The Basics of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios: Dive into the thrilling world of forex trading, where fortunes are made and lost on the razor’s edge of risk. Understanding risk-to-reward ratios isn’t just about managing losses; it’s about strategically maximizing your wins. This isn’t your grandpappy’s investing; this is about calculated gambles and smart money management. Get ready to learn how to stack the odds in your favor.
We’ll unravel the mysteries of calculating risk-to-reward ratios, showing you how to determine your personal risk tolerance, and setting up those crucial stop-loss and take-profit orders. We’ll explore position sizing, diversification strategies, and even dissect common mistakes traders make (so you can avoid them!). Prepare for a deep dive into the practical application of risk management, complete with real-world examples and actionable strategies. Ready to up your forex game? Let’s go.
Introduction to Forex Trading Risk
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, carries significant inherent risks. Understanding these risks is paramount to successful and sustainable trading. Ignoring them can lead to substantial financial losses, even wiping out your entire investment. This section explores the various types of risks involved, emphasizing the importance of robust risk management strategies.
Market Risk
Market risk encompasses the unpredictable fluctuations in currency exchange rates. These fluctuations are influenced by a myriad of factors, including economic data releases (like inflation rates or GDP growth), geopolitical events (wars, political instability), and market sentiment (overall optimism or pessimism). A trader might, for example, open a long position on the EUR/USD pair, anticipating the Euro to appreciate against the US dollar. However, unexpected negative economic news from the Eurozone could cause the Euro to depreciate, resulting in a loss for the trader. This illustrates the unpredictable nature of market risk and the need for careful analysis and diversification.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the potential inability to quickly buy or sell a currency pair at a desired price. This risk is particularly pronounced in less liquid currency pairs or during periods of high market volatility. Imagine a trader attempting to exit a position in a relatively obscure currency pair during a flash crash. The lack of readily available buyers might force the trader to accept a significantly worse price than anticipated, leading to a substantial loss. This highlights the importance of choosing liquid currency pairs and understanding market conditions.
Operational Risk
Operational risk encompasses the risks associated with the trading process itself. This includes errors in order execution, platform malfunctions, internet connectivity issues, and even human error in calculations or analysis. For instance, a trader might accidentally input the wrong trade size, leading to a much larger loss than intended. Similarly, a technical glitch on the trading platform could prevent a trader from closing a position at a favorable price, resulting in increased losses. Therefore, choosing a reliable broker and implementing proper risk management protocols are vital.
Credit Risk
Credit risk, primarily relevant when using leverage, pertains to the risk of a broker defaulting on its obligations. While reputable brokers are highly regulated, there’s always a small risk of insolvency, especially in times of financial crisis. If your broker fails, you could lose access to your funds, even if your trading positions are profitable. Selecting a well-established, regulated broker is crucial to mitigating this risk.
Political Risk
Geopolitical events and political instability in a country whose currency you’re trading can significantly impact exchange rates. Unexpected political shifts, sanctions, or even natural disasters can trigger sudden and drastic currency movements, causing substantial losses for traders unprepared for such events. For example, unexpected political upheaval in a country could lead to a sharp devaluation of its currency, creating significant losses for those holding long positions in that currency. Staying informed about global events is crucial for managing political risk.
Understanding Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. To navigate this volatility and increase your chances of long-term success, understanding and managing risk is paramount. A crucial tool in this process is the risk-to-reward ratio, a simple yet powerful concept that helps you determine the potential profit relative to the potential loss on any given trade. Mastering this ratio is key to consistent profitability.
