
How to learn forex trading? It’s a question buzzing in the minds of many aspiring traders, dreaming of financial freedom. This isn’t just about charts and graphs; it’s about understanding global economics, mastering technical analysis, and developing the mental fortitude to navigate the volatile world of currency exchange. We’ll break down the complexities, from fundamental analysis and risk management to choosing the right broker and building a winning trading plan. Get ready to unlock the secrets of the forex market.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies needed to confidently enter the forex market. We’ll cover everything from the basics of currency pairs and account types to advanced technical analysis and risk management techniques. We’ll also help you navigate the often-confusing world of forex brokers and choosing the right platform for your needs. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation to start your forex trading journey.
Understanding the Forex Market
Forex, or foreign exchange, trading involves buying and selling currencies to profit from their fluctuating values. It’s a massive, decentralized market operating 24/5, offering both incredible opportunities and significant risks. Understanding its mechanics is crucial before diving in.
Forex Trading Mechanics
Forex trading centers around exchanging one currency for another. For example, buying EUR/USD means you’re purchasing Euros and simultaneously selling US Dollars. Your profit or loss depends on the change in the exchange rate between these two currencies. The exchange rate is constantly changing based on various economic and geopolitical factors, creating opportunities for traders to capitalize on price movements. Traders use platforms provided by brokers to place orders, setting their desired entry and exit points. These platforms typically offer charting tools and technical analysis indicators to help inform trading decisions.
Forex Trading Account Types
Different forex brokers offer various account types, each tailored to different trading styles and experience levels. A common distinction is between demo accounts and live accounts. Demo accounts use virtual money, allowing you to practice trading without risking real capital. Live accounts, on the other hand, involve trading with real money, exposing you to potential profits and losses. Some brokers also offer different account types based on minimum deposit requirements, trading tools, and access to advanced features. For example, a “standard” account might have basic charting tools, while a “premium” account might offer more advanced analytics and personalized support.
Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading, allowing you to control a larger position than your initial investment would normally allow. For example, a 1:100 leverage means you can control $100,000 worth of currency with only $1,000 in your account. While leverage amplifies profits, it also magnifies losses. Margin is the amount of money you need to deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. If your position moves against you and your losses reach a certain point (margin call), you may be required to deposit more funds or have your position closed to avoid further losses. Effectively managing leverage and margin is critical for risk management in forex trading. For instance, a trader might use a 1:50 leverage to mitigate risk, while a more experienced trader might utilize a higher leverage, such as 1:200, accepting higher risk for potentially higher rewards.
Major Currency Pairs
The forex market trades numerous currency pairs, but some are more prominent due to higher liquidity and trading volume. These major pairs typically involve the US dollar (USD) against other major global currencies like the Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Swiss Franc (CHF), Australian Dollar (AUD), and Canadian Dollar (CAD). Each pair exhibits unique characteristics and price movements influenced by economic factors specific to the countries involved. For example, EUR/USD is highly sensitive to European Central Bank (ECB) monetary policy decisions, while USD/JPY is often influenced by the interest rate differential between the US and Japan.
Opening a Demo Forex Account
Opening a demo account is a crucial first step for aspiring forex traders. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a Broker: Research and select a reputable forex broker that offers demo accounts. Consider factors such as regulation, trading platform features, and available educational resources.
2. Registration: Visit the broker’s website and complete the registration process, providing necessary information.
3. Account Setup: After registration, you’ll typically need to set up your demo account. This usually involves selecting the account type (often a standard demo account) and setting your preferred currency.
4. Funding (Virtual): The broker will usually automatically provide a virtual amount of money in your demo account to start practicing.
5. Platform Access: Once your account is set up, you can access the trading platform and begin practicing your trading strategies. You can experiment with different order types, technical indicators, and risk management techniques without risking real capital.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex: How To Learn Forex Trading
Forex trading isn’t just about charting patterns; it’s about understanding the global economy. Fundamental analysis helps you predict currency movements by examining the economic and political factors influencing them. By understanding these forces, you can make more informed trading decisions and potentially boost your profitability. Ignoring fundamentals is like navigating a ship without a map – you might get lucky, but you’re more likely to crash.
