Day trading vs forex: Two high-octane worlds vying for your attention. Both promise fast profits, but each demands a unique skillset and risk appetite. This deep dive unpacks the key differences, from market accessibility and capital requirements to trading strategies and regulatory landscapes. We’ll help you navigate the complexities and decide which thrilling arena best suits your trading style.
From understanding the nuances of leverage and margin to mastering the art of risk management, we’ll explore the practicalities of each market. We’ll also delve into the essential tools and resources you need to succeed, comparing the learning curves and educational pathways available for both day traders and forex enthusiasts. Get ready to unleash your inner financial warrior!
Market Accessibility and Liquidity: Day Trading Vs Forex
Day trading and forex trading, while both offering opportunities for quick profits, differ significantly in their accessibility and liquidity. Understanding these differences is crucial for traders to choose the market that best suits their experience, capital, and risk tolerance. This section will delve into the specifics of market accessibility for various trader types and the implications of liquidity differences on trade execution.
The accessibility of day trading and forex markets varies considerably depending on the trader’s profile. For instance, accessing the stock market for day trading typically requires a brokerage account with a reputable firm, which involves meeting certain regulatory requirements and potentially minimum capital thresholds. Forex trading, on the other hand, often boasts lower barriers to entry, with many brokers catering to smaller accounts and offering simplified platforms. However, this ease of access can also attract less experienced traders who might be more susceptible to scams or poor trading decisions. Experienced traders, regardless of the market, typically prefer brokers offering advanced tools, low commissions, and fast execution speeds.
Liquidity Differences and Trade Execution
Liquidity, simply put, refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. Highly liquid markets allow for quick and efficient trade execution, minimizing slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price). The forex market, with its massive daily trading volume exceeding trillions of dollars, is generally considered one of the most liquid markets globally. This high liquidity ensures that traders can typically enter and exit positions quickly at prices close to their desired levels. In contrast, while the stock market offers substantial liquidity for major stocks, less liquid stocks (especially those of smaller companies) can experience significant price slippage, especially during periods of low trading volume. This can be particularly problematic for day traders who rely on quick trades to generate profits. For example, attempting to execute a large order in a thinly traded stock might result in a significantly worse price than anticipated, eating into potential profits or even leading to losses.
Market Comparison Table
The following table summarizes key differences between day trading (stocks) and forex trading in terms of trading hours, available instruments, and typical spreads:
| Feature | Day Trading (Stocks) | Forex Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Hours | Typically 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM (EST) on weekdays, though pre-market and after-hours trading is available. | 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. |
| Available Instruments | Individual stocks, ETFs, options, futures. | Currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, USD/JPY), precious metals, indices, CFDs. |
| Typical Spreads | Varies greatly depending on the stock; can range from fractions of a cent to several cents per share. | Generally tighter than stock spreads, often ranging from a few pips (0.0001) to several pips, depending on the currency pair and market conditions. |
Capital Requirements and Risk Management
Day trading and forex trading, while both offering the allure of quick profits, demand vastly different approaches to capital management and risk mitigation. Understanding these differences is crucial for survival, let alone success, in these volatile markets. Insufficient capital or poor risk management can quickly lead to devastating losses, wiping out your account in a matter of days, or even hours.
The reality is that both require significant discipline and a well-defined strategy to navigate the inherent risks. While the potential rewards are substantial, so are the potential downsides. Let’s delve into the specific capital requirements and risk management techniques needed for each.
Minimum Capital Requirements
The minimum capital needed for successful day trading and forex trading is a hotly debated topic, often varying wildly depending on individual trading styles, risk tolerance, and market conditions. There’s no magic number, but general guidelines exist. For day trading stocks, a generally accepted minimum is around $25,000, though some argue a much larger sum is necessary to weather inevitable losing streaks. This amount allows for more diverse portfolio diversification and helps cushion the impact of significant losses. Forex trading, on the other hand, can technically be started with significantly less capital, even as little as a few hundred dollars with some brokers. However, this drastically limits position sizing and opportunities, making consistent profitability extremely challenging. Successfully navigating the forex market often requires a considerably larger capital base to manage risk effectively and capitalize on opportunities. Think of it this way: a smaller account might allow you to participate, but a larger account allows you to truly compete.
Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management is the bedrock of long-term success in both day trading and forex. This involves carefully controlling position size and employing stop-loss orders. Position sizing dictates the percentage of your capital allocated to each trade. A common rule of thumb is to never risk more than 1-2% of your total capital on any single trade. For example, with a $10,000 account, a 1% risk tolerance means risking no more than $100 on each trade. Stop-loss orders automatically exit a trade when it reaches a predetermined loss level, limiting potential damage. The placement of stop-loss orders is crucial and depends on factors such as volatility and the trader’s risk tolerance. In forex, leverage magnifies both profits and losses, making risk management even more critical. The use of leverage can be incredibly powerful, but without proper management, it can quickly lead to significant losses. Day trading stocks often involves less leverage, but still necessitates careful position sizing and stop-loss orders to mitigate risk.
Potential Risks and Rewards
Understanding the potential risks and rewards is essential before venturing into either market. The following bullet points highlight these aspects:
- Day Trading Risks: High volatility, potential for rapid losses, requires significant time commitment, needs substantial technical analysis skills.
- Day Trading Rewards: Potential for high returns in short periods, flexibility in trading schedule (though demanding), immediate feedback on trading decisions.
- Forex Trading Risks: High leverage amplifies losses, 24/5 market exposure leading to constant monitoring, geopolitical and economic events can significantly impact market movements, requires understanding of global economic factors.
- Forex Trading Rewards: 24/5 market access allows for flexibility in trading hours, high liquidity facilitates easy entry and exit, potential for high returns with proper risk management and leveraging.
Trading Strategies and Techniques
Day trading and forex trading, while both involving the buying and selling of assets to profit from price fluctuations, differ significantly in their time horizons and strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for success in either market. This section will delve into common strategies and techniques employed in each, highlighting their unique characteristics and the technical indicators often used.
Day Trading Strategies and Forex Trading Strategies: A Comparison
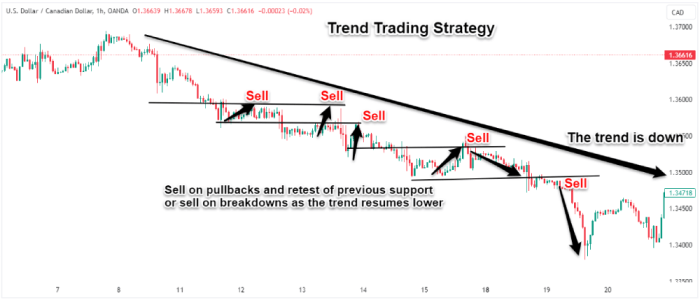
Day trading strategies primarily focus on short-term price movements, often within a single trading day. Scalping, for instance, aims to profit from tiny price changes, requiring rapid execution and high volume. Swing trading, on the other hand, holds positions for a few days to weeks, capitalizing on slightly larger price swings. Forex trading, with its 24/5 market accessibility, allows for a broader range of strategies. Trend following, a popular forex strategy, involves identifying and riding established trends, potentially holding positions for extended periods. The carry trade, conversely, profits from interest rate differentials between currencies, often held for longer durations. Scalping in forex is also possible, but the market’s continuous nature demands constant vigilance. While swing trading principles can be applied to both, the longer timeframe inherent in some forex strategies contrasts with the short-term focus of most day trading.
Technical Indicators in Day Trading and Forex Trading
Technical indicators are tools used to analyze price charts and identify potential trading opportunities. In day trading, fast-moving indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) are frequently employed to identify short-term overbought and oversold conditions, and momentum shifts respectively. These indicators help traders pinpoint entry and exit points within a single trading session. For example, a bullish divergence on the MACD, where the price makes lower lows while the MACD makes higher lows, could signal a potential upward trend reversal for a day trader. In forex, longer-term indicators like moving averages (e.g., 200-day moving average) and Bollinger Bands are also common, providing context for longer-term trends. Bollinger Bands, which show price volatility, can help identify potential breakout points, where a price breaks above or below the bands’ upper or lower limits, indicating a strong directional move. The application of these indicators differs depending on the timeframe and the trader’s chosen strategy. For example, a scalper might use a 5-minute RSI, while a swing trader might prefer a daily RSI.