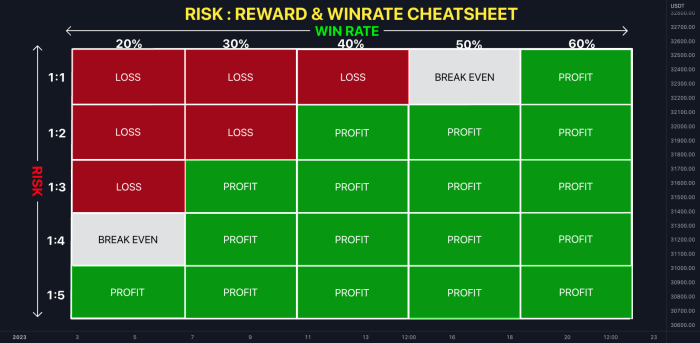
The risk-to-reward ratio is a fundamental concept in forex trading that compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss. It’s expressed as a ratio, for example, 1:2, 1:3, or even 1:1. This ratio essentially quantifies the relationship between how much you stand to lose versus how much you stand to gain. A higher risk-to-reward ratio (e.g., 1:3) suggests a potentially more profitable trade, while a lower ratio (e.g., 1:1) indicates a more conservative approach. Consistent application of favorable risk-to-reward ratios is a cornerstone of successful forex trading strategies.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out What Is Forex Arbitrage and How Does It Work? now.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio Calculation
Calculating your risk-to-reward ratio involves determining your stop-loss and take-profit levels. Your stop-loss order sets the point at which you’ll automatically exit a losing trade to limit your potential losses. Your take-profit order sets the point at which you’ll automatically exit a winning trade to secure your profits.
The formula is: Risk-to-Reward Ratio = (Take-Profit Price – Entry Price) / (Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price)
For example, if you enter a trade at 1.1000, set your stop-loss at 1.0950, and your take-profit at 1.1050, your risk-to-reward ratio would be: (1.1050 – 1.1000) / (1.1000 – 1.0950) = 1:1. This means your potential profit is equal to your potential loss.
Examples of Risk-to-Reward Ratios and Their Implications
Different risk-to-reward ratios carry varying levels of risk and potential reward. A 1:1 ratio is considered neutral, meaning the potential profit equals the potential loss. A 1:2 ratio suggests that for every $1 you risk, you stand to gain $2. This is generally considered a favorable ratio, offering a higher potential reward for the risk taken. Conversely, a 1:0.5 ratio indicates a more conservative approach, where the potential profit is half the potential loss. The optimal ratio depends on individual risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Risk/Reward Scenarios and Potential Outcomes
The following table illustrates various risk/reward scenarios and their potential outcomes, assuming a consistent trade size:
| Scenario | Risk-to-Reward Ratio | Win Rate Needed for Profitability (Approximate) | Outcome Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 1:1 | 50% | Requires a 50% win rate to break even; minimal profit potential. |
| Balanced | 1:2 | 33% | Can be profitable with a lower win rate; higher profit potential. |
| Aggressive | 1:3 | 25% | High profit potential but requires a higher risk tolerance and a disciplined approach. |
| Highly Aggressive (Risky) | 1:5 | 16% | Very high profit potential but extremely risky, requiring exceptional accuracy and risk management. |
Determining Your Risk Tolerance
Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial before diving into the exciting (and sometimes volatile) world of forex trading. It’s not just about how much money you can afford to lose; it’s about your emotional and psychological comfort level with potential losses. Ignoring this crucial step can lead to impulsive decisions, poor trading strategies, and ultimately, significant financial setbacks.
Factors influencing individual risk tolerance levels are multifaceted and deeply personal. They intertwine your financial situation, personality traits, and even your current life circumstances. A high-risk tolerance might stem from a strong financial foundation, a youthful outlook with a longer time horizon for recovery from potential losses, or simply a more aggressive personality. Conversely, a low-risk tolerance often reflects a more conservative financial approach, a shorter time horizon for investment goals, or a greater aversion to uncertainty.
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
Several key factors contribute to an individual’s risk tolerance. These factors aren’t mutually exclusive and often interact in complex ways. For example, a person with a secure job and substantial savings might exhibit a higher risk tolerance than someone facing significant debt and financial instability. Similarly, someone’s age and investment goals will also heavily influence their risk profile. Younger investors with longer time horizons tend to have higher risk tolerance than older investors nearing retirement.
