
The Role of Interest Rates in Forex Trading: Dive into the thrilling world of currency markets where interest rates aren’t just numbers, they’re the puppet masters pulling the strings of exchange rates. Understanding their influence is key to navigating this complex, high-stakes game. We’ll unpack how central bank policies, interest rate differentials, and forecasting techniques shape trading strategies and ultimately, your potential profits (or losses!). Get ready to decode the mysteries of interest rates and unlock the secrets to forex success.
From the impact of a surprise rate cut by the Federal Reserve to the long-term effects of prolonged low interest rates in Japan, we’ll explore real-world scenarios and dissect how these events ripple through the global currency markets. We’ll even delve into the intriguing world of carry trades, examining their potential for high returns alongside their inherent risks. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how interest rates dictate the dance of currencies, empowering you to make informed trading decisions.
Introduction to Interest Rates and Forex
Understanding the intricate dance between interest rates and forex trading is crucial for navigating the volatile world of international currency markets. Essentially, interest rates are the bedrock upon which much of currency valuation rests. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for a country’s currency and thus boosting its value. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to capital outflow and a weakening of the currency. This dynamic interplay is constantly at play, shaping exchange rates and presenting both opportunities and risks for traders.
Interest rate differentials, the difference in interest rates between two countries, are a primary driver of exchange rate fluctuations. Investors seek higher returns, so they’ll often move their funds to countries offering more lucrative interest rates. This increased demand for the high-yield currency strengthens it against the currency of the country with lower rates. The magnitude of this effect is influenced by various factors, including economic stability, political risk, and market sentiment, but the core principle remains consistent: higher interest rates attract capital, strengthening the currency.
Interest Rate Differentials and Exchange Rate Fluctuations
The relationship between interest rate differentials and exchange rates is often explained through the concept of “carry trade.” This involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a high-interest-rate currency to profit from the interest rate differential. For example, if the US interest rate is 2% and the Japanese interest rate is 0.1%, a trader might borrow in Japanese Yen (JPY) and invest in US Dollars (USD). If the exchange rate remains relatively stable, the trader profits from the higher interest earned on the USD investment. However, if the JPY appreciates against the USD, the trader could face losses when converting the USD back to JPY to repay the loan. This highlights the inherent risk in carry trades: fluctuations in exchange rates can easily offset any interest rate gains.
Historical Examples of Interest Rate Impacts on Forex
Several historical events vividly illustrate the significant impact of interest rate changes on forex markets. One prominent example is the period leading up to the 2008 financial crisis. The US Federal Reserve significantly lowered interest rates to stimulate the economy, leading to a weakening of the US dollar against other major currencies. Conversely, during periods of economic strength, such as the late 1990s, the US dollar strengthened significantly as the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to combat inflation. These examples demonstrate how central bank actions directly influence currency values, often with far-reaching consequences for global markets. Another example can be seen in the Eurozone’s sovereign debt crisis. As concerns grew about the solvency of several Eurozone countries, investors moved funds away from these nations, causing their currencies to depreciate against the Euro. This further highlights the sensitivity of exchange rates to perceived risk and the pivotal role of interest rate policies in shaping these perceptions.
