Best time for forex trading? It’s not just about luck; it’s about strategy. Understanding global market overlaps, economic news cycles, and even your own energy levels can dramatically impact your trading success. This isn’t some get-rich-quick scheme; it’s about mastering the rhythm of the forex market to find your edge. We’ll break down the optimal trading times, considering volatility, liquidity, and the psychological factors that often get overlooked.
From the bustling London open to the quieter Asian sessions, we’ll explore how different market timings affect currency pairs. We’ll delve into how major economic news releases can create both high-risk, high-reward scenarios and how to navigate them strategically. Prepare to learn how to harness the power of market timing to boost your forex game.
Global Market Openings and Closings: Best Time For Forex Trading
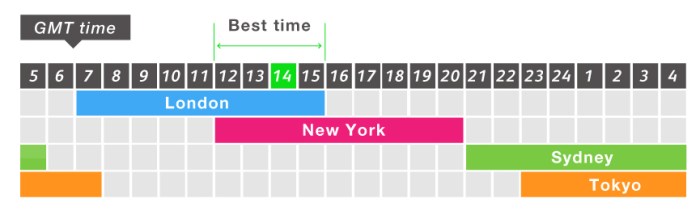
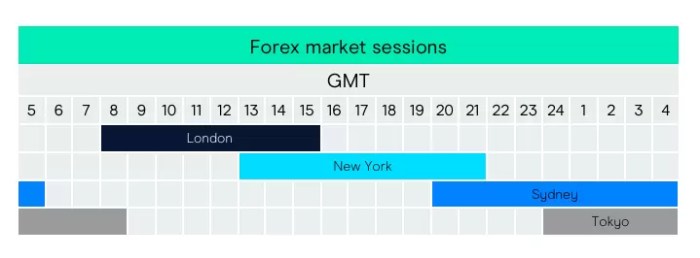
Navigating the forex market successfully hinges on understanding its global nature. Trading isn’t confined to a single time zone; it’s a 24-hour operation, driven by the sequential opening and closing of major financial centers around the world. Knowing when these markets are most active is crucial for maximizing trading opportunities and managing risk.
The overlapping sessions of these major forex markets create periods of high liquidity and volatility, influencing trading strategies and price movements. Let’s break down the opening and closing times of the key players.
Major Forex Market Session Overlaps
The forex market is a global network, and its activity isn’t limited to a single time zone. Instead, trading activity shifts across different geographical locations as their markets open and close. This creates periods of overlap, significantly impacting liquidity and volatility. When multiple major markets are open simultaneously, the volume of trades increases dramatically, leading to higher liquidity. This increased liquidity generally makes it easier to execute trades at favorable prices. However, it also means that price movements can be more rapid and unpredictable, increasing volatility. Conversely, when only one or two major markets are open, liquidity tends to be lower, and price movements are often less dramatic.
Market Session Timing Comparison
The following table shows the approximate opening and closing times for the major forex markets (Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York) in different time zones. Remember that these are approximate times, and slight variations can occur. It’s always best to consult a reliable forex trading platform for the most up-to-date information.
| Market | GMT | EST | AEST |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney | 22:00 – 05:00 | 14:00 – 21:00 | 00:00 – 17:00 |
| Tokyo | 23:00 – 04:00 | 15:00 – 20:00 | 01:00 – 18:00 |
| London | 08:00 – 17:00 | 03:00 – 12:00 | 13:00 – 22:00 |
| New York | 13:00 – 22:00 | 08:00 – 17:00 | 14:00 – 23:00 |
Economic News Releases and Trading

Economic news releases, particularly those of high impact, can significantly alter the forex market’s landscape. Understanding their influence is crucial for navigating the complexities of currency trading and maximizing profit potential while minimizing risk. These announcements often trigger dramatic price swings, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traders.
