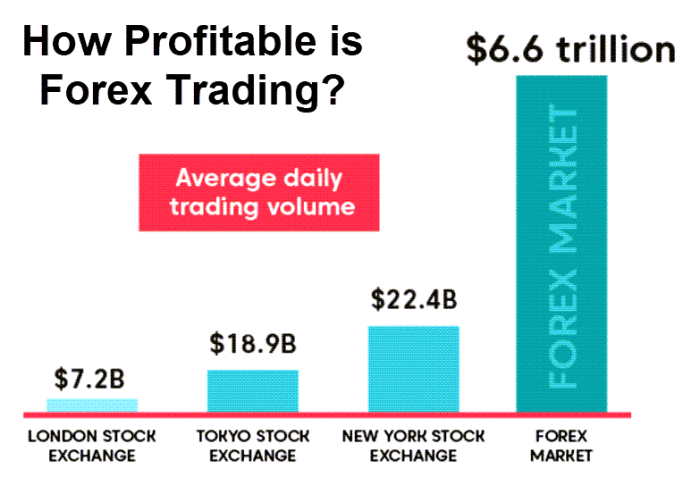
Is forex trading profitable? That’s the million-dollar question, isn’t it? The allure of potentially quick riches in the foreign exchange market is undeniable, but the reality is far more nuanced. This isn’t some get-rich-quick scheme; it’s a complex world of economic indicators, geopolitical shifts, and high-stakes decision-making. We’re diving deep into the world of forex, exploring the strategies, the risks, and ultimately, whether you can realistically profit from trading currencies.
From understanding leverage and margin to mastering technical and fundamental analysis, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to navigate this thrilling yet treacherous landscape. We’ll look at various trading styles – scalping, day trading, swing trading – weighing their pros and cons and helping you determine if forex trading aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Get ready to separate the hype from the reality.
The Nature of Forex Trading Profitability
Forex trading, the global marketplace for exchanging currencies, holds the allure of substantial profits but also carries significant risks. Understanding the inherent volatility and the factors influencing success is crucial before diving in. This section explores the complexities of forex profitability, comparing it to other investment avenues and examining various trading strategies.
Inherent Risks and Rewards of Forex Trading
The forex market’s decentralized nature and 24/5 operation create both opportunities and challenges. High leverage, a key feature allowing traders to control larger positions with smaller capital, magnifies both gains and losses. A small market movement can lead to significant profits or devastating losses. Unforeseen geopolitical events, economic shifts, and sudden market fluctuations can dramatically impact currency values, highlighting the need for careful risk management. Conversely, the market’s liquidity and accessibility offer opportunities for nimble traders to capitalize on short-term price swings. The potential for high returns attracts many, but the risk of substantial losses necessitates a thorough understanding of market dynamics and personal risk tolerance.
Factors Influencing Forex Profitability
Several interconnected factors significantly impact forex profitability. Economic indicators, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and GDP growth, influence currency values. A strong economy generally supports a stronger currency. Geopolitical events, including political instability, wars, and international trade agreements, can cause sudden and dramatic shifts in currency exchange rates. Market sentiment, driven by news reports, analyst opinions, and overall investor confidence, also plays a critical role. Technical analysis, which focuses on chart patterns and price trends, and fundamental analysis, which considers economic and political factors, are often used to predict future price movements. Successful traders often combine both approaches for a comprehensive view.
Comparison with Other Investment Vehicles
Compared to other investment vehicles like stocks and bonds, forex trading offers higher potential returns but also higher risk. Stocks offer ownership in a company, with potential for long-term growth through dividends and capital appreciation. Bonds represent loans to governments or corporations, offering relatively lower risk and stable income streams. Forex trading, with its inherent volatility and leverage, presents a vastly different risk-reward profile. While stocks and bonds might offer steady, albeit slower, growth, forex trading offers the possibility of quick, substantial profits (or losses) in shorter timeframes. The choice depends on an investor’s risk appetite and financial goals.