Assessing Personal Risk Tolerance
Assessing your risk tolerance isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. There’s no single magic formula. However, several effective strategies can help you determine your comfort level with risk. A thorough self-assessment, considering your financial situation, personality, and investment goals, is essential. Honest introspection is key. Consider journaling your feelings about potential losses, both small and large, to understand your emotional response to risk.
Risk Tolerance Questionnaires and Assessments
Many online resources and financial institutions offer risk tolerance questionnaires. These questionnaires typically present hypothetical scenarios involving investment losses and gains, asking you to rate your comfort level with each outcome. These assessments often utilize a scoring system to categorize individuals into low, moderate, or high-risk tolerance categories. A simple example might involve questions like: “How would you feel if your investment lost 10% of its value?” or “What percentage of your investment portfolio would you be comfortable allocating to high-risk assets?” The responses help determine your risk profile. While not perfectly precise, these questionnaires provide a valuable starting point for self-reflection and understanding your risk tolerance. Remember, the results are a guide, not a definitive judgment.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are your best friends in the sometimes-chaotic world of forex trading. They’re not just good practice; they’re essential for managing risk and protecting your hard-earned capital. Think of them as your automated safety net and profit-locking mechanism, ensuring you don’t lose more than you’re willing to risk and that you secure gains when your trade goes your way.
Setting these orders correctly is crucial for achieving your desired risk-to-reward ratio. By defining precise entry and exit points, you can control your potential losses and enhance your chances of profitable trades. Ignoring these orders is like sailing a ship without a rudder – you might get lucky, but you’re also significantly increasing your chances of disaster.
Stop-Loss Order Placement
A stop-loss order automatically closes your position when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. This prevents unlimited losses, a common pitfall for inexperienced traders. The placement of your stop-loss order is directly tied to your risk tolerance and your risk-to-reward ratio. For example, if your risk tolerance is 2% of your account and you’re trading with a $10,000 account, your maximum loss per trade should be $200. You’ll then set your stop-loss order based on the potential price movement that would result in this $200 loss. This requires careful analysis of the chart and an understanding of the asset’s volatility.
Take-Profit Order Placement
The take-profit order, conversely, automatically closes your position when the price moves in your favor by a specified amount. This helps you lock in profits and avoid the temptation to let winning trades run too long, only to see them reverse course and erase your gains. The placement of your take-profit order is determined by your chosen risk-to-reward ratio. A common ratio is 1:2, meaning you aim for twice the profit as your potential loss. If your stop-loss is set at $200, your take-profit order would be set at $400. This ratio, however, can vary depending on your trading strategy and market conditions.
Methods for Determining Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Several methods exist for determining these crucial levels. One common approach is to use technical analysis indicators like support and resistance levels. Support levels represent price points where buying pressure is expected to outweigh selling pressure, while resistance levels mark the opposite. Setting a stop-loss just below a support level and a take-profit above a resistance level can be a robust strategy. Another method involves using chart patterns like triangles or head and shoulders, which can indicate potential price targets. Finally, some traders use a fixed percentage or pip value, regardless of technical indicators, to maintain consistency across trades.
Example Trading Plan
Let’s imagine a trader, let’s call him Alex, is considering a long position on the EUR/USD currency pair. He’s identified a support level at 1.1000 and a resistance level at 1.1100. Alex’s account balance is $5,000, and he’s comfortable risking 1% per trade, meaning a maximum loss of $50. To determine his stop-loss level, he needs to calculate the pip value for his trade size. Let’s assume his trade size equates to a $50 loss at a price of 1.0990. Therefore, his stop-loss order is placed at 1.0990. To achieve a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, his take-profit order would be placed at 1.1090 (1.1000 + 100 pips, twice the distance of the stop-loss). If the price moves to his take-profit level, he secures a profit of $100, doubling his initial investment.
Position Sizing and Risk Management Techniques
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Successfully navigating the market requires not just understanding risk-to-reward ratios, but also mastering the art of position sizing and implementing robust risk management strategies. These techniques act as your safety net, preventing significant losses and allowing you to stay in the game long enough to profit from winning trades.