Economic News and Currency Values
Economic news releases, like employment reports or inflation figures, directly impact currency values. Positive news, such as unexpectedly strong job growth, often strengthens a country’s currency because it signals a healthy economy. Conversely, negative news, such as a sharp increase in inflation, might weaken it. The speed and magnitude of these reactions depend on the significance of the news and market expectations. For example, a surprise interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve typically strengthens the US dollar, as it makes US assets more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns. Conversely, disappointing GDP growth figures can weaken a currency as investors lose confidence in the nation’s economic outlook.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Influence
Several key economic indicators significantly influence forex trading. These indicators provide insights into a country’s economic health and potential future performance. Understanding their implications is crucial for successful fundamental analysis.
| Indicator | Description | Impact on Currency | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | The total value of goods and services produced within a country. | Strong GDP growth usually strengthens the currency; weak growth weakens it. | Strong US GDP growth often leads to a stronger USD. |
| Inflation Rate | The rate at which prices for goods and services are increasing. | High inflation typically weakens a currency; low inflation strengthens it. | High inflation in Argentina has historically weakened the Argentine Peso. |
| Unemployment Rate | The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. | Low unemployment strengthens a currency; high unemployment weakens it. | Low unemployment in Germany often supports the Euro. |
| Interest Rates | The rate at which a central bank lends money to commercial banks. | Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency; lower rates weaken it. | The Bank of England raising interest rates typically strengthens the British Pound. |
Geopolitical Events and Forex Market Movements
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, or trade disputes, can significantly impact currency values. These events create uncertainty, influencing investor sentiment and capital flows. For example, the outbreak of a major war can cause a flight to safety, strengthening currencies of perceived safe-haven countries like the US dollar or the Swiss franc. Conversely, political turmoil in a particular region might weaken its currency as investors withdraw their funds. The Brexit vote in 2016, for example, caused a sharp decline in the value of the British pound due to the uncertainty surrounding the UK’s future relationship with the European Union.
Central Bank Policies and Currency Exchange Rates
Central banks play a vital role in influencing currency exchange rates through monetary policy. Actions such as adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing (QE), or intervening directly in the foreign exchange market can significantly affect a currency’s value. For instance, if a central bank raises interest rates to combat inflation, it typically attracts foreign investment, leading to a stronger currency. Conversely, a central bank might lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, potentially weakening its currency. The European Central Bank’s (ECB) bond-buying programs during the Eurozone crisis are a prime example of how central bank policies can influence exchange rates.
Comparison of Fundamental Analysis Techniques
Different fundamental analysis techniques offer unique strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right approach depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and the specific currency pair you’re trading.
| Technique | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Indicator Analysis | Relatively objective; provides quantifiable data. | Can be lagging; susceptible to revisions; doesn’t account for market sentiment. |
| Geopolitical Analysis | Accounts for unpredictable events; can identify major trends. | Highly subjective; difficult to quantify; relies heavily on interpretation. |
| Central Bank Policy Analysis | Provides insights into future monetary policy; can anticipate currency movements. | Central bank decisions are not always predictable; requires deep understanding of monetary policy. |
| Sentiment Analysis | Captures market mood; can identify potential turning points. | Subjective; prone to manipulation; can be unreliable. |
Technical Analysis in Forex
Unlocking the secrets of the forex market often involves more than just understanding global economics. Technical analysis provides a powerful toolkit for traders to predict price movements based on historical data and chart patterns. By analyzing price action, volume, and various indicators, traders can identify potential entry and exit points, maximizing their profit potential and minimizing risk. Let’s dive into the core elements of this fascinating field.
Common Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations applied to price and/or volume data to generate buy/sell signals or gauge market momentum. Understanding these indicators is crucial for effective technical analysis.