Examples of Successful Forex Trading Strategies
Numerous strategies exist, each with varying levels of risk. Scalping, a short-term strategy focusing on small price movements, involves high frequency trading and requires significant technical expertise. It’s high-risk, high-reward. Swing trading, focusing on medium-term price swings, utilizes technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. It presents a moderate risk-reward profile. Position trading, a long-term strategy, aims to capitalize on major market trends and is considered a lower-risk approach. The success of any strategy depends heavily on the trader’s skill, discipline, and risk management capabilities. A successful forex trader needs adaptability, continuous learning, and a robust risk management plan.
High-Risk vs. Low-Risk Forex Trading Strategies
| Strategy | Risk Level | Reward Potential | Time Horizon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalping | High | High | Minutes to hours |
| Day Trading | Medium | Medium | Hours to a day |
| Swing Trading | Medium-Low | Medium | Days to weeks |
| Position Trading | Low | Low-Medium | Weeks to months |
Factors Affecting Forex Trader Success: Is Forex Trading Profitable

Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is far from a guaranteed path to riches. Consistent profitability hinges on a blend of skills, discipline, and a realistic understanding of market dynamics. It’s a game of skill, not luck, and those who succeed consistently demonstrate specific traits and employ effective strategies.
Key Skills and Characteristics of Successful Forex Traders
Consistently profitable forex traders aren’t just lucky; they possess a unique combination of skills and characteristics. These individuals are typically disciplined, patient, and possess a deep understanding of market mechanics. Beyond technical proficiency, emotional intelligence plays a crucial role. They manage their emotions effectively, avoiding impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Furthermore, successful traders are adaptable, constantly learning and refining their strategies to stay ahead of the curve. They maintain detailed records of their trades, analyze their performance, and adjust their approach accordingly. This continuous self-improvement is a hallmark of their success.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is paramount in forex trading; it’s not about avoiding risk entirely, but about managing it intelligently. Effective risk management involves defining a maximum acceptable loss per trade (often expressed as a percentage of the trading capital), using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and diversifying trades across different currency pairs. For instance, a trader might set a stop-loss order at 2% below their entry price, meaning they’ll automatically exit the trade if the price falls by that amount. This prevents substantial losses from a single unfavorable trade. Another example is position sizing; a trader might allocate only 1% of their capital to any single trade, limiting potential losses to a manageable level even if multiple trades go against their prediction. Diversification further reduces the impact of any one trade going wrong, by spreading risk across different currency pairs or trading strategies.
The Role of Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Technical and fundamental analysis are two distinct, yet often complementary, approaches to forex trading decision-making. Technical analysis involves studying price charts and patterns to identify potential trading opportunities, using indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD to predict future price movements. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, focuses on macroeconomic factors such as economic data releases, interest rates, and geopolitical events, to assess the long-term value of a currency. Successful traders often integrate both approaches, using technical analysis to identify entry and exit points, and fundamental analysis to determine the overall direction of the market. For example, a trader might use technical analysis to pinpoint a precise entry point for a trade based on a chart pattern, while relying on fundamental analysis to confirm the overall bullish or bearish trend.
Common Trading Mistakes Leading to Losses
Overtrading, emotional trading, and neglecting risk management are among the most common mistakes that lead to losses in forex trading. Overtrading, or making too many trades, increases the likelihood of incurring losses. Emotional trading, driven by fear or greed, can lead to impulsive decisions and poor risk management. Neglecting risk management, failing to set stop-loss orders or adequately diversify trades, exposes traders to potentially devastating losses. Another frequent mistake is ignoring market news and events, leading to uninformed trading decisions. Finally, failing to learn from past mistakes and adapt trading strategies based on experience can lead to repeated losses. For example, a trader might consistently enter trades based on gut feeling instead of a solid trading plan, resulting in frequent losses.
