
Can you start forex trading with $10? The short answer is: technically, yes. But the longer answer? It’s a wild ride filled with more risk than a rollercoaster on fire. This isn’t your typical get-rich-quick scheme; it’s a high-stakes gamble where even the smallest misstep can wipe out your entire $10. We’re diving deep into the realities of micro-trading, exploring the potential, the pitfalls, and whether it’s even worth the headache.
This article unpacks the challenges of starting with such a minuscule amount, examining leverage, risk management, broker selection, and the crucial importance of realistic expectations. We’ll also explore alternative routes, like demo accounts, that can help you hone your skills before risking any real money. Get ready for a no-nonsense look at the world of forex trading on a shoestring budget.
Trading Account Minimums
So, you’re dreaming of conquering the forex market, but your starting capital is… modest, to say the least. We’ve already established that yes, you *can* technically start with $10, but let’s delve into the nitty-gritty of what that actually means in terms of account minimums and the realities of trading with such a small sum. It’s a bit like trying to win a marathon on a tricycle – possible, but incredibly challenging.
The minimum deposit required to open a forex trading account varies wildly depending on the broker. Some cater to high-rollers, while others offer accounts designed for beginners with limited funds. However, even those with lower minimums often come with significant limitations. Understanding these differences is crucial before you even think about clicking that “sign-up” button.
Broker Minimum Deposit Requirements
This table compares the minimum deposit requirements of a few popular forex brokers. Remember that these can change, so always check the broker’s website for the most up-to-date information. Leverage, a powerful tool that magnifies both profits and losses, is also a key factor to consider. Higher leverage allows you to control larger positions with a smaller deposit, but it also increases your risk significantly.
| Broker Name | Minimum Deposit (USD) | Account Type | Leverage Offered (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Broker A | $5 | Micro Account | 1:500 |
| Example Broker B | $100 | Standard Account | 1:200 |
| Example Broker C | $250 | Standard Account | 1:100 |
| Example Broker D | $0 (with limitations) | Demo Account | Variable, often limited |
Implications of Trading with a Very Small Account Balance
Trading with only $10 presents significant challenges. The most obvious is the extremely limited position sizing. This means you can only trade incredibly small amounts, making it difficult to generate substantial profits, even with successful trades. Moreover, a single losing trade could wipe out your entire account balance, rendering your efforts futile. The spreads (the difference between the buy and sell price) will also eat into your capital more significantly, relative to the size of your trades.
Challenges and Limitations of Starting with $10
Let’s be frank: starting with $10 is incredibly risky. While some brokers allow it, the potential for loss is far greater than the potential for gain. The low account balance severely limits your trading strategies and significantly increases your vulnerability to market volatility. You’ll have very little room for error, and even minor market fluctuations can lead to substantial losses. Furthermore, the fees associated with trading can quickly consume your small capital, leaving you with little to show for your efforts. Consider it a high-stakes gamble, not a sustainable trading strategy.
Leverage and Risk
Forex trading, even with a small account like $10, offers the possibility of significant returns. However, this potential is inextricably linked to the concept of leverage, a double-edged sword that magnifies both profits and losses. Understanding leverage and its inherent risks is paramount before venturing into the forex market.
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position in the market than their account balance would normally permit. It’s essentially borrowed capital provided by your broker. For example, a 1:100 leverage means that for every $1 in your account, you can control $100 worth of currency. With a $10 account and 1:100 leverage, you could theoretically trade positions worth $1000. This dramatically increases your potential profit, but equally amplifies potential losses.
Leverage’s Impact on Profits and Losses
The impact of leverage on a small account is substantial. A small price movement in your favor can lead to a seemingly large percentage gain. Conversely, an equally small movement against your position can result in significant losses, potentially wiping out your entire account. Let’s illustrate this with examples.
Imagine a scenario where you use 1:100 leverage to buy $1000 worth of EUR/USD at 1.1000. If the price rises to 1.1010 (a 0.1% increase), your $1000 position gains $10. With your 1:100 leverage, this translates to a 100% return on your $10 investment – your account balance doubles. However, if the price falls to 1.0990 (a 0.1% decrease), you lose $10, resulting in a 100% loss, wiping out your initial investment.