Major economic indicators, like Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), Consumer Price Index (CPI), and central bank interest rate decisions, wield considerable power over currency values. Their release times are highly anticipated, creating periods of heightened volatility that savvy traders can exploit or carefully avoid depending on their risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Impact of Major Economic News Announcements on Forex Prices
The impact of major economic news announcements on forex prices is often immediate and dramatic. For example, a surprisingly strong NFP report, indicating robust job growth, might strengthen a nation’s currency as it suggests a healthy economy and potential for future interest rate hikes. Conversely, weaker-than-expected CPI data, suggesting lower inflation, could lead to a currency weakening, as it might signal a less robust economy and potentially lower interest rates. Interest rate decisions themselves have an even more direct and often amplified effect; an unexpected increase in interest rates typically strengthens the associated currency as it makes holding that currency more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. The magnitude of the price movement depends on several factors, including the extent of the surprise, market expectations, and the overall global economic climate. A significant deviation from forecasts can result in sharp and sudden price changes.
Identifying Periods of High Volatility Surrounding News Releases
Identifying periods of high volatility is relatively straightforward. Economic calendars, readily available from numerous financial websites, precisely pinpoint the release times of major economic indicators. The period immediately surrounding these releases, typically within 30 minutes to an hour before and after, is usually characterized by increased volatility. Traders can also observe increased trading volume and wider bid-ask spreads as a visual indicator of heightened market activity. Experienced traders often monitor the market’s behavior in the hours leading up to the release to gauge the prevailing sentiment and anticipate the potential direction of price movements.
Strategies for Managing Risk During Periods of High Volatility
Managing risk during periods of high volatility requires a disciplined approach. One effective strategy is to avoid trading altogether during the most volatile periods. This “wait-and-see” approach minimizes the chances of experiencing significant losses due to unpredictable price swings. Alternatively, traders can employ tighter stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. A stop-loss order automatically closes a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, protecting against substantial losses. Another strategy involves reducing position size, thereby limiting exposure to market fluctuations. Finally, careful analysis of market sentiment and economic forecasts can help traders anticipate the likely direction of price movements, allowing them to adjust their trading strategies accordingly. Diversification across different currency pairs can also mitigate risk.
Volatility and Trading Opportunities
Forex trading success hinges significantly on understanding and leveraging market volatility. Volatility, simply put, refers to the rate at which a currency pair’s price fluctuates. Higher volatility means bigger price swings, presenting both greater profit potential and increased risk. Conversely, lower volatility implies smaller price movements, potentially leading to slower, steadier gains but reduced risk. Knowing when volatility is high or low is key to strategic trading.
Understanding the relationship between time of day and volatility is crucial for maximizing trading opportunities. Different currency pairs exhibit varying volatility levels throughout the day, influenced by overlapping trading sessions across different global financial centers.
Volatility Across Currency Pairs and Timeframes, Best time for forex trading
The volatility of a currency pair depends on several factors, including economic news releases, geopolitical events, and the overall market sentiment. Generally, major currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD tend to be more volatile than minor or exotic pairs. However, even within these major pairs, volatility fluctuates throughout the day.
The period encompassing the overlap of major trading sessions—typically between 8:00 AM and 12:00 PM GMT—often displays the highest volatility. This is because traders from London, New York, and other centers are simultaneously active, creating a surge in trading volume and price action. Conversely, periods outside these peak hours, such as early morning in London or late night in New York, usually experience lower volatility. The specific times of heightened or diminished volatility can shift slightly based on economic calendar events. For example, the release of significant economic data, like Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) figures in the US, can cause temporary spikes in volatility across multiple currency pairs regardless of the time of day.