Resources for Improving Forex Trading Skills
Numerous resources are available to enhance forex trading skills. Several reputable books offer valuable insights into trading strategies and market analysis. Online courses from established providers can provide structured learning paths, covering fundamental and advanced trading concepts. Active participation in online forex trading communities facilitates knowledge sharing, peer learning, and access to expert opinions. This includes forums, blogs, and social media groups dedicated to forex trading, where traders can discuss strategies, share experiences, and learn from others. Moreover, seeking mentorship from experienced traders can provide invaluable guidance and accelerate the learning process.
Trading Strategies and Their Profit Potential

Forex trading offers a diverse range of strategies, each with its own approach to profit generation and risk management. Understanding these strategies and their inherent characteristics is crucial for developing a successful trading plan. The choice of strategy significantly impacts potential profits and the level of risk involved.
Scalping, Day Trading, and Swing Trading: A Comparison
Scalping, day trading, and swing trading represent three distinct approaches to forex trading, each differing in their timeframe and trading philosophy. Scalpers aim for small profits on numerous trades within minutes or even seconds, while day traders hold positions throughout the trading day, closing them before the market closes. Swing traders, on the other hand, hold positions for several days or even weeks, capitalizing on larger price swings.
Scalping: High-Frequency, Low-Profit Strategy
Scalping involves executing many trades within a short period, aiming for small profits on each transaction. This strategy requires intense focus, rapid decision-making, and low spreads.
Advantages:
* Potential for high frequency of profits, accumulating significant gains over many trades.
* Lower risk per trade due to short holding periods.
* Adaptability to various market conditions, though best suited for highly liquid markets.
Disadvantages:
* Requires significant technical expertise and a fast internet connection with low latency.
* High transaction costs can eat into profits if not managed carefully.
* Can be mentally exhausting due to the constant monitoring and rapid decision-making.
* Prone to losses due to sudden market shifts or slippage.
Market Conditions: Scalping thrives in highly liquid markets with frequent price fluctuations. News releases and high-volume trading periods are often favorable.
Steps to Implement:
* Identify highly liquid currency pairs.
* Use technical indicators to identify short-term price movements.
* Set strict stop-loss and take-profit orders.
* Execute trades quickly and decisively.
* Monitor positions closely and adjust as needed.
Day Trading: Intraday Price Movements
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within a single trading day. Traders aim to profit from intraday price swings, using technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points.
Advantages:
* Less time commitment compared to swing trading.
* Reduced overnight risk as positions are closed before market closure.
* Ability to react quickly to market changes.
Disadvantages:
* Requires constant monitoring of the market.
* Higher stress levels compared to swing trading.
* Susceptible to losses if market moves against the trader’s position.
* Transaction costs can impact profitability.
Market Conditions: Day trading is effective in volatile markets with clear intraday trends. Economic news releases and high trading volumes often create opportunities.
Steps to Implement:
* Develop a detailed trading plan.
* Identify potential trading opportunities using technical analysis.
* Set stop-loss and take-profit orders.
* Monitor positions throughout the day.
* Close all positions before the market closes.
Swing Trading: Capitalizing on Longer-Term Trends
Swing trading focuses on capturing price swings over several days or weeks. Traders identify potential trends using a combination of technical and fundamental analysis, holding positions until the trend reverses or reaches a predetermined target.
Advantages:
* Less time-intensive than scalping or day trading.
* Lower transaction costs due to fewer trades.
* Potential for larger profits compared to scalping.
* Reduced stress levels compared to shorter-term strategies.
Disadvantages:
* Higher risk of losses due to longer holding periods.
* Exposure to overnight gaps and unexpected market events.
* Requires a strong understanding of fundamental analysis.
Market Conditions: Swing trading is suitable for markets exhibiting clear trends, either upward or downward. Major economic events or geopolitical shifts can create significant opportunities.
Steps to Implement:
* Identify potential trends using technical and fundamental analysis.
