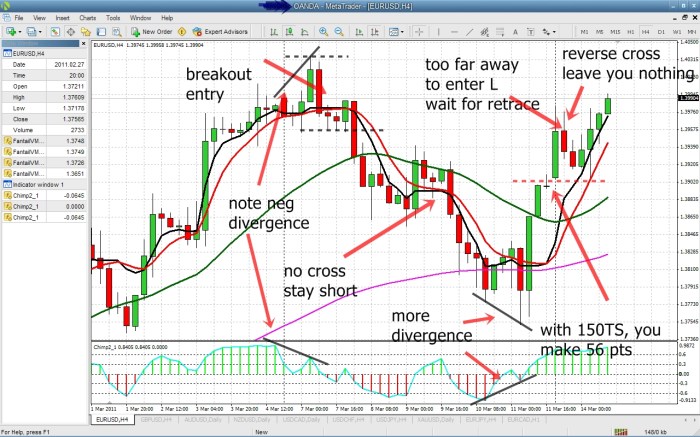
Swing trading forex: It sounds thrilling, right? Imagine harnessing the power of global currency markets to potentially rake in profits, holding trades for days or even weeks instead of frantic seconds. This isn’t your grandpa’s slow-and-steady investing; it’s a dynamic dance with market forces, a high-stakes game of identifying trends and capitalizing on price swings. This guide breaks down the core principles, strategies, and risk management techniques you need to navigate this exciting world.
We’ll dive deep into technical analysis, exploring price action, candlestick patterns, and key indicators to help you spot those juicy swing trade setups. We’ll also cover crucial risk management strategies, because let’s face it, even the most seasoned traders can get burned without a solid plan. We’ll explore various swing trading methods, from trend following to mean reversion, and offer a step-by-step process for executing and monitoring your trades. Finally, we’ll address the often-overlooked psychological aspects of trading, helping you stay disciplined and avoid emotional pitfalls.
Defining Swing Trading in Forex
Swing trading in forex is a strategy that aims to capitalize on price swings lasting from a few days to several weeks. Unlike day trading, which focuses on short-term price movements within a single day, swing traders hold their positions for a longer period, allowing for larger price fluctuations to generate profits. This approach requires a different mindset and skillset compared to other forex trading styles.
Core Principles of Swing Trading in Forex
Swing trading relies on identifying and exploiting intermediate-term price trends. Traders look for setups that suggest a significant price move is likely, using technical analysis to pinpoint entry and exit points. Patience is key, as traders must be comfortable holding positions for several days or weeks, waiting for the predicted price swing to materialize. Risk management is also crucial, with stop-loss orders used to limit potential losses. Successful swing traders carefully analyze charts, identifying support and resistance levels, trendlines, and candlestick patterns to inform their trading decisions.
Swing Trading vs. Other Forex Strategies
Swing trading differs significantly from other forex trading strategies. Day trading, for instance, involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day. Scalping, an even more aggressive short-term strategy, aims to profit from tiny price fluctuations, often holding positions for mere seconds or minutes. In contrast, swing trading offers a more relaxed approach, requiring less constant monitoring and allowing traders more time to focus on other aspects of their lives. The table below illustrates the key differences in risk and reward profiles.
| Strategy | Holding Period | Risk | Reward |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swing Trading | Days to Weeks | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Day Trading | Intraday | High | Moderate |
| Scalping | Seconds to Minutes | Very High | Low |
Common Swing Trading Setups in Forex
Several common setups are frequently used by swing traders. One example is the breakout strategy, where a trader identifies a range-bound market and enters a position when the price decisively breaks above resistance or below support. Another popular setup involves identifying trend reversals using indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or moving averages. For instance, a bearish divergence between price and RSI might signal an upcoming price decline, providing a potential short selling opportunity. Finally, traders often utilize candlestick patterns, such as engulfing patterns or hammer/hanging man patterns, to identify potential reversal points. These patterns, when combined with other technical indicators and confirmation from price action, can help to increase the probability of successful trades.