- Moving Averages (MAs): MAs smooth out price fluctuations, revealing underlying trends. Simple Moving Averages (SMA) calculate the average price over a specified period, while Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) give more weight to recent prices. A common strategy involves using a combination of short-term and long-term MAs; a crossover (short-term MA crossing above a long-term MA) often signals a bullish trend, while a bearish crossover suggests a potential downtrend. For example, a trader might use a 50-day EMA and a 200-day EMA to identify long-term trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. Values above 70 generally indicate an overbought market (potential for a price correction), while values below 30 suggest an oversold market (potential for a price rebound). It’s important to note that RSI can generate false signals, so it’s best used in conjunction with other indicators.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): MACD uses a combination of moving averages to identify momentum changes. It consists of a MACD line (difference between two EMAs) and a signal line (EMA of the MACD line). Bullish crossovers (MACD line crossing above the signal line) and bearish crossovers (MACD line crossing below the signal line) can indicate potential trend changes. MACD divergence, where price action and the MACD indicator show conflicting signals, can also be a valuable trading signal.
Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are recurring formations on price charts that can predict future price movements. Recognizing these patterns can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to anticipate market trends.
- Head and Shoulders: This pattern suggests a trend reversal. It consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being the highest. A break below the neckline (a line connecting the troughs) often signals a bearish trend.
- Double Tops/Bottoms: These patterns indicate potential trend reversals. A double top forms when the price reaches a similar high twice, followed by a break below the support level. Conversely, a double bottom forms when the price reaches a similar low twice, followed by a break above the resistance level.
- Triangles: Triangles are consolidation patterns that indicate a period of indecision before a potential breakout. Symmetrical triangles, ascending triangles, and descending triangles all have distinct implications for trading decisions.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels represent price points where buying pressure is expected to overcome selling pressure, preventing further price declines. Resistance levels are price points where selling pressure is expected to overcome buying pressure, preventing further price increases. These levels are often identified by horizontal lines drawn on price charts at previous price highs (resistance) and lows (support). A break above resistance or below support can signal a significant trend change. For example, if a currency pair repeatedly finds support at 1.1000, this level becomes a key support level to watch.
Technical Analysis Strategies
Various technical analysis strategies exist, combining different indicators and chart patterns to generate trading signals.
- Moving Average Crossover Strategy: This strategy involves using two moving averages (e.g., a short-term and a long-term MA) to generate buy and sell signals based on their crossovers.
- RSI Divergence Strategy: This strategy uses RSI divergence to identify potential trend reversals. Bullish divergence occurs when the price makes lower lows, but the RSI makes higher lows. Bearish divergence is the opposite.
- Chart Pattern Breakout Strategy: This strategy involves identifying chart patterns (e.g., triangles, head and shoulders) and entering trades after a breakout from the pattern.
Charting Platforms Comparison
This table compares popular charting platforms, highlighting key features. Remember that the best platform depends on your individual needs and trading style.
| Platform | Features | Cost | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| TradingView | Extensive charting tools, indicators, social features | Free (limited) to paid subscriptions | User-friendly interface |
| MetaTrader 4 (MT4) | Widely used, many indicators and Expert Advisors (EAs) | Free (broker-dependent) | Steeper learning curve than TradingView |
| MetaTrader 5 (MT5) | Similar to MT4 but with enhanced features and more sophisticated order types | Free (broker-dependent) | Steeper learning curve than TradingView |
| cTrader | Focus on speed and execution, advanced charting capabilities | Free (broker-dependent) | Moderately user-friendly |
Developing a Trading Plan

A solid trading plan is your roadmap to success in the forex market. It’s not just about making money; it’s about managing risk, controlling emotions, and consistently applying your trading strategy. Without a plan, you’re essentially gambling, and in the forex world, that’s a recipe for disaster. A well-defined plan provides structure, discipline, and the crucial ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Sample Forex Trading Plan with Risk Management
A sample trading plan should include specific details tailored to your individual trading style and risk tolerance. However, a robust plan generally encompasses several key elements. For instance, consider a trader focusing on EUR/USD pairs using a swing trading strategy. Their plan might specify trading only during specific market hours (e.g., London and New York overlap), aiming for 1-2% profit per trade with a maximum loss of 1% per trade. This trader might further detail their entry and exit strategies, utilizing technical indicators like moving averages and RSI to identify potential trades and manage their positions. Their risk management would involve using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade, and possibly taking profits at pre-determined levels. This meticulous approach ensures that their trades are well-defined and disciplined.