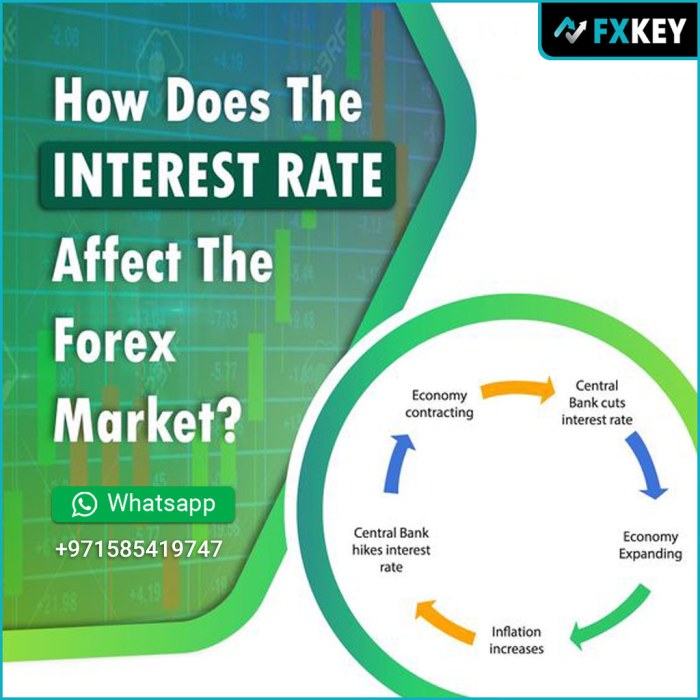
Central Bank Policies and Their Impact
Central banks are the puppet masters of interest rates, and their decisions have a seismic impact on the forex market. These institutions wield considerable power, influencing everything from inflation and employment to the value of national currencies. Understanding their policies is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of forex trading.
The primary tool central banks use to manage their economies is the manipulation of interest rates. By raising or lowering these rates, they influence borrowing costs, investment levels, and ultimately, the flow of capital into and out of a country. This, in turn, directly impacts the value of its currency. A higher interest rate generally attracts foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and strengthening its value. Conversely, lower rates can weaken a currency as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
The Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of Japan (BOJ): A Comparison
The Fed, ECB, and BOJ, three of the world’s most influential central banks, employ varying approaches to monetary policy. The Fed, known for its data-driven approach, often adjusts interest rates based on inflation and employment figures. The ECB, operating within the Eurozone, faces the added complexity of managing multiple economies with varying economic conditions. Their policies often reflect a balancing act to address the diverse needs of the member states. The BOJ, meanwhile, has historically pursued more unconventional policies, including quantitative easing (QE), to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation. These differing approaches highlight the nuances of central banking and their impact on currency values. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Fed might aggressively raise interest rates, strengthening the dollar against other currencies. Conversely, if the BOJ implements QE, the yen might weaken relative to other major currencies.
Anticipated Changes in Interest Rate Policies and Currency Speculation
Market participants constantly scrutinize central bank announcements, statements, and economic data releases to anticipate future interest rate changes. This anticipation plays a crucial role in currency speculation. Traders use forward-looking indicators, such as inflation expectations and economic growth forecasts, to predict central bank actions. If the market anticipates a rate hike, for example, traders might buy the currency in advance, driving up its value before the official announcement. Conversely, if a rate cut is expected, traders might sell the currency, potentially leading to a devaluation. The impact is magnified when the anticipation differs from the actual central bank decision, creating volatility in the forex market. For instance, a surprise rate cut by a central bank could trigger a sharp and immediate depreciation of its currency, potentially causing significant losses for those who hadn’t anticipated the move. Conversely, a surprise rate hike could lead to rapid appreciation.
Interest Rate Forecasts and Trading Strategies

Interest rate forecasts are crucial for forex traders, acting as a compass guiding their investment decisions. By anticipating future interest rate movements, traders can position themselves to profit from the resulting shifts in currency values. Accurate forecasting, however, is far from a guaranteed win, requiring a blend of analytical skills and a deep understanding of global economic factors.
Predicting interest rate changes involves analyzing a multitude of economic indicators and central bank communications. These forecasts then form the foundation of various trading strategies, allowing traders to capitalize on the expected changes in currency exchange rates. The accuracy of these forecasts, naturally, significantly impacts the success or failure of the trading strategy.
Interest Rate Forecasting Methods
Several methods exist for analyzing interest rate data and predicting future movements. These range from simple technical analysis to complex econometric models. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice often depends on the trader’s experience, risk tolerance, and access to data.