* Determine entry and exit points using chart patterns and indicators.
* Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
* Monitor positions regularly and adjust as needed.
* Hold positions for several days or weeks.
Hypothetical Trading Plan for a Beginner (Swing Trading)
A beginner might start with a $1,000 account and choose a swing trading strategy focusing on the EUR/USD pair. They might identify a potential upward trend using moving averages and chart patterns. They could enter a long position with a stop-loss at $1.1000 and a take-profit at $1.1200.
Profit Scenario: If the EUR/USD reaches $1.1200, the trader would realize a profit of approximately $200 (assuming a standard lot size).
Loss Scenario: If the EUR/USD falls to $1.1000, the trader would lose approximately $100. This demonstrates the importance of risk management. This is a simplified example and does not account for spreads or commissions.
The Role of Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading Profitability

Leverage and margin are two sides of the same coin in forex trading, significantly impacting both the potential for profit and the risk of substantial losses. Understanding their interplay is crucial for navigating the forex market successfully. While leverage can amplify gains, it equally amplifies losses, making risk management paramount.
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses by allowing traders to control a larger position than their initial capital would normally permit. Essentially, it’s borrowed money used to increase trading power. A 1:100 leverage ratio, for instance, means a trader can control $100,000 worth of currency with only $1,000 of their own funds. This can lead to substantial profits on relatively small price movements. However, the same leverage also magnifies losses; a small adverse price movement can quickly wipe out a trader’s account.
Margin Requirements and Their Impact on Trading Capital
Margin is the amount of money a trader must deposit with their broker to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as collateral, ensuring the broker is protected against potential losses. Margin requirements vary depending on the broker, the currency pair being traded, and the leverage level. Understanding margin requirements is crucial because insufficient margin can lead to a margin call, forcing the trader to deposit more funds or have their position liquidated. This liquidation can result in significant losses, potentially exceeding the initial investment. A trader needs to carefully calculate their margin requirements before entering a trade to avoid such scenarios. For example, if a trader opens a position requiring $500 margin with only $400 in their account, they are already at risk of a margin call should the market move against them.
The Effect of Different Leverage Levels on Potential Returns and Risks
Let’s illustrate the impact of leverage with hypothetical examples. Suppose a trader has $1,000 in their account and wants to trade EUR/USD.
| Leverage | Position Size | 1% Price Movement Profit/Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 1:100 | $100,000 | $1,000 |
| 1:50 | $50,000 | $500 |
| 1:10 | $10,000 | $100 |
As the table shows, higher leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses. With 1:100 leverage, a 1% price movement results in a $1,000 profit or loss, equaling the entire trading capital. With 1:10 leverage, the same movement yields a $100 profit or loss, a much smaller impact.
Strategies for Managing Risk When Using Leverage
Effective risk management is paramount when employing leverage. Key strategies include:
* Using stop-loss orders: These automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
* Diversifying trades: Spreading investments across multiple currency pairs reduces the impact of losses on any single trade.
* Employing position sizing techniques: Calculating position sizes based on a percentage of trading capital, rather than a fixed amount, helps control risk. For example, risking only 1-2% of the trading capital per trade is a common strategy.
* Thorough market analysis: Conducting in-depth research before entering any trade, considering fundamental and technical factors, is crucial.
* Using lower leverage: Starting with lower leverage levels allows traders to gain experience and better understand the market before increasing their exposure.
Consequences of Insufficient Margin and Avoiding Margin Calls
Insufficient margin leads to a margin call, a notification from the broker demanding additional funds to maintain the open position. Failure to meet a margin call results in the broker forcibly closing the trader’s position (liquidation) to cover potential losses. This can result in substantial losses, often exceeding the initial margin. To avoid margin calls, traders should:
* Monitor their account balance and margin levels regularly.
* Use appropriate leverage levels.
* Implement effective risk management strategies.