Examples of Different Trading Strategies
Different trading strategies cater to varying risk tolerances and time commitments. Scalping involves making many small profits throughout the day, requiring constant monitoring and quick execution. Day trading focuses on closing all positions before the market closes, demanding intense focus and market analysis. Swing trading, on the other hand, holds positions for several days or weeks, capitalizing on larger price swings and requiring less frequent monitoring. Each strategy demands a different approach to risk management and emotional control. For example, a scalper might need to be exceptionally disciplined to avoid emotional reactions to small, quick losses, while a swing trader might need to be patient and trust their analysis over shorter-term market fluctuations.
Position Sizing and Risk Management
Position sizing, determining how much capital to allocate to each trade, is crucial for risk management. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any single trade. This means if you have $10,000 in your trading account, you shouldn’t risk more than $100-$200 on a single trade. Risk management goes hand-in-hand with position sizing and involves utilizing stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to secure profits. Proper position sizing and risk management prevent devastating losses and help preserve your trading capital. For example, if a trader risks 2% of their capital on a trade and the trade goes against them, they only lose 2% of their account balance. This controlled risk ensures they can continue trading even after incurring losses.
Psychological Aspects of Trading and Emotional Control
Forex trading can be emotionally taxing. Fear, greed, and impatience can lead to poor decision-making. Developing emotional control is as crucial as mastering technical and fundamental analysis. Techniques like journaling, meditation, and practicing discipline can help manage trading emotions. For example, keeping a detailed trading journal allows you to analyze your past trades and identify emotional biases that might have influenced your decisions. This self-reflection helps in developing strategies to overcome these biases in future trades.
Checklist for Evaluating Trading Opportunities
Before entering a trade, a checklist can help ensure you’re making informed decisions. This checklist should include confirming your trade aligns with your overall trading plan, verifying your entry and exit points, checking for sufficient liquidity, and assessing current market conditions and news events. It should also involve confirming your stop-loss and take-profit orders are appropriately set based on your risk tolerance and the identified trading opportunity. A disciplined approach to using this checklist will greatly improve your trading consistency and reduce the chance of emotional trading decisions.
Risk Management and Money Management
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Ignoring risk management is like sailing a ship without a rudder – you might get lucky, but you’re far more likely to crash. Effective risk and money management aren’t just good practices; they’re essential for long-term survival in the forex market. They’re the safety net that keeps your trading account from plummeting into the abyss.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are your best friends in forex. A stop-loss order automatically closes a losing trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. A take-profit order automatically closes a winning trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, securing your profits. Think of them as automated safety mechanisms that protect you from emotional decision-making during market volatility. For example, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, you might set a stop-loss at 1.0950 (limiting your loss to 50 pips) and a take-profit at 1.1050 (securing a 50-pip profit).
Risk Management Techniques for Minimizing Losses
Several techniques can significantly reduce your risk. Diversification, spreading your investments across different currency pairs, reduces the impact of a single losing trade. Position sizing, calculating the appropriate amount to invest in each trade based on your risk tolerance, prevents devastating losses. Furthermore, adhering to a strict trading plan, which includes clear entry and exit strategies, and avoiding overtrading (making too many trades), prevents impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Backtesting your strategies on historical data can also help identify potential weaknesses and refine your approach.
Calculating Position Size Based on Risk Tolerance
Determining your position size is crucial. A common approach involves defining your risk percentage per trade (e.g., 1-2% of your account balance). Then, you calculate the number of units to trade based on your stop-loss order and account size. For example, with a $10,000 account, a 1% risk tolerance, and a stop-loss of 50 pips, you would calculate your position size as follows: Risk amount = $10,000 * 0.01 = $100; Position size = $100 / (50 pips * pip value). The pip value depends on the currency pair and your broker’s leverage. This calculation ensures you don’t risk more than your predetermined percentage on any single trade.
Risk amount = Account balance * Risk percentage
Managing Emotions During Losing Trades
Emotions are the enemy of a successful forex trader. Losing streaks are inevitable, but letting emotions dictate your actions can lead to disastrous results. Strategies for managing these emotions include maintaining a trading journal to track your trades and identify patterns, sticking to your trading plan regardless of your emotional state, and taking breaks when feeling overwhelmed. Remember that forex trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Consistency and discipline are key.