Developing a Trading Plan: Risk Management Considerations
A well-defined trading plan is essential for success in both day trading and forex trading. This plan should Artikel your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and money management rules. For day trading, the plan might specify the number of trades per day, the maximum loss per trade (stop-loss order), and the target profit per trade (take-profit order). A key aspect is position sizing, which dictates how much capital to allocate to each trade based on risk tolerance. For instance, a trader might risk only 1% of their capital on any single trade. In forex, the plan might incorporate longer-term trend analysis, fundamental factors like economic news, and risk management techniques like hedging or using trailing stop-loss orders to protect profits. The longer time horizons in forex often require a more nuanced approach to risk management, given the potential for larger price swings. Regardless of the market, meticulous record-keeping is vital for analyzing performance and refining the trading plan. Regularly reviewing and adapting the plan based on market conditions and trading results is crucial for long-term success. Effective risk management ensures capital preservation and prevents significant losses.
Leverage and Margin

Day trading and forex trading both offer the enticing possibility of high returns, but this potential is inextricably linked to the use of leverage and the management of margin. Understanding these concepts is crucial for navigating the inherent risks and maximizing potential profits in both markets. Let’s dive into the mechanics and implications.
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. In essence, it allows you to control a larger position than your initial capital would normally permit. For instance, a 10:1 leverage ratio in forex means you can control $10,000 worth of currency with only $1,000 of your own money. This amplifies gains, but equally, amplifies losses. A small market movement against your position can quickly wipe out your initial investment and lead to further losses. Day trading, while often using leverage, generally involves less extreme ratios than forex, but the principle remains the same: leverage increases the risk-reward spectrum.
Leverage in Day Trading and Forex
Leverage in day trading is often provided by brokers through margin accounts. The amount of leverage available varies depending on the broker, the asset being traded (stocks, options, futures), and the trader’s account status. Forex trading typically offers higher leverage ratios compared to day trading in other markets. This higher leverage, while offering the potential for substantial profits, also significantly increases the risk of substantial losses. A small adverse price movement can quickly lead to a margin call, forcing the trader to deposit more funds or liquidate their position.
Margin Requirements and Implications
Margin is the amount of money a trader must deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. In forex, margin requirements are expressed as a percentage of the total trade value. For example, a 2% margin requirement on a $10,000 trade would necessitate a $200 margin deposit. Day trading margin requirements vary depending on the asset class. Trading stocks on margin typically involves lower leverage ratios than forex, leading to higher margin requirements. Failing to maintain the required margin can result in a margin call, where the broker demands additional funds to cover potential losses. If the trader cannot meet the margin call, the broker may liquidate the position to cover its exposure.
Comparison of Leverage Effects on Risk Tolerance and Capital Preservation
The following table compares the effects of leverage on risk tolerance and capital preservation in day trading and forex.
| Factor | Day Trading (e.g., Stocks) | Forex Trading | Impact on Risk Tolerance | Impact on Capital Preservation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leverage Ratios | Typically lower (e.g., 2:1, 4:1) | Typically higher (e.g., 10:1, 50:1, even higher in some cases) | Lower leverage generally equates to lower risk tolerance, but still significant | Higher chance of capital preservation due to lower leverage |
| Margin Requirements | Higher due to lower leverage | Lower due to higher leverage | Higher margin requirements necessitate a more cautious approach. | Reduces the immediate risk of margin calls, but doesn’t eliminate the risk of losses. |
| Potential for Profit/Loss | Lower potential for both profit and loss compared to forex | Higher potential for both profit and loss compared to day trading stocks | Higher potential gains incentivize higher risk tolerance but with increased risk of substantial losses | Higher potential losses increase the risk of losing a significant portion or all of the initial capital |
| Margin Calls | Less frequent due to higher margin requirements | More frequent due to lower margin requirements and higher leverage | Less frequent margin calls contribute to a lower-stress trading experience. | Reduces the chance of forced liquidation due to insufficient funds. |
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
Navigating the world of day trading and forex requires understanding the complex web of regulations designed to protect investors and maintain market integrity. These regulations vary significantly depending on your location, impacting everything from account opening to tax reporting. Ignoring these rules can lead to hefty fines, account suspension, and even legal action.
