Understanding the Forex Trading Spread: It’s the silent cost of your forex trades, the invisible hand shaping your profits (or losses!). This isn’t just about bid and ask prices; it’s about understanding market dynamics, broker choices, and how even tiny differences can significantly impact your bottom line. We’re diving deep into the world of spreads, decoding the jargon, and equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this crucial aspect of forex trading like a pro.
From fixed versus variable spreads to the factors influencing their size – liquidity, volatility, even news events – we’ll break it all down. Learn how to calculate spread costs, spot opportunities in spread changes, and ultimately, choose a broker that aligns with your trading style and risk tolerance. Get ready to master the spread and level up your forex game.
Defining the Forex Spread: Understanding The Forex Trading Spread
Understanding the forex spread is crucial for anyone venturing into the exciting (and sometimes volatile!) world of foreign exchange trading. It’s a fundamental concept that directly impacts your profitability, so getting a firm grasp on it is paramount. Think of it as the cost of doing business in the forex market.
Components of a Forex Spread
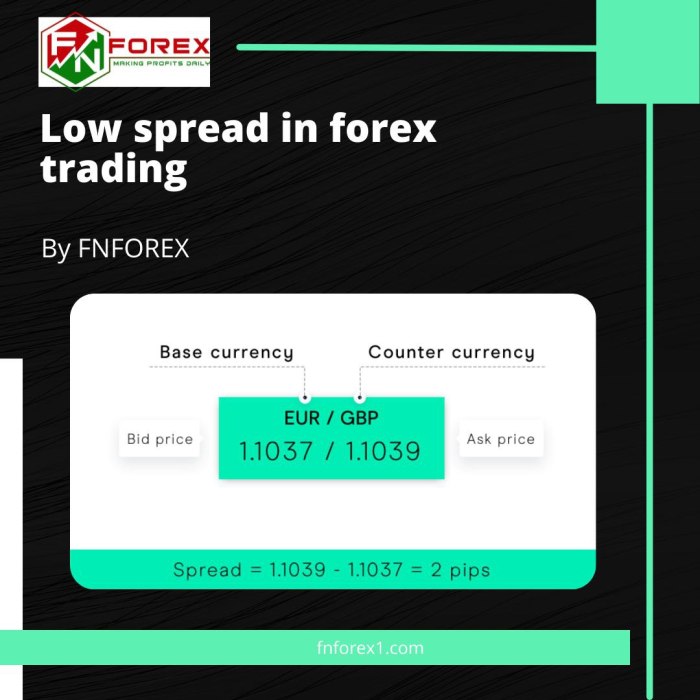
The forex spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair. The bid price is the price at which a market maker (like a bank or broker) is willing to buy a currency pair from you, while the ask price is the price at which they’re willing to sell it to you. You always buy at the ask and sell at the bid. This seemingly small difference is how brokers and market makers generate their profit.
Visual Representation of the Spread on a Trading Platform
On most trading platforms, you’ll see the bid and ask prices displayed side-by-side. For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted as 1.1000/1.1005, the bid price is 1.1000, and the ask price is 1.1005. The spread, in this case, is 5 pips (points in percentage). This visual representation is usually clear and readily accessible, allowing traders to quickly assess the cost of their trades. The spread is often displayed directly next to the currency pair’s price.
Types of Forex Spreads: Fixed vs. Variable
Forex spreads come in two main varieties: fixed and variable. Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions, while variable spreads fluctuate based on market volatility and liquidity. Understanding the differences is vital for choosing a trading strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance and trading style.
Comparison of Fixed and Variable Spreads
| Feature | Fixed Spread | Variable Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The spread remains constant throughout the trading day. | The spread fluctuates depending on market conditions. |
| Predictability | Highly predictable; traders know the exact cost upfront. | Less predictable; the spread can widen significantly during periods of high volatility. |
| Trading Costs | Potentially higher overall costs, especially during periods of low volatility. | Potentially lower costs during periods of low volatility; can be significantly higher during high volatility. |
| Suitability | Ideal for scalpers and traders who prefer predictable trading costs. | Suitable for swing traders and long-term investors who are comfortable with fluctuating costs and can adapt their strategies. |
Factors Influencing Forex Spreads
Forex spreads, the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair, aren’t static; they fluctuate constantly. Understanding what drives these changes is crucial for successful trading. Several key factors interplay to determine the spread’s size at any given moment, impacting your trading costs and overall profitability.
Liquidity’s Role in Spread Size
Liquidity, simply put, refers to the ease with which a currency pair can be bought or sold. Highly liquid pairs, like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, generally boast tighter spreads because there are many buyers and sellers constantly active in the market. Conversely, less liquid pairs, often those involving emerging market currencies, tend to have wider spreads due to the lower trading volume and increased difficulty in finding a counterparty for your trade. Think of it like a busy highway versus a quiet country road; the highway (high liquidity) allows for smoother, faster transactions, while the country road (low liquidity) requires more time and effort.