Typical Daily Volatility Pattern for EUR/USD
Imagine a graph charting the EUR/USD exchange rate over a 24-hour period. The x-axis represents time (in GMT), and the y-axis represents the EUR/USD price. The graph would illustrate a relatively calm period during the early Asian trading hours (around midnight to 8:00 AM GMT). As the London session begins (around 8:00 AM GMT), volatility would start to increase gradually. The highest volatility would be observed during the overlap of the London and New York sessions (approximately 8:00 AM to 12:00 PM GMT), represented by a steeper, more erratic line on the graph. This period shows a wider range of price fluctuations. As the New York session closes and the trading activity diminishes, volatility would decrease again during the late afternoon and evening (12:00 PM to midnight GMT), shown as a smoother, less dramatic line on the graph. This pattern isn’t absolute; significant news events can dramatically alter this typical curve. For instance, a surprise interest rate announcement could cause a sharp spike in volatility at any time of day, resulting in a dramatic peak on the graph outside of the usual high-volatility period.
Liquidity and Order Execution
Navigating the forex market successfully hinges on understanding liquidity and its impact on order execution. Liquidity, simply put, refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. This is crucial because variations in liquidity directly affect how quickly and efficiently your trades are filled, and at what price.
Liquidity varies dramatically throughout the forex trading day, mirroring the ebb and flow of global market activity. This fluctuation is primarily driven by the opening and closing times of major financial centers, as trading volume and the number of market participants change accordingly. The interplay between liquidity, slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price), and order execution speed is a key factor in determining profitability.
Liquidity Variation Throughout the Trading Day
Liquidity is generally highest during the overlapping trading hours of major financial centers. For example, when London and New York markets are both open, the volume of trades is significantly higher, leading to greater liquidity. Conversely, during periods when major markets are closed, liquidity tends to be lower, making it harder to execute large orders without significant price impact. The quietest periods often occur during the Asian overnight sessions before the European markets open. Consider the example of a trader attempting to execute a large order during the Asian session versus during the London/New York overlap: the Asian session might see increased slippage and a slower execution speed compared to the busier period when multiple major centers are open. This difference can directly affect the profitability of the trade.
Relationship Between Liquidity, Slippage, and Order Execution Speed
The relationship between liquidity, slippage, and order execution speed is inversely proportional. In highly liquid markets, orders are executed quickly and at prices close to the quoted price, resulting in minimal slippage. Conversely, in illiquid markets, the execution speed slows down, and slippage increases as the market struggles to absorb large orders without significant price movement. For instance, a large buy order in an illiquid market might push the price up significantly before the order is fully filled, resulting in a less favorable execution price than anticipated. This highlights the importance of understanding liquidity levels when placing trades, especially larger ones. A trader needs to be aware of the potential for increased slippage in less liquid markets and adjust their trading strategy accordingly, perhaps by using limit orders or reducing order size.
Order Execution Process at Different Times of Day
The following flowchart illustrates the order execution process considering varying liquidity levels throughout the trading day:
[Descriptive Flowchart]
Imagine a flowchart with three main branches representing different times of day: High Liquidity (London/New York overlap), Medium Liquidity (European session only), and Low Liquidity (Asian overnight session). Each branch shows a simplified process:
* High Liquidity: Order placed -> Order routed to multiple liquidity providers -> Immediate execution at or near quoted price -> Minimal slippage.
* Medium Liquidity: Order placed -> Order routed to fewer liquidity providers -> Execution within a few seconds to minutes -> Potential for slight slippage.
* Low Liquidity: Order placed -> Order routed to limited liquidity providers -> Execution may take longer (minutes to hours) -> Potential for significant slippage or partial fills.
This flowchart visually represents how the speed and efficiency of order execution, along with the degree of slippage, directly relate to the prevailing liquidity conditions at different points in the trading day. Understanding this dynamic is key to successful forex trading.
Trading Strategies and Best Times
Forex trading offers a diverse landscape of strategies, each with its own optimal timeframe and risk profile. Choosing the right strategy depends heavily on your trading goals, risk tolerance, and understanding of market dynamics. Successfully navigating this landscape requires a keen awareness of how different strategies align with specific market conditions throughout the trading day.
The best time to trade often hinges on the chosen strategy. High-volatility periods, usually coinciding with market openings, are attractive to some, while others prefer the calmer waters of the midday session. Understanding this relationship is key to consistent profitability.