Identifying Swing Trading Opportunities
Swing trading forex, unlike its scalping cousin, focuses on capturing price movements over several days or even weeks. This longer timeframe allows for a more relaxed trading style, but requires a keen eye for identifying significant price shifts. Successfully navigating this strategy hinges on a deep understanding of technical analysis and a disciplined approach to identifying high-probability setups.
Technical analysis forms the bedrock of successful swing trading. It’s the art of interpreting price charts and indicators to predict future price movements. While fundamental analysis (news, economic data, etc.) plays a role, swing traders primarily rely on the visual cues presented by the market itself.
Price Action, Candlestick Patterns, and Chart Patterns
Price action, the simplest form of technical analysis, involves observing the raw price movements on a chart. By analyzing highs, lows, and closing prices, traders can identify potential support and resistance levels – key areas where price is likely to bounce or break. Candlestick patterns, which visually represent price movements over a specific period, offer additional insights. For example, a bullish engulfing pattern, where a large green candle completely swallows a preceding red candle, suggests a potential upward price reversal. Similarly, chart patterns like head and shoulders, triangles, and flags, reveal potential changes in momentum and can indicate upcoming breakouts or breakdowns. These patterns, when coupled with other confirming signals, significantly increase the probability of a successful swing trade. For instance, a head and shoulders pattern breaking below the neckline, combined with high volume, is a strong bearish signal.
Reliable Indicators for Confirmation
While price action and patterns provide the primary signals, confirming them with reliable indicators adds another layer of confidence. Moving averages, such as the 20-period and 50-period simple moving averages (SMAs), can help identify trends and potential entry/exit points. A bullish crossover (20-period SMA crossing above the 50-period SMA) often suggests a strengthening uptrend, while a bearish crossover indicates the opposite. Relative Strength Index (RSI) and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) are further examples of momentum indicators that can confirm swing trade signals. High RSI values (above 70) often suggest overbought conditions, hinting at a potential price correction, while low values (below 30) suggest oversold conditions and a potential bounce. MACD crossover signals, combined with divergence between price and the MACD indicator, can also provide strong confirmation signals.
Step-by-Step Process for Identifying High-Probability Swing Trade Setups
Identifying a high-probability swing trade involves a systematic approach:
1. Identify a potential trend: Analyze the higher timeframe charts (e.g., daily or weekly) to determine the overall market direction. Look for clear trends, either bullish or bearish.
2. Find support and resistance levels: On lower timeframe charts (e.g., 4-hour or 1-hour), pinpoint key support and resistance levels using price action or indicators.
3. Look for candlestick patterns and chart patterns: Identify potential reversal or continuation patterns that align with the overall trend.
4. Confirm signals with indicators: Use indicators like moving averages, RSI, or MACD to confirm the signals generated by price action and patterns.
5. Manage risk: Determine a stop-loss order to limit potential losses and a take-profit order to secure profits. The stop-loss should be placed below the support level (for long positions) or above the resistance level (for short positions). The take-profit level could be determined by using Fibonacci retracements or other technical analysis tools.
6. Execute the trade: Enter the trade when the price breaks through a support or resistance level, confirmed by the indicators and patterns.
7. Monitor and manage the trade: Continuously monitor the trade and adjust the stop-loss or take-profit orders as needed.
Risk Management in Swing Trading Forex

Swing trading forex offers the potential for significant profits, but it also carries substantial risk. Successfully navigating the forex market as a swing trader hinges not just on identifying profitable opportunities, but crucially, on implementing a robust risk management strategy. Without a disciplined approach to risk, even the most astute trader can quickly find themselves facing substantial losses. This section will delve into the essential aspects of risk management tailored specifically for swing trading in the forex market.