Risks Associated with High Leverage
High leverage significantly increases the risk of substantial losses, especially with a limited account balance. A single unfavorable trade can easily erase your entire capital. The margin call is a critical element of this risk. A margin call occurs when your losses reach a certain point, forcing your broker to close your position to prevent further losses. This often happens suddenly and unexpectedly, especially with high leverage and volatile market conditions. The margin call doesn’t offer an opportunity to react and limit losses, leaving your account depleted. The speed at which losses can accumulate with high leverage is alarming.
Examples of High Leverage Gains and Losses with a $10 Account
Let’s consider two scenarios, one positive and one negative, to illustrate the extreme volatility.
Scenario 1: Successful Trade
You buy $1000 worth of GBP/USD at 1.2500 with 1:100 leverage. The price rises to 1.2550 (a 0.4% increase). Your profit is $50, representing a 500% return on your $10 investment. Your account balance becomes $60.
Scenario 2: Unsuccessful Trade
You buy $1000 worth of USD/JPY at 110.00 with 1:100 leverage. The price falls to 109.50 (a 0.45% decrease). Your loss is $50, resulting in a complete loss of your initial $10 investment. Your account balance reaches zero. This highlights how quickly a small account can be liquidated with high leverage and an adverse market movement.
These examples emphasize the extreme risk involved in using high leverage with a small trading capital. While the potential for profit is enticing, the likelihood of substantial and rapid losses is equally significant.
Trading Strategies and Methods: Can You Start Forex Trading With
Starting forex trading with a meager $10 requires a laser focus on risk management and realistic expectations. Forget about getting rich quick; this is about learning, honing your skills, and gradually building your capital. The strategies employed need to be meticulously planned and executed, prioritizing preservation of capital over chasing large profits.
Sample Trading Plan for a $10 Account, Can you start forex trading with
A successful trading plan, even with limited capital, hinges on three pillars: risk management, strategy selection, and consistent execution. For a $10 account, consider a micro-lot strategy (typically 1000 units of base currency). This allows for small position sizes, minimizing the impact of potential losses. A conservative risk-reward ratio of 1:1 (or even 1:0.5, risking less to gain less) is crucial. This means that for every $0.10 risked, you aim for a $0.10 (or $0.05) profit. Only trade during periods of low volatility to reduce the chance of sudden, large price swings wiping out your account. Avoid trading news events, as these are known for high volatility. Your profit target should be modest; aim for a small percentage increase daily or weekly, rather than a massive overnight gain. Consistent, small profits are far more sustainable than infrequent, large wins and frequent losses. Regularly review and adjust your plan based on market conditions and your performance.
Low-Risk Trading Strategies
Scalping and range trading are suitable strategies for low-capital accounts. Scalping involves taking small profits from tiny price movements within a short time frame. For example, if a currency pair moves 2 pips (points), you might close your position and take your small profit. Range trading involves identifying support and resistance levels within a currency pair’s price range. You would buy near support levels and sell near resistance levels, aiming to profit from the price bouncing within the defined range. Both strategies require diligent monitoring of the market and quick execution of trades. It’s vital to use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Suitable Trading Indicators for Low-Capital Trading
Choosing the right indicators can significantly improve your trading decisions. Over-reliance on complex indicators is counterproductive with limited capital. Simple, reliable indicators are key. The Simple Moving Average (SMA) helps identify trends; a 20-period SMA could be used to spot short-term trends. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) can help identify overbought and oversold conditions, signaling potential reversal points. The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can indicate momentum shifts. However, remember that no indicator is perfect, and using them in conjunction with price action analysis is crucial. Over-reliance on any single indicator can lead to inaccurate signals and losses. Avoid using too many indicators simultaneously, as this can lead to “indicator overload” and confusing signals. Start with one or two and gradually add more as your understanding and experience grow.