Position sizing is crucial because it determines the amount of capital you risk on each trade. Without proper position sizing, even a well-researched trade with a favorable risk-to-reward ratio can wipe out your account if you’re overly aggressive. Think of it like this: a single, poorly sized trade is like a single, massive bet at the casino; while a well-sized trade is a series of smaller, manageable bets.
Position Sizing Methods
Several methods help determine the appropriate position size for your trades. Choosing the right method depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and overall trading goals. Two common approaches are:
- Percentage of Account: This method involves risking a fixed percentage of your trading capital on each trade. For example, a trader might risk only 1% to 2% per trade. This limits potential losses to a manageable level even if multiple trades fail. If you have a $10,000 account and risk 1%, your maximum loss per trade would be $100.
- Fixed Lot Size: This involves trading a consistent lot size regardless of your account balance. This approach is simpler to manage but less flexible than percentage-based sizing. It might be suitable for traders with larger accounts who are comfortable with a consistent risk level.
Risk Management Techniques Beyond Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential, but they’re not the only risk management tool in your arsenal. Diversification and hedging play crucial roles in protecting your capital and mitigating overall risk.
- Diversification: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversifying your portfolio across different currency pairs reduces your dependence on any single market’s performance. If one pair performs poorly, others might compensate for the losses.
- Hedging: Hedging involves taking offsetting positions in related markets to reduce risk. For instance, if you’re long on EUR/USD, you might simultaneously take a short position on a correlated pair to limit potential losses if the EUR weakens unexpectedly. However, hedging can also limit potential profits.
Best Practices for Risk Management in Forex Trading
Effective risk management is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s an ongoing process that requires discipline and adaptation. Here are some key practices:
- Develop a Trading Plan: A well-defined trading plan Artikels your risk tolerance, position sizing strategy, and entry/exit rules. This plan should be followed consistently to maintain discipline.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Market conditions change, and so should your risk management approach. Regularly review your trading performance and adjust your strategies accordingly.
- Emotional Discipline: Avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Stick to your trading plan and avoid chasing losses or letting emotions dictate your trades.
- Paper Trading: Practice your trading strategies on a demo account before risking real money. This allows you to refine your techniques and gain confidence without significant financial consequences.
- Continuous Learning: The forex market is constantly evolving. Stay updated on market trends, news, and new trading techniques to improve your risk management capabilities.
Analyzing Past Trades and Refining Your Strategy: The Basics Of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios

Post-trade analysis isn’t just about congratulating yourself on wins or dwelling on losses; it’s the cornerstone of consistent improvement in forex trading. By meticulously reviewing your past trades, you can identify recurring patterns, pinpoint weaknesses in your strategy, and ultimately refine your approach to maximize profitability and minimize risk. This systematic approach transforms your trading journey from a series of isolated events into a process of continuous learning and growth.
A structured approach to reviewing your trades involves more than just glancing at your profit and loss. It requires a detailed examination of your decision-making process, market conditions, and the execution of your trades. Consider it a post-mortem for each trade, designed to uncover valuable insights that can be applied to future trades.
Obtain access to How to Analyze Forex News for Better Trading Decisions to private resources that are additional.
Structured Trade Review Process
To effectively analyze your past trades, follow a structured process. First, document every trade, including the entry and exit points, your rationale for entering the trade, the market conditions at the time, and your initial risk-to-reward ratio. Next, compare your initial plan with the actual outcome. Identify any deviations from your plan and analyze the reasons behind them. Finally, assess the overall performance of the trade and determine what you could have done differently. This process helps transform sporadic wins into consistent profitability.