Position Sizing and Stop-Loss Orders
Position sizing and stop-loss orders are the cornerstones of effective risk management in forex swing trading. Position sizing determines how much capital you allocate to each trade, directly influencing your potential profit and loss. A well-defined stop-loss order, on the other hand, limits your potential losses on any given trade by automatically closing your position when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. The interplay between these two elements is critical in ensuring your trading capital remains protected while pursuing potential gains. Ignoring either one significantly increases your risk profile.
Risk Management Techniques in Forex Swing Trading
Several techniques enhance risk management in swing trading. One effective strategy is the use of a fixed fractional position sizing approach. This involves risking a consistent percentage of your trading capital on each trade, regardless of the expected profit. For example, risking only 1% or 2% per trade ensures that a series of losing trades won’t wipe out your account. Another technique involves diversifying your trades across multiple currency pairs, reducing the impact of a single losing trade. Furthermore, using trailing stop-loss orders allows you to lock in profits as the price moves in your favor while simultaneously limiting potential losses if the trend reverses. Finally, maintaining a detailed trading journal meticulously recording each trade, including entry and exit points, profits and losses, and the reasoning behind each decision, provides invaluable insights for refining your risk management strategy over time.
Calculating Appropriate Position Sizes
Calculating appropriate position sizes is crucial for managing risk effectively. A common method involves determining your maximum acceptable loss per trade (often a percentage of your account balance, e.g., 1% or 2%) and then calculating the position size that corresponds to that loss. For instance, if your account balance is $10,000 and your risk tolerance is 1%, your maximum loss per trade is $100. If your stop-loss order is set at 50 pips, then your position size should be calculated as follows:
Position Size = (Maximum Loss per Trade in USD) / (Stop Loss in Pips * Pip Value)
Assuming a pip value of $10 per lot (this varies based on the currency pair and leverage), your position size would be:
Position Size = $100 / (50 pips * $10/lot) = 0.2 lots
This calculation ensures that even if the trade goes against you and hits your stop-loss, your maximum loss remains within your predetermined risk tolerance. Remember to always adjust this calculation based on the specific currency pair, leverage, and your account’s pip value.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Risk Management
Several common mistakes can severely undermine your risk management efforts. Over-leveraging, where you borrow excessive funds to increase your position size, significantly amplifies both profits and losses, potentially leading to substantial losses if trades go against you. Ignoring stop-loss orders, or placing them too far away from your entry point, increases your exposure to significant losses. Failing to diversify your trades by concentrating your capital on a single currency pair or a small number of highly correlated pairs, makes your portfolio vulnerable to significant losses if the market moves against you in those specific areas. Finally, neglecting to keep a detailed trading journal and reviewing your performance regularly prevents you from identifying patterns and improving your risk management strategies over time. Consistent, disciplined adherence to a well-defined risk management plan is crucial for long-term success in swing trading forex.
Swing Trading Strategies and Methods
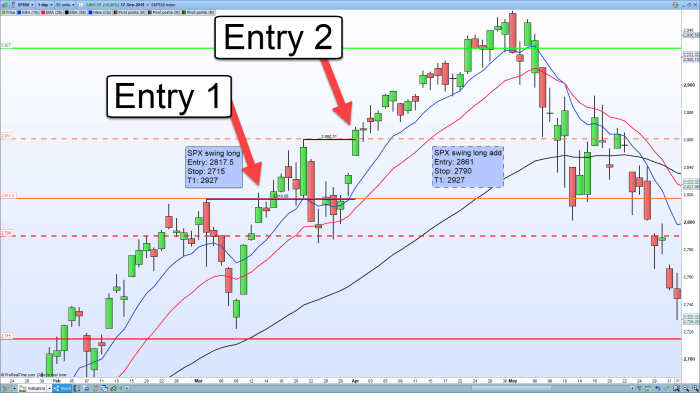
Swing trading forex, at its core, involves capitalizing on price fluctuations over a few days to several weeks. Unlike day trading’s frantic pace, swing trading allows for a more relaxed approach, focusing on identifying and exploiting significant price swings. Choosing the right strategy is crucial for success, and understanding the nuances of each method is key to navigating the forex market effectively.