Broker Selection and Fees

Starting forex trading with a meager $10 demands meticulous broker selection. Your choice significantly impacts your trading experience, especially concerning fees that can quickly eat into your small capital. Finding a broker with transparent and competitive pricing is paramount for survival in this high-stakes game.
Choosing the right forex broker when you’re starting with limited capital requires careful consideration of several key factors. The fees you pay—in the form of spreads and commissions—can make or break your trading journey. A seemingly small difference in fees can dramatically affect your profitability, particularly with a small account balance like $10. Understanding these fee structures is crucial before committing to any broker.
Commission Structures and Spreads
The two primary fee structures you’ll encounter are commission-based and spread-based. Commission-based brokers charge a fee per trade, typically a small amount per lot. Spread-based brokers incorporate the commission into the spread—the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair. For a $10 account, spread-based brokers might seem initially attractive due to the absence of an explicit commission, but the spreads themselves can be wider, potentially offsetting any perceived savings. Some brokers even offer a hybrid model, combining both commissions and spreads. It’s crucial to compare the total cost of trading across different brokers, considering both spreads and commissions to determine the most cost-effective option. For example, a broker advertising a low spread of 1 pip might have hidden commissions that negate the advantage, while a broker with a slightly higher spread of 1.2 pips but zero commission might prove more beneficial for a small account.
Broker Fee Comparison: Impact on a $10 Account
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: you’re trading a micro lot (0.01 lot) of EUR/USD. Broker A charges a spread of 1.5 pips and no commission, while Broker B charges a spread of 1 pip and a $2 commission per trade. If the price moves 10 pips in your favor, you might make a profit of roughly $10 (the exact amount varies based on leverage and lot size). With Broker A, your profit would be reduced by the 1.5-pip spread, whereas with Broker B, your profit would be reduced by the 1-pip spread and the $2 commission. In this instance, Broker B might be less favorable due to the fixed commission, which represents a significant portion of your initial capital. The impact of fees becomes even more pronounced when considering multiple trades.
Questions to Ask Potential Brokers
Before opening an account, clarify several crucial points with potential brokers. This proactive approach protects your limited capital and ensures a transparent trading relationship.
- What are your minimum deposit requirements and account types?
- What are your spread and commission structures for the currency pairs I intend to trade?
- Do you offer any educational resources or demo accounts to practice trading risk-free?
- What is your leverage policy, and what are the associated risks?
- What are your withdrawal policies and fees?
- What regulatory bodies oversee your operations, and what is your track record?
- What customer support channels do you offer, and what are their response times?
Realistic Expectations and Education
Starting forex trading with a limited budget like $10 requires a brutally honest assessment of your potential. Forget get-rich-quick schemes; this isn’t a lottery ticket. Success in forex trading, regardless of your starting capital, hinges on realistic expectations and a dedicated commitment to learning. The path to profitability is long, demanding, and filled with setbacks.
Understanding that consistent, sustainable profits take time is crucial. With $10, your initial trades will be tiny, and your potential earnings will be correspondingly small. This isn’t inherently bad; it’s a realistic starting point that allows you to practice and refine your skills without risking significant losses. The focus should be on mastering the fundamentals, not immediate riches.
The Importance of Forex Education
Acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills for forex trading isn’t a quick process. It demands a structured approach. This involves more than just watching a few YouTube videos. You need a deep understanding of fundamental and technical analysis, risk management, and market psychology. Consider dedicating time to studying reputable sources such as books written by experienced traders, online courses from recognized institutions, and educational materials provided by your chosen broker. Focus on building a solid foundation in economic indicators, chart patterns, and trading strategies. Don’t jump into live trading until you feel comfortable with these concepts.
Time Commitment and Effort Required for Forex Trading
Forex trading is not a passive income stream; it demands significant time and effort. Expect to dedicate hours each week to learning, researching, analyzing charts, and practicing your strategies. This isn’t a part-time hobby; it’s a demanding endeavor that requires consistent attention. Successful traders often spend many hours studying market trends, backtesting strategies, and adapting their approaches based on market conditions. Realistically, expect this commitment to increase as you gain experience and manage a more complex trading strategy. For example, a beginner might dedicate 10-15 hours per week to learning and practice, while a more experienced trader might spend significantly more time managing their trades and analyzing the market. Remember that even experienced traders experience losses; it’s part of the process.