One common approach is analyzing central bank statements and press conferences. Central banks often hint at future policy decisions through their communication, providing clues about potential interest rate changes. For example, if a central bank expresses concern about inflation, it may suggest an upcoming interest rate hike. Another method involves examining economic indicators like inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth. Strong economic data often leads to expectations of higher interest rates, while weak data may suggest rate cuts. Technical analysis, using charts and indicators, can also be used to identify trends and patterns in interest rate movements. However, this method relies heavily on historical data and may not always accurately predict future movements. Finally, sophisticated econometric models, often employed by large financial institutions, use complex statistical techniques to forecast interest rate changes based on a wide range of economic variables.
A Hypothetical Trading Strategy Based on Interest Rate Forecasts
Let’s imagine a scenario where analysts widely predict that the European Central Bank (ECB) will raise interest rates by 0.25% in the next monetary policy meeting. This prediction is based on consistently high inflation figures within the Eurozone and statements from ECB officials hinting at further tightening of monetary policy. A trader believing this forecast might adopt a long position in the EUR/USD currency pair. The rationale is that a higher interest rate in the Eurozone will attract more foreign investment, increasing demand for the euro and thus strengthening its value against the US dollar. The trader would then profit if the EUR/USD exchange rate rises as predicted following the ECB’s announcement. Conversely, if the forecast is incorrect and the ECB keeps rates unchanged or even lowers them, the trader would experience a loss. This simple example highlights the inherent risk involved in trading based on interest rate forecasts. Effective risk management strategies, including stop-loss orders, are crucial to mitigate potential losses.
Comparison of Interest Rate Forecasting Models
The accuracy of interest rate forecasts varies significantly depending on the model used. No single model consistently outperforms others, and the best approach often depends on the specific circumstances and data available.
| Model | Description | Accuracy (Illustrative) | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Moving Average | Calculates the average interest rate over a specific period. | Moderate; susceptible to noise. | Ignores fundamental economic factors. |
| Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) | Statistical model using past interest rate data to predict future values. | High in stable periods; less accurate during significant economic shifts. | Assumes stationarity of data; may not capture structural breaks. |
| Econometric Models (e.g., Vector Autoregression – VAR) | Complex models incorporating multiple economic variables. | Potentially high, but requires significant data and expertise. | Data intensive; model specification crucial; susceptible to errors in underlying data. |
| Qualitative Analysis (Expert Opinions) | Based on the analysis of economic reports, central bank statements, and expert opinions. | Varies widely depending on expertise and information available. | Subjective; susceptible to bias; may lag behind market movements. |
*Note: Accuracy figures are illustrative and can vary significantly depending on the specific implementation and data used.*
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Different Currency Pairs
Interest rate differentials are a cornerstone of forex trading, driving significant movements in currency pairs. Understanding how these changes affect various pairs is crucial for successful trading. The sensitivity to these changes isn’t uniform across all pairs; some are significantly more reactive than others. This section delves into the nuances of this impact, highlighting key currency pairs and the timing element of rate announcements.
The magnitude of the impact of interest rate changes on a currency pair depends on several factors, including the relative size of the rate change, the economic strength of the underlying countries, and market sentiment. A larger rate hike in one country compared to another will generally lead to a more pronounced appreciation of the former’s currency. However, the overall economic outlook and market expectations also play a significant role in shaping the final outcome.
Currency Pairs Most Sensitive to Interest Rate Changes
Major currency pairs, particularly those involving the US dollar (USD), the Euro (EUR), the British Pound (GBP), the Japanese Yen (JPY), and the Swiss Franc (CHF), are generally more sensitive to interest rate changes due to their higher liquidity and the influence of their respective central banks on global markets. Pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CHF often experience pronounced volatility following interest rate announcements from the Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB), the Bank of England (BoE), the Bank of Japan (BOJ), and the Swiss National Bank (SNB). These central banks’ decisions directly impact their respective currencies’ attractiveness to investors seeking higher returns. For example, a surprise rate hike by the Fed often leads to a strengthening of the USD against other currencies.
Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on Different Currency Pairs
A rate hike in a country generally strengthens its currency relative to others. For instance, if the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates while other major central banks maintain their rates, the USD is likely to appreciate against currencies like the EUR, GBP, or JPY. Investors move their funds to the US to benefit from higher yields, increasing demand for the USD. Conversely, a rate cut would likely lead to a depreciation of the USD. The extent of the currency movement depends on several factors, including the magnitude of the rate change, market expectations, and the overall economic climate. A larger-than-expected rate hike might cause a sharper appreciation than a smaller, anticipated one.
Consider the EUR/USD pair. A rate hike by the ECB, assuming the Fed’s rates remain unchanged, would strengthen the Euro against the dollar. However, if the market had already anticipated this hike, the impact might be muted. Conversely, a surprise rate hike by the Fed while the ECB keeps rates constant could lead to a sharp decline in the EUR/USD rate.
Timing of Interest Rate Announcements and Short-Term Price Movements
The period surrounding interest rate announcements is characterized by heightened volatility. In the days leading up to the announcement, the market anticipates the decision, resulting in price fluctuations reflecting different expectations. Immediately after the announcement, there’s often a sharp, short-term price movement. If the announcement aligns with market expectations, the impact might be relatively small. However, a surprise announcement—either a larger or smaller rate change than expected—can trigger significant and swift price swings. Traders often employ strategies like scalping or news trading to capitalize on these short-term movements. For example, a surprise rate cut could cause a sharp and immediate depreciation of the currency, offering a brief window for profitable trades. Conversely, a surprise rate hike would present a short-term opportunity for those betting on an appreciation.
Risk Management in Interest Rate-Driven Forex Trading
Trading forex based on interest rate differentials can be incredibly lucrative, but it’s also a high-stakes game. The inherent volatility of interest rates, often influenced by unpredictable economic events and central bank decisions, introduces significant risk to your trading capital. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for long-term success.
Interest rate movements directly impact currency values. A surprise interest rate hike, for instance, typically strengthens the associated currency as it attracts foreign investment seeking higher returns. Conversely, a rate cut can weaken the currency. However, the market’s reaction isn’t always predictable, and unexpected events or shifts in market sentiment can lead to sharp and rapid price swings, potentially resulting in significant losses. Furthermore, leverage, commonly used in forex trading, amplifies both profits and losses, making risk management even more critical in this context.
Identifying and Assessing Interest Rate Risks
Several key risks are associated with interest rate-driven forex trading. These include the risk of unexpected interest rate changes by central banks, the risk of inaccurate interest rate forecasts leading to incorrect trading decisions, and the risk of significant market volatility resulting from these changes. The impact of these risks can be magnified by leverage, leading to substantial losses if the market moves against your position. For example, a trader leveraged 10:1 who incorrectly predicted an interest rate cut could see a 10% loss in their account if the currency moves only 1% against their prediction.
Strategies for Mitigating Interest Rate Volatility Risks
Effective risk management in interest rate-driven forex trading requires a multi-pronged approach. Diversification across multiple currency pairs reduces exposure to the risks associated with any single currency or interest rate decision. Hedging strategies, such as using options or futures contracts, can limit potential losses. Additionally, employing stop-loss orders helps automatically exit a trade when the market moves against you, preventing further losses. Finally, thorough research and analysis of economic indicators and central bank statements are crucial for making informed trading decisions. For instance, analyzing inflation data before a central bank meeting can provide insights into the likelihood of a rate change, improving the accuracy of your trading decisions.
Implementing a Risk Management Plan, The Role of Interest Rates in Forex Trading
A robust risk management plan should be a cornerstone of your interest rate trading strategy. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define your risk tolerance: Determine the maximum percentage of your trading capital you are willing to lose on any single trade. This is a crucial first step. A conservative approach might limit losses to 1-2% per trade.
- Set stop-loss orders: For every trade, place a stop-loss order to automatically exit the position if the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. This limits potential losses to a manageable level.
- Use appropriate leverage: Avoid excessive leverage, as it significantly amplifies both profits and losses. Start with smaller leverage ratios and gradually increase them as your experience and confidence grow.