Forex Trading Strategy Comparison
Let’s examine three popular forex trading strategies: scalping, day trading, and swing trading. Each demands a different approach and timing to maximize potential gains.
- Scalping: This high-frequency strategy involves holding positions for very short periods, often just seconds or minutes, to capitalize on small price movements. Scalpers typically target highly liquid currency pairs during periods of high volatility, such as the London and New York market overlaps. The risk is high due to the speed and frequency of trades, but the potential for small, quick profits is also significant. A successful scalper needs lightning-fast reflexes and a robust trading platform.
- Day Trading: Day traders open and close positions within a single trading day. They aim to profit from intraday price fluctuations, often employing technical analysis to identify short-term trends. Optimal times for day trading often align with major market openings (London, New York) when volatility is relatively high and liquidity is ample. Risk is moderate, depending on position sizing and risk management techniques. Day trading requires a good understanding of technical indicators and chart patterns.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days or even weeks, capitalizing on larger price swings. They may use a combination of fundamental and technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. Swing trading is less time-intensive than scalping or day trading, and the risk profile is generally lower. Successful swing trading relies on accurate market analysis and patience. Optimal times are less critical as the timeframe is longer, focusing instead on identifying trends that can sustain for several days.
Trading Strategy Timeframes and Risk Profiles
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of each strategy, highlighting their suitable timeframes and associated risk levels.
Investigate the pros of accepting forex trading alerts in your business strategies.
| Strategy | Timeframe | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Scalping | Seconds to minutes | High |
| Day Trading | Minutes to hours | Moderate |
| Swing Trading | Days to weeks | Low |
Adapting Strategies to Market Conditions
The effectiveness of a trading strategy is heavily influenced by market conditions. For example, a scalping strategy might be highly profitable during periods of high volatility, such as the overlap of the London and New York sessions. However, during quieter periods, the same strategy might yield minimal returns. Conversely, a swing trading strategy, which relies on longer-term trends, might be less successful during highly volatile periods.
Notice trading cfd forex for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Adaptability is crucial. A skilled trader might switch between strategies depending on the market’s behavior. For instance, during a period of low volatility, a day trader might shift to a swing trading approach, focusing on longer-term trends rather than short-term price fluctuations. This adaptability ensures that the trader can capitalize on market conditions regardless of the overall volatility.
Technical Analysis and Time of Day
Technical analysis, the art of predicting future price movements based on past market data, isn’t immune to the rhythm of the trading day. Market conditions fluctuate dramatically throughout the 24-hour forex cycle, influencing the reliability and effectiveness of various technical indicators. Understanding these fluctuations is crucial for optimizing your trading strategy and maximizing your chances of success.
The performance of technical indicators is directly impacted by the ebb and flow of liquidity and volatility across different trading sessions. For instance, a breakout signal generated during the quiet Asian session might be less reliable than a similar signal during the more volatile London or New York sessions. Similarly, the accuracy of moving averages can be affected by the volume of trading activity; during periods of low liquidity, a moving average might lag significantly behind actual price movements.
Time Zones and Technical Analysis
Ignoring time zones when applying technical analysis is akin to navigating with a faulty compass. Forex markets are global, operating across multiple time zones. A candlestick pattern appearing bullish in one time zone might simultaneously be interpreted as bearish in another due to differing market pressures and liquidity levels. A trader analyzing charts using their local time might miss crucial signals that emerge during the peak trading hours of other major financial centers. For example, a strong bullish candlestick pattern forming during the early hours of the Asian session might be overlooked by a trader primarily focused on the London or New York sessions, potentially leading to missed opportunities. Conversely, a seemingly bearish pattern might appear during the quieter Asian session, prompting a premature exit from a profitable trade.