Volatility and its Impact on Spreads
Market volatility, or the degree of price fluctuation, significantly affects spreads. During periods of high volatility, such as major news announcements or geopolitical events, spreads widen considerably. This is because market makers need to account for the increased risk of sudden price movements. They widen spreads to protect themselves from potential losses. Conversely, during calmer periods with low volatility, spreads tend to narrow as the risk is reduced. Imagine a calm sea versus a stormy ocean; a calm sea (low volatility) allows for easier navigation (tighter spreads), while a stormy ocean (high volatility) makes navigation more challenging and risky (wider spreads).
Trading Time and Spread Variation
The time of day also plays a role. Spreads are typically tightest during periods of high trading volume, such as the overlap between the London and New York trading sessions. This is because increased activity boosts liquidity. Conversely, during quieter periods, such as overnight or weekends, spreads tend to widen due to reduced liquidity. The difference can be significant; you might see a spread of 1 pip during peak trading hours and 3 pips or more during off-peak times. This illustrates how the timing of your trades can directly influence your costs.
Spread Size and Trading Volume: A Correlation
A direct relationship exists between trading volume and spread size. High trading volume generally leads to tighter spreads because of increased liquidity and competition among market makers. Conversely, low trading volume results in wider spreads as there are fewer buyers and sellers, making it more difficult to execute trades quickly and efficiently. This is a fundamental principle of market dynamics; greater activity equates to more efficient pricing.
Market News and its Effect on Spreads
Major news events, such as central bank announcements, economic data releases, or geopolitical developments, can significantly impact forex spreads. The anticipation and reaction to these events often lead to increased volatility, resulting in wider spreads. Traders often increase their activity during these times, creating a temporary surge in volatility, widening the spreads until the market stabilizes. For example, the release of unexpectedly strong US employment data might cause a significant price swing in the USD, widening spreads across many currency pairs involving the dollar. Conversely, if the news is as expected, the impact on spreads may be minimal.
Spread Costs and their Impact on Trading
Forex spreads, while seemingly small, significantly impact your trading profitability. Understanding how spreads eat into your profits is crucial for successful forex trading. Ignoring spread costs can lead to disappointing results, even with seemingly profitable trades. This section will delve into the specifics of spread costs and provide strategies to mitigate their impact.
The spread, remember, is the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair. This difference represents the broker’s profit and your trading cost. Every trade you make involves paying this spread, directly impacting your potential returns. Let’s explore how this plays out in different scenarios.
Learn about more about the process of The Pros and Cons of Trading Forex Full-Time in the field.
Spread Costs on Different Trade Sizes
The impact of spreads varies directly with the size of your trade. A larger trade will incur a proportionally larger spread cost. Consider these examples:
| Trade Size (Lots) | Spread (pips) | Spread Cost (USD) per lot (assuming 1 pip = $10) | Total Spread Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | $15 | $15 |
| 0.1 | 1.5 | $15 | $1.50 |
| 5 | 1.5 | $15 | $75 |
As you can see, a 5-lot trade with a 1.5-pip spread costs $75, while a 0.1-lot trade costs only $1.50. This highlights the importance of considering your trade size in relation to your risk tolerance and the spread cost.
Finish your research with information from Forex Trading Hours Explained: When to Trade for Maximum Profit.
Comparing Broker Spreads
Different forex brokers offer varying spreads. Choosing a broker with tighter spreads can significantly reduce your trading costs over time. For example, Broker A might offer a EUR/USD spread of 1 pip, while Broker B offers 1.5 pips. On a 1-lot trade, this difference translates to a $5 cost saving per trade with Broker A. Over many trades, this adds up considerably.
It’s crucial to compare spreads across multiple brokers before settling on one. Don’t solely focus on the advertised spread; consider the typical spread during your trading hours, as spreads can fluctuate based on market conditions and liquidity.
Calculating Total Spread Cost
Calculating the total spread cost is straightforward. You need the spread in pips, the lot size, and the pip value for the specific currency pair. The formula is:
Total Spread Cost = Spread (pips) * Lot Size * Pip Value
For instance, a 0.5-lot trade on EUR/USD with a 1.2-pip spread and a pip value of $10 would cost: 1.2 pips * 0.5 lots * $10/pip = $6
Strategies for Minimizing Spread Impact
Several strategies can help minimize the negative impact of spreads on your trading performance:
- Choose a broker with tight spreads: Research and compare brokers to find one offering consistently low spreads, especially during your active trading hours.
- Trade higher-liquidity currency pairs: Major currency pairs generally have tighter spreads than minor or exotic pairs.