Trend Following Strategies
Trend following strategies aim to profit from established price trends. Traders using this approach identify a trending market (either uptrend or downtrend) and enter trades in the direction of the trend. They typically use technical indicators like moving averages to confirm the trend’s strength and direction. For example, a trader might use a 20-period and 50-period moving average crossover to signal entry points. A bullish crossover (20-period MA crossing above the 50-period MA) suggests a strengthening uptrend, prompting a long position. Conversely, a bearish crossover signals a potential downtrend, indicating a short position. The key to success here is patience; waiting for clear trend confirmation minimizes false signals and improves risk management.
Mean Reversion Strategies
In contrast to trend following, mean reversion strategies capitalize on the tendency of prices to revert to their average or mean value after temporary deviations. This approach assumes that prices will eventually return to a central point, offering opportunities to buy low and sell high. Common indicators used include the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands. For example, an RSI reading below 30 might signal an oversold condition, suggesting a potential bounce back, while a reading above 70 could indicate an overbought condition, prompting a short position. Bollinger Bands, showing price volatility, can also identify potential reversal points when prices touch the upper or lower bands. Successful mean reversion requires precise timing and an understanding of market dynamics, as not all price deviations revert to the mean.
Using Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are crucial in swing trading. Support represents a price level where buying pressure is expected to outweigh selling pressure, preventing further price declines. Resistance, conversely, is a level where selling pressure is likely to overcome buying pressure, halting price increases. These levels can be identified using previous price highs and lows, trendlines, or technical indicators. Traders often look for price bounces off support levels as potential long entry points and price reversals at resistance levels as potential short entry points. A breakout above resistance or below support can also signal a significant trend change, providing another opportunity for entry. However, it’s important to remember that support and resistance are not guaranteed levels; price can break through them.
Challenges in Implementing Swing Trading Strategies
Implementing swing trading strategies in forex presents several challenges. Market volatility can significantly impact trade outcomes, leading to unexpected losses. Gaps, which occur when the market opens at a price different from the previous close, can trigger stop-loss orders prematurely, resulting in losses even if the overall trend remains favorable. News events and economic announcements can create substantial price swings, making it difficult to predict price movements accurately. Furthermore, managing emotions, such as fear and greed, is crucial; impulsive decisions based on fear or greed can lead to poor trading outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Forex Swing Trading Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Trend Following | Captures large price movements, relatively simple to implement. | Requires patience, susceptible to whipsaws (false signals), late entry may miss significant gains. |
| Mean Reversion | Potentially high returns, can profit from short-term price fluctuations. | Requires precise timing, not all price deviations revert to the mean, risk of losses if the trend continues. |
Trade Execution and Monitoring
Swing trading forex, while potentially lucrative, demands meticulous execution and constant vigilance. Successfully navigating the market requires a disciplined approach to order placement, unwavering monitoring of open positions, and the adaptability to adjust your strategy based on evolving market dynamics. Ignoring these crucial aspects can quickly transform promising trades into significant losses.
Successful trade execution begins with a clear understanding of your trading plan. This isn’t just about identifying entry and exit points; it’s about knowing precisely how and when you’ll place your orders, considering factors like slippage and potential delays. Consistent monitoring allows you to react proactively to market shifts, protecting your profits and minimizing potential damage.
Order Placement and Confirmation
Executing a forex swing trade involves placing an order specifying the currency pair, the trade direction (long or short), the volume (lot size), and the entry price (market or limit order). Confirmation is crucial; you need to verify the order has been successfully placed and is reflected in your trading platform. A confirmation screen or email notification should detail all order parameters. Any discrepancy necessitates immediate action to rectify the issue with your broker. For instance, a misplaced decimal point in your order volume could lead to significantly larger losses than anticipated.
