is bright, promising even more sophisticated strategies and technological integration. As the global economy continues its interconnected dance, the role of the forex trading manager will only grow in significance, demanding a constant evolution of skills and adaptability in the face of ever-shifting market conditions. The challenge is immense, the rewards potentially enormous, and the journey, undeniably captivating.