Adjusting Risk-to-Reward Ratios Based on Past Performance
Your risk-to-reward ratio isn’t set in stone. Analyzing past trades allows you to dynamically adjust this ratio based on your performance. For example, if you consistently find that trades with a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio are more profitable, you might shift your focus toward this ratio. Conversely, if you discover that trades with a 1:1 ratio result in more frequent losses, you may opt to increase your risk-to-reward ratio to 1:3 or higher, or adjust your entry and exit strategies. Remember, the goal is to optimize your strategy for consistent, long-term profitability.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio Performance Comparison
The following table illustrates how different risk-to-reward ratios can impact your overall trading performance. This is a simplified example, and actual results will vary depending on market conditions and individual trading strategies.
| Trade | Risk-to-Reward Ratio | Profit/Loss ($) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trade 1 | 1:2 | $200 | Profitable |
| Trade 2 | 1:1 | -$100 | Loss |
| Trade 3 | 1:3 | $300 | Profitable |
| Trade 4 | 1:2 | -$50 | Loss |
Common Mistakes in Forex Risk Management
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Many traders, especially beginners, fall prey to common mistakes that can significantly impact their profitability and even lead to substantial losses. Understanding these pitfalls and implementing preventative strategies is crucial for long-term success. This section will highlight some of the most prevalent errors and offer practical solutions.
Ignoring Position Sizing and Risk Tolerance
Overlooking proper position sizing is a major pitfall. Many traders jump into trades without considering how much they’re willing to lose on any single trade relative to their entire account balance. This reckless approach can lead to devastating losses if a trade goes against them. For example, a trader with a $10,000 account might risk 10% on a single trade ($1000), which is generally considered excessive for a single trade. If that trade loses, the account is immediately down by 10%. Subsequent losses could quickly deplete the account, leading to margin calls and account closure. The consequence is a significant reduction or complete loss of capital. To avoid this, traders should determine their risk tolerance, which represents the maximum percentage of their account they are comfortable losing on any given trade. A more conservative approach might involve risking only 1-2% per trade.
Overtrading and Emotional Decisions
The excitement of forex trading can lead to overtrading, making numerous trades without proper analysis or strategy. This impulsive approach often results from emotional reactions to market fluctuations, like fear of missing out (FOMO) or the desire to recoup losses quickly. The consequences are clear: increased risk exposure, potential for significant losses due to poor decision-making, and ultimately, a damaged trading strategy. To mitigate this, establishing a well-defined trading plan with clear entry and exit rules is crucial. Sticking to the plan, even during periods of market volatility, helps minimize emotional trading and promotes disciplined decision-making. Maintaining a trading journal to track performance and identify emotional biases can also be beneficial.
Neglecting Stop-Loss Orders, The Basics of Forex Trading Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Stop-loss orders are essential risk management tools that automatically exit a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. Many traders fail to use them, or they place them too far from their entry point, rendering them ineffective. The consequence of not using stop-loss orders is unlimited potential loss on a trade that goes significantly against the trader’s position. For instance, a trader without a stop-loss on a losing trade might see their account wiped out if the market moves drastically against their position. Always setting a stop-loss order, positioned strategically based on technical analysis or risk tolerance, is vital. Regularly reviewing and adjusting stop-losses as the market evolves is also a good practice.
Ignoring Risk-Reward Ratios
Failing to consider the risk-reward ratio – the relationship between the potential profit and potential loss of a trade – is a significant error. Traders should strive for trades where the potential reward outweighs the potential risk, for example, a 1:2 or 1:3 risk-reward ratio. Consistently entering trades with unfavorable risk-reward ratios will lead to long-term losses, even if a significant percentage of trades are profitable. For instance, if a trader consistently risks $100 to potentially gain $50, they need to win more than 66% of their trades to break even. This is difficult to achieve consistently. Therefore, focusing on trades with a favorable risk-reward ratio is paramount.
Failing to Diversify
Concentrating all trading capital on a single currency pair or strategy creates excessive risk. Market conditions can change rapidly, and a strategy that worked well in the past might not be effective in the future. The consequence of this lack of diversification is a heightened vulnerability to significant losses if the chosen asset or strategy performs poorly. To avoid this, a diversified portfolio across different currency pairs and trading strategies is recommended. This approach spreads risk and reduces the impact of losses on any single position.
Illustrative Examples of Risk-to-Reward Scenarios
Understanding risk-to-reward ratios in theory is one thing; seeing them in action is quite another. Let’s dive into some real-world scenarios to illustrate how different risk-to-reward setups play out in the forex market. Remember, past performance is not indicative of future results, and these examples are for illustrative purposes only.