- Trade larger lot sizes (with caution): While larger trades incur higher spread costs in absolute terms, the cost per pip is lower, improving efficiency. However, this increases risk, so manage your position size carefully.
- Use scalping strategies (with caution): Scalpers often focus on small price movements, making spreads a larger percentage of their profit. However, if successful, the frequency of trades can offset the impact of individual spread costs. This strategy is highly risky and requires significant experience.
- Avoid trading during periods of low liquidity: Spreads widen significantly during news releases or periods of low trading volume, increasing your trading costs.
Spread Interpretation and Analysis
Understanding how forex spreads behave is crucial for successful trading. Spread widening and narrowing aren’t just random fluctuations; they often reflect underlying market dynamics and can offer valuable insights for traders. By analyzing spread movements, you can improve your order execution and potentially enhance your trading strategy.
Spread widening and narrowing act as market signals, reflecting shifts in liquidity and volatility. A widening spread typically indicates increased uncertainty or decreased liquidity in the market, making it more expensive to enter or exit a position. Conversely, a narrowing spread suggests increased liquidity and potentially lower volatility, signifying a more favorable environment for trading.
Spread Widening as a Market Signal, Understanding the Forex Trading Spread
A widening spread often precedes significant market events or periods of heightened volatility. For example, during major news announcements, spreads tend to widen as traders react to the information, creating temporary imbalances in supply and demand. This widening makes it more difficult to execute trades at desired prices, increasing the risk of slippage. Consider a scenario where a central bank unexpectedly raises interest rates. The immediate market reaction would likely be increased volatility and uncertainty, resulting in a wider spread for the affected currency pair. Traders might choose to postpone entries until the market stabilizes, indicated by a narrowing spread.
Spread Narrowing as a Market Signal
Conversely, a narrowing spread often suggests a calmer market with increased liquidity. This indicates a higher probability of executing trades at or near the desired price. For instance, during periods of low volatility, such as overnight trading sessions or weekends when news is less prevalent, spreads generally narrow. This provides opportunities for traders who employ strategies that benefit from tight spreads, such as scalping or arbitrage. A consistently narrow spread in a particular currency pair might also suggest increased confidence and stability in that market.
Using Spread Information in Trading Strategies
Traders can integrate spread information into their strategies in several ways. One approach involves avoiding trading when spreads are significantly wider than usual. This minimizes the risk of slippage and unfavorable order execution. Another strategy might involve using spread widening as a signal to exit existing positions, especially if the widening is accompanied by other bearish signals. Conversely, a narrowing spread might signal a good opportunity to enter a trade, particularly if combined with other bullish indicators. A trader might even incorporate spread analysis into their risk management by setting dynamic stop-loss orders that adjust based on spread fluctuations.
Spread and Order Execution
The relationship between spreads and order execution is direct. Wider spreads increase the likelihood of slippage, where the actual execution price differs from the intended price. This is particularly relevant for traders using market orders, which execute immediately at the best available price. Limit orders, while offering more control, are not immune to slippage, especially in volatile markets with wide spreads. The impact of slippage can be substantial, particularly on larger trades.
Widening Spread vs. Slippage
While closely related, a widening spread and slippage are distinct concepts. A widening spread reflects the market condition, increasing the *potential* for slippage. Slippage, on the other hand, is the *actual* difference between the expected execution price and the actual execution price. A widening spread increases the risk of slippage, but slippage only occurs when an order is executed at a less favorable price than anticipated. For example, a trader might place a market order during a news event when spreads are significantly wide. The resulting execution price could be considerably worse than the quoted price, representing slippage. The wide spread itself is not slippage, but it created the condition that made slippage more likely.
Choosing a Broker Based on Spreads
Selecting the right forex broker is crucial for successful trading, and a key factor in this decision is the spread offered. Spreads, the difference between the bid and ask price, directly impact your profitability. Understanding how different brokers price their spreads and comparing their offerings is essential for maximizing your returns.
Spread Comparison Across Brokers
Choosing a broker solely based on the lowest spread isn’t always the best strategy. Reputation, regulation, and other fees also play a significant role. Let’s compare the spread offerings of three hypothetical brokers for the EUR/USD pair (a major currency pair) at a specific point in time. Remember that spreads fluctuate constantly.
| Broker | EUR/USD Spread (pips) | Minimum Deposit | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broker A | 0.8 | $500 | FCA Regulated |
| Broker B | 1.2 | $1000 | CySEC Regulated |
| Broker C | 0.5 | $2000 | Unregulated |
Importance of Considering Other Broker Fees
While spreads are a significant cost, they’re not the only fee you’ll encounter. Many brokers charge commissions, inactivity fees, overnight swap fees, and deposit/withdrawal fees. These fees can accumulate and significantly impact your overall profitability, potentially offsetting the advantage of a low spread. For example, Broker A might offer a low spread but charge a high commission per trade, making it less cost-effective than Broker B with a slightly higher spread but lower commission. Carefully review the complete fee schedule before committing to a broker.