Managing Expectations with Limited Capital
Trading with $10 means extremely small position sizes. Your potential profits will be modest, and even small market fluctuations can significantly impact your account balance. This requires extreme discipline in risk management. Avoid leveraging your account aggressively; a single losing trade could wipe out your entire balance. Focus on developing a robust trading plan that includes clear entry and exit strategies, stop-loss orders, and a well-defined risk tolerance. Celebrate small wins, learn from losses, and remember that consistent, gradual growth is more realistic than overnight riches. Consider this initial $10 as an investment in your education, not a fast track to wealth. The goal is to learn and grow your skills, gradually increasing your capital as your expertise develops.
Alternative Options

So, you’re dreaming of forex trading, but the initial investment feels a bit daunting? Don’t worry, you don’t need a king’s ransom to dip your toes into the exciting (and sometimes treacherous) waters of the forex market. There are excellent ways to gain experience and hone your skills without risking your hard-earned cash. Let’s explore some alternatives.
Before diving headfirst into live trading, even with a small account, consider the power of practice. This is where demo accounts and paper trading shine. They offer a risk-free environment to test your strategies, learn the ropes, and build confidence without the fear of losing money. Understanding the differences between these methods and live trading is key to choosing the right path for your learning journey.
Demo Account Trading
A demo account mirrors a real forex trading environment, but without the real money. Brokers typically provide these accounts with virtual funds, allowing you to execute trades and experience the market’s dynamics without financial consequences. This is a fantastic way to experiment with different trading strategies, test your risk management techniques, and get accustomed to the trading platform’s interface. You can practice placing orders, setting stop-loss and take-profit levels, and analyzing charts – all without the pressure of potential losses. Many brokers offer demo accounts with unlimited virtual funds, allowing for extended practice and experimentation. Think of it as a forex trading simulator, perfect for refining your skills before entering the real arena.
Paper Trading
Paper trading is similar to demo trading but offers a slightly different approach. Instead of using a broker’s simulated platform, you can use spreadsheet software or specialized applications to track your trades using historical or real-time market data. This method gives you more control over the data you’re working with and can be helpful for backtesting strategies. However, it lacks the immediate feedback and emotional experience of a live trading environment, which can be a crucial aspect of learning. You won’t experience the adrenaline rush of a winning trade or the sting of a losing one, which can significantly impact your decision-making in a live market setting.
Demo Account vs. Live Trading with a Small Account: A Comparison
| Feature | Demo Account | Live Trading (Small Account) |
|---|---|---|
| Risk | None | High (potential for significant losses) |
| Emotional Impact | Limited | Significant (stress, excitement, fear) |
| Real-World Experience | Simulated | Authentic |
| Learning Curve | Steeper initially (platform familiarity), but safer | Steeper initially (risk management, emotional control), but faster adaptation |
| Cost | Free | Broker fees, potential losses |
Setting Up and Utilizing a Demo Trading Account
Setting up a demo account is generally straightforward. First, choose a reputable forex broker that offers demo accounts. Many well-known brokers provide this service. Next, register for an account, providing the necessary information. Once your account is created, you’ll typically be given a virtual amount of funds to start trading. The process varies slightly depending on the broker, but most platforms provide intuitive tutorials and support to guide you through the initial steps. Before starting to trade, familiarize yourself with the platform’s interface, features, and order execution process. Experiment with different order types, chart analysis tools, and indicators. Use this opportunity to develop and refine your trading strategies without any financial risk. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering the art of forex trading.