Monitoring Open Positions and Adjusting Trades
Continuous monitoring of open positions is paramount. This involves regularly checking your charts for price action, assessing the validity of your initial trade setup, and monitoring relevant economic news releases. The forex market is dynamic; factors like unexpected geopolitical events or significant economic data releases can drastically impact your trade. If the market moves against your position, you might consider adjusting your stop-loss order to limit potential losses or even closing the position entirely if your initial assumptions prove invalid. Consider, for example, a long position in EUR/USD based on positive economic indicators. If a sudden negative news report emerges about the Eurozone economy, you might need to adjust your stop-loss or consider closing the position to prevent significant losses.
Managing Trades Based on Changing Market Conditions
Adaptability is key. Sticking rigidly to a plan in the face of drastically changing market conditions is a recipe for disaster. Effective trade management involves analyzing the market’s reaction to news events, technical indicators, and overall market sentiment. Let’s say you’re in a long position in GBP/USD, anticipating a positive economic outlook for the UK. However, if the market shows a persistent downward trend despite your initial expectations, you might decide to trail your stop-loss order to lock in profits or even cut your losses to avoid further declines. Alternatively, if the market is showing unexpected strength, you could consider adjusting your take-profit level to capture greater potential gains.
Maintaining a Trading Journal
A meticulously kept trading journal is invaluable for improving your trading performance. This journal should detail every trade, including entry and exit points, reasons for entering and exiting the trade, the outcome (profit or loss), and any lessons learned. This detailed record allows you to identify patterns in your successes and failures, helping you refine your strategy and avoid repeating mistakes. For example, consistently losing trades on a specific currency pair might indicate a need to improve your analysis of that pair, or perhaps avoid it altogether. Regular review of your journal allows for continuous self-improvement and adaptation of your trading approach.
Psychological Aspects of Swing Trading: Swing Trading Forex
Swing trading forex, while potentially lucrative, is a rollercoaster ride for your emotions. Success hinges not just on technical analysis and strategy, but crucially, on your ability to manage the psychological pressures inherent in the market. Ignoring the mental game can lead to costly mistakes, even with the best trading plan in place.
Discipline and Emotional Control in Swing Trading
Discipline and emotional control are the cornerstones of successful swing trading. They prevent impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed, which often lead to losses. A disciplined trader sticks to their pre-defined strategy, resisting the urge to deviate based on short-term market fluctuations or emotional reactions to news events. Emotional control involves maintaining a calm and objective perspective, even during periods of significant market volatility or personal setbacks. This requires consistent self-awareness and the ability to manage stress effectively. A trader who can detach their emotions from their trading decisions is far more likely to achieve long-term success.
Common Psychological Biases Affecting Trading Decisions
Several psychological biases can significantly impact trading decisions. Confirmation bias, for instance, leads traders to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs, ignoring contradictory evidence. This can result in holding onto losing trades for too long or entering trades based on incomplete or biased information. Overconfidence bias, on the other hand, can lead to excessive risk-taking and neglecting proper risk management protocols. Similarly, herd behavior, the tendency to follow the crowd, can cause traders to make irrational decisions based on popular sentiment rather than their own analysis. These biases, if unchecked, can systematically erode trading profits.
Strategies for Managing Emotions and Avoiding Impulsive Trading
Managing emotions requires a multifaceted approach. Developing a robust trading plan with clear entry and exit rules is paramount. This plan should be followed meticulously, regardless of emotional urges. Maintaining a trading journal to track trades, including emotional states during decision-making, can provide valuable insights into personal biases and help identify areas for improvement. Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help center the mind and reduce stress levels during periods of market uncertainty. Furthermore, setting realistic profit targets and accepting losses as part of the trading process can help manage expectations and prevent emotional overreactions. Finally, taking regular breaks from trading to avoid emotional fatigue is crucial for maintaining a clear and objective perspective.