- Diversify your portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across multiple currency pairs to reduce the impact of losses on any single trade.
- Regularly monitor your positions: Keep a close eye on your trades and the overall market conditions. Be prepared to adjust your positions or exit trades if necessary.
- Continuously learn and adapt: The forex market is dynamic. Stay updated on economic news, central bank policies, and market trends to refine your trading strategies and risk management approach.
Always remember that no strategy guarantees profits in forex trading. Risk management is about minimizing potential losses and maximizing the chances of long-term success.
Interest Rates and Carry Trade Strategies
Carry trades are a popular forex trading strategy that exploits interest rate differentials between countries. Essentially, it involves borrowing in a currency with a low interest rate and investing in a currency with a high interest rate, aiming to profit from the interest rate difference. The success of a carry trade hinges on the expectation that the interest rate differential will be greater than any losses incurred from currency fluctuations.
The allure of carry trades lies in the potential for relatively high returns, particularly in environments with stable exchange rates. However, this strategy is not without significant risks. The primary risk is that the exchange rate of the borrowed currency could appreciate against the invested currency, leading to losses that outweigh the interest earned. Other risks include unforeseen economic events, changes in central bank policies, and general market volatility.
Carry Trade Mechanics and Profit Calculation
A carry trade involves two key steps: borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a high-interest-rate currency. Let’s illustrate with a simplified example. Suppose the interest rate in Japan (JPY) is 0.1% per annum, and the interest rate in the United States (USD) is 5% per annum. An investor borrows 1,000,000 JPY at 0.1% and converts it to USD at the current exchange rate (let’s assume 1 USD = 110 JPY for simplicity). This yields approximately 9090.91 USD. This amount is then invested in a USD-denominated asset earning 5% interest.
After one year, the investor receives 9090.91 USD * 0.05 = 454.55 USD in interest. However, the crucial factor is the exchange rate at the end of the year. If the exchange rate remains at 1 USD = 110 JPY, the investor converts the principal plus interest (9090.91 USD + 454.55 USD = 9545.46 USD) back to JPY, receiving 9545.46 USD * 110 JPY/USD = 1,049,990.6 JPY. Subtracting the initial loan amount (1,000,000 JPY) and the interest paid on the loan (1,000,000 JPY * 0.001 = 1000 JPY), the net profit is approximately 49,990.6 JPY. But if the USD depreciates significantly against the JPY during the year, this profit could be reduced or even turn into a loss.
Risk Management in Carry Trades
The inherent volatility of exchange rates necessitates robust risk management in carry trades. Diversification across multiple currency pairs can help mitigate risk, as can hedging strategies using forward contracts or options. Setting stop-loss orders is crucial to limit potential losses if the exchange rate moves against the trader’s position. Furthermore, understanding the economic and political factors influencing interest rates and exchange rates is vital for informed decision-making. Thorough research and a clear understanding of the risks involved are paramount before embarking on a carry trade strategy.
Carry Trade Examples: Illustrative Scenarios
Consider a carry trade involving the Australian dollar (AUD) and the Japanese yen (JPY). If the AUD interest rate is significantly higher than the JPY rate, a trader might borrow JPY, convert to AUD, and invest in AUD-denominated assets. However, if the AUD depreciates sharply against the JPY, the trader’s profit from the interest rate differential could be offset by exchange rate losses. Conversely, a strengthening AUD would amplify the profits. The same principle applies to other currency pairs, with the potential for profit or loss depending on the interplay between interest rate differentials and exchange rate movements. Real-world examples abound, with some traders achieving significant gains, while others have experienced substantial losses due to unexpected exchange rate fluctuations. The key is diligent research, prudent risk management, and a realistic assessment of potential outcomes.
Illustrative Examples of Interest Rate Impact
Understanding how interest rate changes ripple through the forex market requires looking at real-world scenarios. These examples illustrate the complex interplay between monetary policy, market sentiment, and currency valuations. We’ll explore both short-term shocks and the longer-term effects of sustained interest rate policies.