Risk Management and Stop-Loss Orders
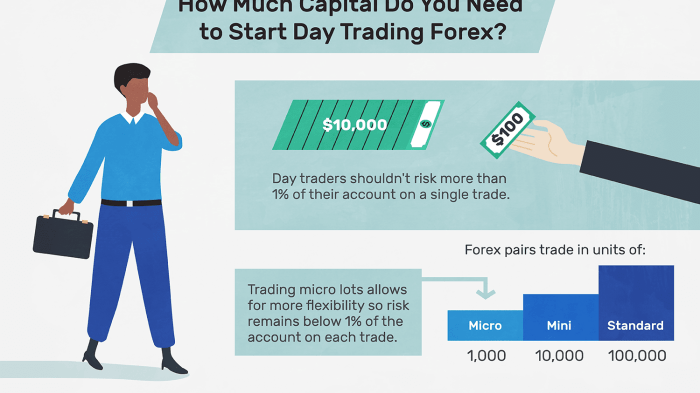
Starting forex trading with a small account like $10 demands an almost obsessive focus on risk management. It’s not about getting rich quick; it’s about surviving long enough to learn and potentially grow your capital. Losing your entire $10 in a single trade is game over, so safeguarding your funds is paramount. This involves understanding and diligently employing stop-loss orders.
Risk management in forex trading, especially with limited capital, is about preserving your trading account. Every trade carries inherent risk, and the smaller your account, the more devastating even a small loss can be. Effective risk management strategies help you control potential losses, preventing a single bad trade from wiping out your entire investment. This is where stop-loss orders become indispensable.
Stop-Loss Order Functionality
A stop-loss order is a crucial tool that automatically closes a losing trade when the price reaches a predetermined level. You set this level based on your risk tolerance, aiming to limit potential losses to an acceptable amount. Imagine it as a safety net preventing your account from plummeting. For example, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000 and set a stop-loss at 1.0980, your trade will automatically close if the price drops to 1.0980, limiting your loss to 20 pips (0.0020). This prevents further losses if the market moves unexpectedly against your position.
Stop-Loss Order Strategies
The effectiveness of a stop-loss order depends on its placement. Several strategies exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right strategy requires considering your trading style, risk appetite, and the specific market conditions.
| Stop-Loss Strategy | Description | Example | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Stop-Loss | A fixed number of pips from your entry price. | Buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, stop-loss at 1.0980 (20 pips). | Simple, easy to implement. | May not always be optimal in volatile markets. |
| Percentage-Based Stop-Loss | A percentage of your initial investment. | Risk 2% of your $10 account ($0.20) per trade. | Maintains consistent risk per trade. | Requires precise calculation based on position size. |
| Trailing Stop-Loss | Moves the stop-loss as the price moves in your favor, locking in profits. | Buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, trailing stop-loss at 10 pips behind the price. | Protects profits, allows for larger price movements. | Can lead to smaller profits if the price reverses sharply. |
| Support/Resistance-Based Stop-Loss | Places the stop-loss just below a support level (for long positions) or above a resistance level (for short positions). | Buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, stop-loss at the nearest support level (e.g., 1.0970). | Utilizes technical analysis for more informed stop-loss placement. | Requires accurate identification of support/resistance levels. |
Position Sizing and Stop-Loss Interaction
The amount of money you risk on each trade (position sizing) is directly related to your stop-loss order. With a $10 account, you must be extremely conservative. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your account balance on any single trade. This means risking only $0.10-$0.20 per trade. This will significantly impact your position size and the number of pips you can afford to lose before hitting your stop-loss. It’s crucial to calculate this precisely to prevent substantial losses. For example, if you risk $0.20 and your stop-loss is 20 pips, you can calculate your position size accordingly. Remember, smaller position sizes mean more trades, but they also reduce your risk of significant losses.
Closure
So, can you start forex trading with $10? Yes, but proceed with extreme caution. While technically possible, the reality is harsh: the odds are stacked against you. High leverage magnifies both wins and losses, and with only $10, one bad trade can be game over. Instead of jumping straight into live trading with such a small sum, consider mastering the fundamentals, practicing with a demo account, and focusing on building a solid understanding of the market before risking any real capital. Think of it as learning to swim in a kiddie pool before attempting the ocean. Your $10 will thank you for it.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of best indicator for forex trading through case studies.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of forex trading plan template.