Candlestick Patterns and Liquidity
Candlestick patterns, often relied upon by technical traders, can exhibit different characteristics depending on market liquidity. A classic engulfing pattern, for instance, might signal a significant reversal during a high-liquidity period like the overlap between the London and New York sessions. However, the same pattern emerging during the relatively quiet Tokyo session might hold less predictive power, potentially representing a temporary fluctuation rather than a major trend reversal. Similarly, hammer and hanging man candlestick patterns, typically used to identify potential reversals, might be less reliable during low-liquidity periods where price movements can be influenced by smaller order flows. The lack of substantial trading volume can make it difficult to confirm the significance of these patterns.
Moving Averages and Volatility
Moving averages, commonly used to smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends, are also influenced by the time of day and associated volatility levels. During periods of high volatility, such as the overlap of major trading sessions, moving averages can be less effective in providing clear signals. The rapid price swings can cause the moving average to lag behind the current price action, leading to delayed or inaccurate signals. Conversely, during quieter periods with lower volatility, moving averages can provide more reliable trend indications, allowing for smoother entry and exit points. For example, a 20-day moving average might accurately reflect the underlying trend during the Asian session, while the same average might be significantly less informative during the highly volatile London open.
Psychological Factors and Trading Performance
The forex market is a relentless test of not just your trading strategy, but also your mental fortitude. While technical analysis and market knowledge are crucial, understanding and managing your own psychological biases is arguably the key differentiator between consistent profitability and frustrating losses. Your emotional state significantly impacts your decision-making, often leading to impulsive trades and poor risk management. Ignoring this aspect is like sailing a ship without a compass – you might reach your destination, but the journey will be significantly riskier and less efficient.
Successful forex trading requires a disciplined approach to managing emotions and mitigating the impact of psychological biases that frequently arise throughout the trading day. These biases can subtly undermine even the most well-researched strategies, leading to costly errors. Recognizing these patterns and proactively implementing strategies to counteract them is essential for long-term success.
Common Psychological Biases in Forex Trading
The forex market, with its constant fluctuations and high-stakes environment, can trigger a range of psychological biases. These biases often manifest differently depending on the time of day, influenced by factors like fatigue and stress levels. For example, early morning trading might be affected by pre-market anxieties, while late-day trading could suffer from decision fatigue. Understanding these biases is the first step towards overcoming them.
Strategies for Managing Psychological Biases
Effective strategies for managing these biases involve a combination of self-awareness, proactive planning, and disciplined execution. This includes maintaining a detailed trading journal to track not only trades but also the emotional state during those trades. Identifying patterns and triggers can be incredibly valuable in anticipating and mitigating future emotional reactions. Another key strategy is establishing a strict risk management plan and adhering to it rigorously. This prevents emotional decisions driven by fear or greed from derailing your trading strategy. Finally, regular self-reflection and seeking feedback from mentors or peers can help identify blind spots and develop a more objective perspective on your trading performance.
Optimizing Trading Schedules for Personal Well-being
The best time to trade forex isn’t necessarily the time with the highest volatility, but the time when you are most alert, focused, and emotionally stable. Consider your personal chronotype – are you a morning person or a night owl? Scheduling your trading sessions around your peak cognitive function will significantly improve your performance. For example, a night owl might find that their best trading is done in the late evening, when the European markets are open and they feel most energized. Conversely, a morning person might prefer to focus their trading during the Asian market open. This personalized approach to scheduling maximizes your trading effectiveness while prioritizing your mental well-being. Avoid trading when you are overly tired, stressed, or emotionally overwhelmed; it’s better to take a break and return when you are in a more optimal state.
Concluding Remarks
Ultimately, the best time for forex trading isn’t a single magic hour, but a strategic understanding of market dynamics. By combining knowledge of global market openings, economic news cycles, and your own trading style, you can significantly improve your chances of success. Remember, consistency, risk management, and understanding your own psychological tendencies are just as crucial as picking the right time to trade. So, dive in, learn the rhythms of the forex market, and start making smarter trading decisions.