Successful Trade with a 1:2 Risk-to-Reward Ratio
EUR/USD Long Position
This example showcases a long position on the EUR/USD pair. We observed a bullish price action pattern forming on the daily chart – a clear breakout from a consolidation pattern accompanied by increased trading volume. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) was showing oversold conditions, suggesting potential upward momentum. Our entry point was at 1.1000, with a stop-loss order placed at 1.0970 (30 pips risk). Our take-profit order was set at 1.1060 (60 pips target). The market moved as anticipated, breaking through our target price. The trade resulted in a profit of 60 pips, achieving a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio (60 pips profit / 30 pips risk). The chart displayed a clear upward trend after the breakout, confirming our analysis. We saw strong bullish momentum supported by increased volume.
Unsuccessful Trade with a 1:3 Risk-to-Reward Ratio
GBP/USD Short Position
This trade involved a short position on the GBP/USD pair. Technical indicators like the moving average convergence divergence (MACD) showed a bearish crossover, suggesting a potential downward trend. However, fundamental news regarding the UK economy unexpectedly boosted the pound. Our entry point was at 1.3000, with a stop-loss order at 1.3030 (30 pips risk), and a take-profit order at 1.2940 (60 pips target – a 1:3 risk-to-reward ratio). Despite the initial bearish signal, the unexpected positive news caused the GBP/USD to surge, hitting our stop-loss and resulting in a 30-pip loss. The chart showed a sudden reversal of the bearish trend, highlighting the impact of unforeseen fundamental news.
Successful Trade with a 1:1 Risk-to-Reward Ratio
USD/JPY Scalp Trade
This example focuses on a scalp trade on the USD/JPY pair. Using a 5-minute chart, we identified a minor support level and observed a bounce in price. The RSI indicated a slight oversold condition. Our entry was at 110.00, with a stop-loss at 109.95 (5 pips risk) and a take-profit at 110.05 (5 pips target), resulting in a 1:1 risk-to-reward ratio. The price moved favorably, hitting our take-profit target quickly, generating a small but consistent profit. This demonstrates that even small, well-managed trades can contribute to overall profitability. The chart displayed a brief but clear price reversal at the support level.
Unsuccessful Trade with a 1:1 Risk-to-Reward Ratio
AUD/USD Swing Trade
This swing trade on the AUD/USD pair demonstrates the limitations of even a conservative risk-to-reward ratio. Based on a longer-term chart analysis, we anticipated a continuation of an established uptrend. We entered a long position at 0.7500 with a stop-loss at 0.7480 (20 pips risk) and a take-profit at 0.7520 (20 pips target) – a 1:1 risk-to-reward ratio. However, unexpected negative economic data released during the trade period triggered a sharp reversal, hitting our stop-loss and resulting in a loss. The chart showed a significant price drop, highlighting the unpredictable nature of the forex market, even with well-defined strategies.
Closing Notes
Mastering forex trading isn’t about avoiding risk entirely – it’s about intelligently managing it. By understanding and applying the basics of risk-to-reward ratios, you’ll transform from a reactive trader to a proactive strategist. Remember, consistent profitability in forex comes from a well-defined trading plan, disciplined execution, and a relentless focus on risk management. So, ditch the guesswork, embrace the strategy, and start building your forex empire.
Questions and Answers
What’s the ideal risk-to-reward ratio?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Many traders aim for a 1:2 or 1:3 ratio (risking $1 to potentially gain $2 or $3), but the best ratio depends on your trading style and risk tolerance.
How often should I review my risk-to-reward ratio?
Regularly! At least monthly, or even after a series of trades, to see if your strategy needs tweaking based on market conditions and your performance.
Can I use risk-to-reward ratios with all trading strategies?
Yes, the concept applies across various strategies, though the specific calculation and application might vary.
What if my trades consistently lose despite a good risk-to-reward ratio?
This points to potential issues with your entry/exit points, trade selection, or overall trading strategy. Re-evaluate your approach.