Tips for Maintaining a Positive Trading Mindset
Maintaining a positive trading mindset is crucial for long-term success. This involves focusing on continuous learning and improvement, seeking feedback from experienced traders, and celebrating small wins along the way. It’s also essential to maintain a healthy work-life balance, avoiding over-trading and burnout. Regularly reviewing past trades to identify areas for improvement, rather than dwelling on losses, is a vital part of this process. Finally, building a supportive community of like-minded traders can provide encouragement and accountability, fostering a positive and constructive trading environment. Remember, trading is a marathon, not a sprint, and maintaining a positive and resilient mindset is key to navigating the inevitable challenges.
Illustrative Example of a Forex Swing Trade
Let’s dive into a hypothetical swing trade scenario to illustrate the practical application of the strategies we’ve discussed. This example focuses on the EUR/USD pair, a highly liquid and popular currency pair among swing traders. Remember, past performance is not indicative of future results. This is purely for educational purposes.
Trade Setup: Identifying the Opportunity, Swing trading forex
Our hypothetical trade begins with identifying a potential swing trading opportunity on the EUR/USD pair. We observe a clear bearish head and shoulders pattern forming on the daily chart. This pattern, often indicating a price reversal, is accompanied by a bearish divergence on the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator. The RSI, typically ranging from 0 to 100, shows momentum; a bearish divergence occurs when the price makes higher highs, but the RSI makes lower highs, suggesting weakening bullish momentum. This combination signals a potential short-selling opportunity.
Entry Point and Rationale
The right shoulder of the head and shoulders pattern provides our entry point. We wait for a decisive break below the neckline support level, confirming the pattern’s validity. This break is also confirmed by a bearish candlestick pattern, such as an engulfing candle or a shooting star, adding further confidence to our entry. We place our short order just below the neckline, aiming for a favorable risk-reward ratio. Our rationale is based on the confluence of the bearish head and shoulders pattern, the bearish RSI divergence, and the confirmation provided by the candlestick pattern.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
To manage risk, we place a stop-loss order above the recent swing high, just above the right shoulder of the head and shoulders pattern. This stop-loss level limits our potential losses if the trade moves against us. Our take-profit level is determined using a combination of technical analysis and risk management principles. We target a profit level that is at least twice the size of our potential stop-loss, aiming for a favorable risk-reward ratio of 2:1 or better. Specifically, we identify a key support level further down the chart, representing a potential price target for our short trade.
Trade Monitoring and Exit Strategy
After entering the trade, we monitor the position closely. We pay attention to the price action, looking for any signs of reversal or significant changes in market sentiment. If the price moves significantly against our position, we may consider adjusting our stop-loss to protect our capital. If the price reaches our predetermined take-profit level, we close the position and secure our profits. We might also consider trailing our stop-loss order as the trade moves in our favor, locking in profits and protecting against potential reversals.
Chart Pattern and Indicator Details
The head and shoulders pattern is a classic reversal pattern characterized by three peaks (the head and two shoulders) and a neckline. A break below the neckline is considered a bearish signal. The RSI is a momentum oscillator used to identify overbought and oversold conditions. Bearish divergence, as mentioned, occurs when the price makes higher highs, but the RSI makes lower highs, indicating weakening bullish momentum. The candlestick patterns, like engulfing candles or shooting stars, provide additional confirmation of the price action. These indicators, when used in conjunction, enhance the accuracy and confidence of our trade setup.
Conclusion
Swing trading forex isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme, but with the right knowledge, strategy, and discipline, it can be a powerful tool for building wealth. Mastering technical analysis, implementing robust risk management, and cultivating emotional control are all key ingredients to success. This journey requires dedication and consistent learning, but the potential rewards—and the thrill of the ride—make it well worth the effort. So buckle up, and let’s conquer the forex markets!
Find out about how trading cfd forex can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Finish your research with information from forex trading mentors.