The regulatory landscape for day trading and forex differs substantially between regions like the US and the EU, reflecting different approaches to market oversight and investor protection. Understanding these differences is crucial for traders operating internationally or considering cross-border transactions.
Regulatory Bodies in the US
The US boasts a multi-layered regulatory system for financial markets. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees the securities markets, including stocks and options often used in day trading. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) regulates futures and options contracts, which are prevalent in forex trading. Furthermore, self-regulatory organizations (SROs) like the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) play a significant role in enforcing rules and monitoring member firms’ activities. These bodies work in concert to ensure market fairness and prevent fraud.
Compliance Requirements for US Day Traders and Forex Traders
US-based day traders and forex traders face numerous compliance obligations. These include adhering to Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, maintaining accurate trading records, and reporting income appropriately for tax purposes. The specific requirements vary depending on the trader’s trading volume and the type of instruments traded. For example, frequent traders might need to file more comprehensive reports than those who trade less often. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties.
Regulatory Bodies in the EU
The European Union’s regulatory framework for financial markets is primarily governed by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA). ESMA coordinates and enforces regulations across member states, aiming for a consistent approach to market supervision. Individual member states also have their own regulatory bodies, responsible for overseeing market participants within their jurisdictions. The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the presence of directives and regulations such as MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II), which aims to enhance market transparency and investor protection.
Compliance Requirements for EU Day Traders and Forex Traders
Similar to the US, EU-based day traders and forex traders must comply with various regulations. These include KYC and AML rules, record-keeping obligations, and reporting requirements related to taxation. MiFID II introduces additional requirements, such as best execution obligations for brokers and enhanced transparency in pricing and order execution. Traders must be aware of the specific rules applicable in their respective member states, as national regulations can vary. Non-compliance can lead to sanctions from both national and EU-level authorities.
Differences in Regulatory Oversight and Influence on Trading Practices
The differences in regulatory oversight between the US and the EU significantly influence trading practices. For instance, the US regulatory environment is often considered more stringent, leading to stricter rules regarding leverage and margin requirements for retail traders. In contrast, the EU’s approach might be more focused on harmonization across member states, aiming for a level playing field but potentially resulting in less granular control in some areas. These differences can impact a trader’s choice of broker, trading strategies, and risk management approach. For example, higher leverage restrictions might encourage traders to adopt more conservative strategies. The level of regulatory scrutiny also influences the types of trading products available and the level of investor protection offered.
Technological Requirements and Tools
Day trading and forex trading, while sharing similarities in their reliance on technology, have distinct technological needs. The speed and efficiency demanded by day trading necessitate powerful hardware and specialized software, while forex trading, with its 24/5 market accessibility, requires robust connectivity and tools capable of handling vast amounts of data. Understanding these differences is crucial for success in either market.
The technological landscape of both day trading and forex trading is constantly evolving, with new platforms and tools emerging regularly. Choosing the right tools depends heavily on individual trading styles, risk tolerance, and capital. The key is to select a setup that supports your strategy and allows for efficient execution.
Trading Platforms and Charting Tools, Day trading vs forex
Selecting the right trading platform and charting tools is paramount for both day traders and forex traders. The platform acts as the central hub for order execution, market analysis, and risk management. Charting tools provide the visual representation of market data, allowing traders to identify trends and patterns. The quality and features of these tools directly impact trading performance.
Day trading platforms often prioritize speed and order execution capabilities. They typically offer advanced charting tools with real-time data feeds and technical indicators. Popular platforms include TradeStation, NinjaTrader, and thinkorswim. These platforms are often designed with intuitive interfaces and tools to support rapid decision-making.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting the forex trading coach today.
Forex trading platforms, on the other hand, need to handle the global nature of the market and the constant flow of data from multiple currency pairs. MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5) are widely used platforms in the forex market, known for their extensive charting capabilities, automated trading options (Expert Advisors), and large community support. cTrader is another popular choice, known for its speed and advanced charting features. Many forex brokers offer proprietary platforms with varying levels of functionality.