* Avoid overtrading.
* Understand the margin requirements for each trade before entering it.
The Psychological Aspects of Forex Trading
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, presents a significant psychological challenge. The constant fluctuations, the pressure of potential losses, and the allure of quick profits can significantly impact a trader’s decision-making, often leading to impulsive actions and ultimately, financial setbacks. Understanding and managing these emotional aspects is crucial for long-term success in this volatile market.
Emotional Challenges and Decision-Making
The emotional rollercoaster inherent in forex trading is well-documented. Fear, greed, and hope—these powerful emotions can cloud judgment, leading traders to make irrational choices. Fear of loss might prompt premature exits from profitable trades, while greed can cause traders to hold onto losing positions for too long, hoping for a reversal that may never come. Conversely, excessive hope can lead to overconfidence and neglecting risk management strategies. These emotional responses frequently override rational analysis, resulting in suboptimal trading decisions and reduced profitability. For example, a trader might panic-sell during a temporary market dip, missing out on potential gains, or stubbornly hold onto a losing trade, hoping it will recover, leading to even larger losses.
Strategies for Maintaining Emotional Discipline
Developing emotional discipline is paramount. This involves recognizing and managing emotional responses, preventing them from dictating trading decisions. Techniques like mindfulness and meditation can help traders stay grounded and centered, promoting clearer thinking during stressful market conditions. Keeping a detailed trading journal, documenting both successes and failures along with the emotional state at the time, can provide valuable insights into personal biases and triggers. This self-reflection is key to identifying patterns of impulsive trading and developing strategies to mitigate them. Additionally, setting realistic profit targets and stop-loss orders helps to control risk and prevents emotional over-extension.
The Importance of a Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan serves as a crucial anchor during periods of market volatility and emotional turmoil. It Artikels specific entry and exit strategies, risk management protocols, and personal trading rules. Adhering to the plan consistently, regardless of emotional fluctuations, is vital. A plan should be based on thorough market research and analysis, not on gut feelings or impulsive reactions. By sticking to the plan, traders create a structured approach that minimizes emotional decision-making and maximizes the potential for consistent profitability. A successful trading plan acts as a safety net, providing a framework for rational decision-making even when emotions run high.
Self-Awareness and Continuous Learning
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of successful forex trading. Recognizing one’s emotional weaknesses and biases is the first step toward mitigating their negative impact. Continuous learning, through education, mentorship, and staying updated on market trends, is essential for adapting to the ever-changing forex landscape. Regularly reviewing past trades, analyzing mistakes, and learning from both successes and failures contribute to improved decision-making and emotional resilience. This iterative process of self-reflection and learning allows traders to refine their strategies, enhance their emotional intelligence, and ultimately improve their trading performance.
The Emotional Cycle of a Trader, Is forex trading profitable
Imagine a visual representation: A cyclical graph depicting a trader’s emotional state. The upward curve represents a winning streak, starting with cautious optimism, progressing to confidence, then potentially to overconfidence and recklessness. The downward curve represents a losing streak, starting with disappointment, progressing to frustration, then potentially to despair and panic. The cycle illustrates how success can breed overconfidence, leading to risky behavior, while losses can trigger fear and impulsive decisions. The key is to recognize these patterns and develop strategies to navigate both the highs and lows, maintaining a balanced and disciplined approach.
Final Thoughts
So, is forex trading profitable? The short answer is: it can be, but it’s far from guaranteed. Success hinges on a potent blend of skill, discipline, and a realistic understanding of the inherent risks. It’s not a lottery ticket; it’s a marathon, requiring continuous learning, meticulous risk management, and the emotional fortitude to weather inevitable losses. While the potential for significant returns exists, responsible trading, informed decision-making, and a well-defined strategy are paramount. The journey to forex profitability is a personal one – are you ready to embark?
Expand your understanding about forex trading contest with the sources we offer.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about forex trading strategy pdf.