Effective Money Management Techniques to Protect Capital
Effective money management involves several key strategies. Regularly reviewing your trading performance and adjusting your approach as needed is crucial. Setting aside a separate trading account, distinct from your personal funds, protects your capital. Regularly withdrawing profits ensures you’re not risking more than you’re comfortable with. Avoiding leverage beyond your understanding and comfort level prevents rapid account depletion. Finally, continuously learning and improving your trading skills helps mitigate risk over the long term.
Educational Resources and Practice

So, you’ve grasped the fundamentals of forex trading – congrats! Now, it’s time to dive into the practical side, honing your skills and building a solid foundation for success. This involves choosing the right learning resources, mastering simulation tools, and building a supportive network. Let’s get started.
Learning forex trading is a journey, not a sprint. It requires consistent effort, dedication, and a willingness to learn from both successes and failures. The resources and strategies Artikeld below will help you navigate this exciting and potentially lucrative path.
Reputable Sources for Forex Education
Finding reliable information in the often-noisy world of forex is crucial. Avoid get-rich-quick schemes and focus on established educational platforms offering structured learning paths. A mix of resources often provides the most comprehensive understanding.
Here are some examples of reputable sources:
- Books: “Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques” by Steve Nison provides a deep dive into technical analysis. “Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas focuses on the psychological aspects of trading, crucial for long-term success. Many other books offer specific strategies or market analyses, but always vet the author’s credibility.
- Websites: Websites like Babypips offer beginner-friendly tutorials and explanations of forex concepts. However, always cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and avoid biased opinions. Reputable financial news sites like Bloomberg or Reuters also offer valuable market insights.
- Courses: Many online platforms (Coursera, Udemy, etc.) offer forex trading courses, ranging from beginner to advanced levels. Look for courses with high ratings and reviews, and check the instructor’s qualifications and experience. Beware of courses promising unrealistic returns.
Forex Trading Simulators: Benefits and Drawbacks
Forex simulators, also known as demo accounts, allow you to practice trading with virtual money before risking real capital. This is an invaluable tool for beginners.
Benefits include risk-free practice, the ability to test different strategies, and familiarization with trading platforms. However, it’s important to note that simulated trading doesn’t perfectly replicate the emotional and psychological pressures of real-world trading. The lack of real consequences can lead to overconfidence or a disregard for risk management.
Discover the crucial elements that make forex trading api the top choice.
Key Terms and Concepts for Beginners
A strong vocabulary is essential for understanding forex trading. Familiarize yourself with these core concepts:
Understanding these terms is foundational. Mastering them will significantly improve your comprehension of market dynamics and trading strategies.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out is iraqi dinar trading on forex now.
- Pip (Point in Percentage): The smallest price movement in a currency pair.
- Lot: The unit of currency traded in forex.
- Leverage: Borrowing funds to amplify trading profits (and losses).
- Spread: The difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair.
- Margin: The amount of money required to open and maintain a position.
- Slippage: The difference between the expected price and the actual execution price of a trade.
Finding a Mentor or Trading Community, How to learn forex trading
Learning from experienced traders can significantly accelerate your progress. A mentor can provide guidance, feedback, and support, while a community offers peer learning and shared experiences.
Finding a mentor requires research and networking. Look for individuals with a proven track record and a willingness to share their knowledge. Online forex forums and social media groups can be valuable resources for connecting with other traders.
Structured Learning Plan for Beginners
A structured approach is key to effective learning. This plan Artikels a progressive learning path:
This plan provides a framework. Adjust the timeline based on your learning pace and available time.
- Weeks 1-4: Focus on foundational knowledge – market structure, terminology, basic chart reading.
- Weeks 5-8: Learn fundamental analysis – economic indicators, news events, geopolitical factors.
- Weeks 9-12: Master technical analysis – chart patterns, indicators, candlestick analysis.
- Weeks 13-16: Develop a trading plan – define your strategy, risk tolerance, and entry/exit rules.
- Weeks 17-20: Practice with a demo account, refining your strategy and risk management techniques.