Broker Selection Checklist
Before selecting a forex broker, consider these factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Spreads | Compare spreads across multiple currency pairs (major, minor, exotic). Consider average spreads and potential widening during news events. |
| Commissions | Determine if commissions are charged per trade and how they compare to spreads. |
| Other Fees | Review the full fee schedule for inactivity, overnight swaps, and deposits/withdrawals. |
| Regulation | Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority to protect your funds. |
| Trading Platform | Choose a platform that is user-friendly, reliable, and provides the tools you need. |
| Customer Support | Assess the quality and responsiveness of the broker’s customer support. |
| Account Types | Compare different account types and their minimum deposit requirements. |
Typical Spreads Offered by a Hypothetical Broker
This table illustrates typical spreads for different currency pairs offered by a hypothetical broker. These are examples and actual spreads will vary.
| Currency Pair | Spread (pips) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.9 | Major |
| GBP/USD | 1.1 | Major |
| USD/JPY | 0.7 | Major |
| EUR/GBP | 1.3 | Minor |
| USD/CHF | 1.0 | Minor |
| USD/CAD | 1.2 | Minor |
| USD/TRY | 2.5 | Exotic |
| EUR/TRY | 3.0 | Exotic |
Visual Representation of Spreads

Forex spreads, the difference between the bid and ask prices, aren’t just numbers on a screen; they’re visually represented on your trading charts, offering clues to market liquidity and potential trading opportunities. Understanding this visual representation is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Understanding how bid and ask prices are displayed on a chart allows traders to quickly assess the spread and its impact on potential profits. The bid price (what you’ll get if you sell) is usually displayed slightly lower than the ask price (what you’ll pay if you buy). The difference between these two prices is the spread, often visually subtle but impactful on your bottom line. Many platforms will clearly show the bid and ask prices, often with the spread value displayed numerically as well.
Widening Spreads on Candlestick Charts
A widening spread visually manifests as an increase in the distance between the bid and ask prices. On a candlestick chart, this isn’t always immediately obvious as a single, easily-identifiable element, but it reflects in the candlestick’s body and wicks. A widening spread often accompanies increased market volatility or uncertainty. For example, during periods of significant news releases or geopolitical events, you might see longer candlestick bodies (reflecting larger price movements) and longer wicks (indicating indecision and price reversals). The increased price volatility directly contributes to the spread widening as market makers adjust their pricing to account for the heightened risk. Consider a scenario where a major economic announcement is expected. Before the announcement, the candles might be relatively small with short wicks, reflecting a tight spread. Immediately after the announcement, however, we might see significantly larger candles with long upper and lower wicks, signifying a much wider spread as market participants react to the new information and prices fluctuate wildly. The larger the price swings within the candle, the larger the potential spread widening that might be implied.
Identifying Opportunities Based on Spread Changes
Traders can use visual cues to identify potential trading opportunities related to spread changes. A consistently narrowing spread might signal increased market liquidity and potentially favorable conditions for trading. Conversely, a widening spread might indicate decreased liquidity and increased risk. However, it’s crucial to remember that spread changes alone don’t dictate trading decisions. A trader should consider the spread in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis indicators. For instance, a narrowing spread coupled with a bullish trend might signal a potential entry point for a long position. Conversely, a widening spread during a bearish trend might signal a need for caution or an opportunity for short selling, provided other indicators confirm the bearish momentum. Successful traders use spread analysis as one piece of a larger puzzle, integrating it with their overall trading strategy.
Ultimate Conclusion
So, you’ve cracked the code on forex trading spreads! You now understand the hidden costs, the market forces at play, and how to leverage this knowledge for smarter trading decisions. Remember, understanding spreads isn’t just about minimizing costs; it’s about gaining a deeper insight into market sentiment and improving your overall trading strategy. Armed with this knowledge, you’re better equipped to navigate the forex market with confidence and potentially maximize your returns. Happy trading!
FAQ
What’s the difference between a market order and a limit order when it comes to spreads?
Market orders execute immediately at the best available price, potentially incurring a wider spread during volatile times. Limit orders, however, let you specify the price, potentially missing out on opportunities if the price doesn’t reach your limit but offering better control over spread costs.
How do overnight swaps affect spread calculations?
Overnight swaps (rollover fees) are separate from the spread but can influence your overall trading cost. They are added or subtracted depending on the position and currency pair, impacting your profitability alongside the spread.
Are there any strategies to minimize slippage besides choosing a low-spread broker?
Yes! Using limit orders, avoiding trading during high-volatility periods, and choosing less volatile currency pairs can all help mitigate slippage, which is related to but distinct from the spread.