Suitable Trading Environment
A well-structured trading environment is essential for consistent performance. This encompasses both the hardware and software aspects, alongside the overall workspace setup. A poorly configured environment can lead to missed opportunities, increased stress, and ultimately, financial losses.
For day trading, a high-speed internet connection is crucial for real-time data and quick order execution. A powerful computer with a fast processor, ample RAM, and multiple monitors is recommended to handle the demands of multiple charts, news feeds, and analytical tools. A comfortable and ergonomically designed workspace is vital to prevent fatigue and maintain focus throughout the trading day.
Remember to click forex trading systems to understand more comprehensive aspects of the forex trading systems topic.
Forex trading, with its 24/5 nature, may require a more adaptable setup. While a fast internet connection remains essential, the trading hours can be spread across different time zones, potentially requiring flexibility in scheduling. A reliable backup power source is also crucial to avoid disruptions during critical trading moments. Similarly, a comfortable and organized workspace remains paramount for long-term success.
Educational Resources and Learning Curve
Navigating the worlds of day trading and forex requires dedicated learning. Both markets offer a wealth of educational resources, but their nature and accessibility differ significantly, impacting the overall learning curve and time investment needed for proficiency. Understanding these differences is crucial for aspiring traders to choose the path best suited to their learning style and goals.
The availability and quality of educational resources for day trading and forex trading are surprisingly diverse. While both markets boast a plethora of online courses, books, and webinars, the specific focus and depth of these resources vary. Day trading often emphasizes technical analysis, chart patterns, and specific trading strategies tailored to short-term market movements. Forex, with its global reach and 24/5 availability, tends to incorporate more fundamental analysis, macroeconomic factors, and geopolitical influences into its educational materials.
Educational Resource Comparison
Day trading educational resources often concentrate on platforms like TradingView, offering charting tools, technical indicators, and educational content specifically geared towards intraday trading. Forex education frequently integrates fundamental analysis, covering economic calendars, news events, and central bank announcements alongside technical analysis. Many reputable forex brokers provide educational materials as part of their services, while dedicated day trading education might be found through independent educators or specialized online platforms. Books on technical analysis are commonly applicable to both, though the specific application and timeframes differ significantly.
Learning Curve and Time Commitment
Becoming proficient in either day trading or forex trading requires significant time and dedication. The learning curve for day trading is often considered steeper due to the fast-paced nature of the market and the need for quick decision-making. Mastering technical analysis, reading charts effectively, and managing risk within tight timeframes demands intensive practice and a keen understanding of market dynamics. Successful day traders often spend years honing their skills and developing their strategies. Forex, while also demanding, might offer a gentler learning curve for some, as fundamental analysis allows for longer-term perspectives and potentially less pressure-cooker trading environments. However, understanding global economic forces and geopolitical risks adds complexity. Both markets require consistent learning and adaptation, as market conditions and trading strategies are constantly evolving. Expecting immediate success is unrealistic in either field.
Essential Skills and Knowledge
| Day Trading | Forex Trading |
|---|---|
| Proficiency in technical analysis (chart patterns, indicators) | Understanding of fundamental analysis (economic indicators, geopolitical events) |
| Mastering order execution and risk management techniques for short-term trades | Knowledge of currency pairs, exchange rates, and global economic forces |
| Ability to read and interpret market data quickly and efficiently | Skill in managing risk across multiple currency pairs and timeframes |
| Deep understanding of specific trading strategies for intraday trading | Awareness of leverage and margin requirements in forex trading |
| Experience with various trading platforms and tools | Familiarity with forex trading platforms and charting tools |
Conclusive Thoughts
So, day trading or forex? The ultimate victor depends entirely on your individual goals, risk tolerance, and trading personality. Both offer immense potential for reward, but also significant risk. By carefully weighing the pros and cons Artikeld above – market accessibility, capital needs, trading strategies, and regulatory considerations – you can make an informed decision and embark on your trading journey with confidence. Remember, thorough research and a well-defined trading plan are your best allies in this exciting, yet demanding, world.