Understanding Forex Brokerage
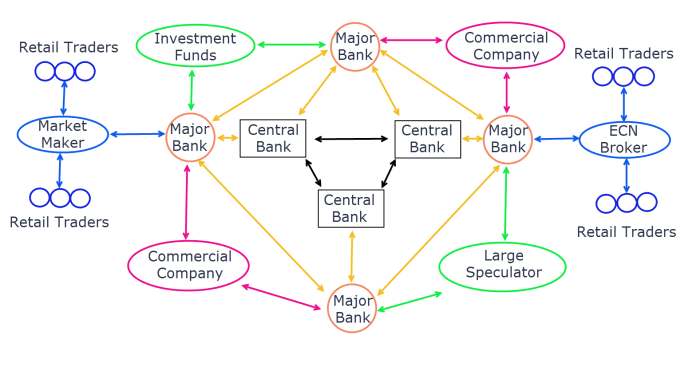
Choosing the right forex broker is crucial for a successful trading journey. It’s like picking the right car for a road trip – the wrong choice can lead to a bumpy, expensive ride. Understanding the different types of brokers and the factors to consider in your selection is paramount to minimizing risks and maximizing your trading potential.
Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers operate in various ways, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Two main categories are Market Makers and Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs). Market makers act as the counterparty to your trades, directly profiting from your losses. ECNs, on the other hand, act as a platform connecting you with other traders and liquidity providers, offering potentially tighter spreads and greater transparency. Choosing between them depends heavily on your trading style and risk tolerance. Market makers often offer faster execution and lower minimum deposits, while ECNs might require larger deposits and offer more transparency but potentially slower execution speeds in some instances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Forex Broker
Selecting a forex broker requires careful consideration of several key factors. Regulation ensures the broker adheres to specific standards, protecting your funds and offering a degree of oversight. Spreads, the difference between the bid and ask price, directly impact your profitability. Lower spreads are generally preferred. Leverage, the ability to control larger positions with smaller amounts of capital, magnifies both profits and losses; therefore, understanding and responsibly managing leverage is critical. A reputable broker will clearly display its regulatory status, spread costs, and leverage offerings.
Broker Fees and Commissions
Understanding the fee structure is non-negotiable. Brokers charge various fees, including spreads (as discussed above), commissions (a percentage or fixed fee per trade), overnight swap fees (for holding positions open overnight), and inactivity fees. These fees can significantly impact your overall profitability. It’s crucial to compare the total cost of trading across different brokers, not just focusing on a single aspect like the spread. For instance, a broker with a slightly higher spread but no commissions might be more cost-effective than one with lower spreads but significant commissions.
Account Verification Process
Verifying your account is a standard procedure to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations. This usually involves providing identification documents such as a passport or driver’s license, proof of address, and potentially other documentation as requested by the broker. The verification process helps ensure the security and integrity of the trading platform and protects both the broker and the trader from fraudulent activities. The length of this process varies depending on the broker and the efficiency of the document submission.
Evaluating Broker Reliability and Trustworthiness
Thorough due diligence is vital before entrusting your funds to a forex broker. A checklist can be helpful:
| Factor | Description | Example | Positive Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulation | Is the broker regulated by a reputable financial authority? | FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), NFA (USA) | Clear display of regulatory licenses on the broker’s website. |
| Reputation | Check online reviews and forums for client feedback. | Forex Peace Army, Trustpilot | Mostly positive and consistent reviews, addressing concerns transparently. |
| Spreads & Fees | Are the spreads competitive and fees clearly disclosed? | Compare spreads and fees with other brokers. | Transparent fee schedule with no hidden charges. |
| Security | Does the broker utilize secure encryption and segregation of client funds? | SSL certificates, client fund segregation in separate accounts. | Clear statements about security measures on the website. |
Final Thoughts
So, you’re ready to dive into the exciting, yet challenging world of forex trading? Remember, success in forex isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme; it’s a journey of continuous learning, discipline, and adaptation. Mastering the fundamentals, honing your analytical skills, and implementing a robust risk management strategy are key. This guide provides a solid foundation, but remember to practice diligently, stay updated on market trends, and never stop learning. The forex market is constantly evolving, and your ability to adapt will determine your success. Good luck, and happy trading!