Surprise Interest Rate Cut Impacts EUR/USD
Imagine the European Central Bank (ECB) unexpectedly cuts its benchmark interest rate by 50 basis points. This surprise move signals a more dovish monetary policy stance, indicating the ECB is concerned about slowing economic growth and is willing to stimulate the economy through lower borrowing costs. The immediate market reaction would likely see a sharp depreciation of the Euro (EUR) against the US Dollar (USD). Investors, anticipating lower returns on Euro-denominated assets, would sell EUR and buy USD, driving the EUR/USD exchange rate lower. For traders, this could present a short-term opportunity. A trader could have profited by shorting EUR/USD (betting on its decline) immediately after the announcement, aiming to capitalize on the initial price drop. However, the market’s reaction wouldn’t be solely driven by the interest rate cut; other factors like market sentiment and speculation about future ECB actions would also play significant roles, potentially leading to volatility and creating further trading opportunities. A successful trade would require careful risk management and a keen understanding of the broader economic context.
Prolonged Low Interest Rates Impact the Japanese Yen
Japan’s prolonged period of near-zero interest rates, implemented to combat deflation, provides a compelling example of the long-term effects of low interest rates on a major currency. The Yen (JPY) has experienced periods of significant weakness against other major currencies, particularly the US dollar. Investors seeking higher returns have moved away from JPY-denominated assets, leading to a decline in demand for the Yen. This situation has created challenges for Japanese exporters, who benefit from a weaker Yen, but also created concerns about the potential for inflationary pressures if the policy persists too long. This example underscores that while low interest rates might stimulate domestic economies, they can also lead to currency depreciation over the long term, impacting various aspects of the economy.
Visual Representation of Interest Rates and Currency Value Fluctuations
Imagine a graph with two lines. The x-axis represents time, spanning several months. The y-axis on the left represents the interest rate differential between two currencies (e.g., US Dollar and Euro interest rates). The y-axis on the right represents the exchange rate of the currency pair (e.g., EUR/USD). The interest rate differential line would show fluctuations reflecting changes in central bank policies. The exchange rate line would generally show an inverse relationship to the interest rate differential. When the interest rate differential is high (favoring one currency), the corresponding currency would tend to appreciate (its exchange rate goes up), and vice versa. However, the relationship isn’t always perfectly linear. Other factors, such as market sentiment, geopolitical events, and economic data releases, can influence the exchange rate, creating deviations from the expected relationship. The graph would visually demonstrate how interest rate changes are a key driver of currency value fluctuations, but not the sole determinant. Periods of significant divergence between the two lines would highlight the influence of non-interest rate factors on currency movements.
Wrap-Up: The Role Of Interest Rates In Forex Trading
Mastering the role of interest rates in forex trading isn’t just about understanding the mechanics; it’s about developing a keen eye for market trends and a robust risk management strategy. While predicting interest rate movements isn’t an exact science, by combining rigorous analysis with a disciplined approach, you can significantly improve your chances of success in this dynamic market. Remember, knowledge is power, and in the world of forex, that power translates directly to potential profits. So, sharpen your analytical skills, stay informed, and navigate the exciting world of currency trading with confidence.
FAQ Corner
What are the biggest risks involved in interest rate-based forex trading?
The biggest risks include unexpected interest rate changes, inaccurate forecasts, and high leverage leading to significant losses. Volatility in the market can also quickly wipe out profits.
How often are interest rates adjusted by central banks?
It varies widely depending on the central bank and economic conditions. Some adjust rates several times a year, others less frequently.
Are there any free resources to help me learn more about interest rate forecasting?
Yes! Many central banks publish economic reports and forecasts on their websites. Financial news sites and reputable blogs also offer analysis and commentary.
How can I stay updated on upcoming interest rate announcements?
Follow the central bank’s website for announcements and subscribe to financial news alerts. Many forex brokers also provide calendars of upcoming events.






