Forex trading strategies for beginners: Dive into the exciting world of currency trading! This isn’t your grandpa’s investment – it’s a fast-paced, globally connected market where you can potentially profit from currency fluctuations. But before you jump in headfirst, understanding the basics is key. We’ll break down essential strategies, risk management techniques, and the importance of practice, guiding you through the steps to navigate this thrilling yet challenging market.
From grasping currency pairs and order types to mastering technical and fundamental analysis, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. We’ll also explore the crucial role of demo accounts in honing your skills before risking real capital. Get ready to unlock the potential of forex trading – responsibly and strategically.
Understanding the Forex Market
So, you’re diving into the world of forex trading? Awesome! It’s a thrilling market, but understanding the basics is crucial before you even think about placing a trade. Think of it like learning the rules of a game before you start playing – you wouldn’t want to get penalized for not knowing the basics, right? This section will break down the essentials, making the forex market less intimidating and more accessible.
Currency Pairs and Their Mechanics
The forex market, or foreign exchange market, is where currencies are traded against each other. These trades happen in pairs, like EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). The first currency in the pair is called the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency. For example, if EUR/USD is 1.10, it means you need $1.10 to buy €1. These rates are constantly fluctuating, creating opportunities (and risks!) for traders.
Factors Influencing Forex Prices
Numerous factors influence forex prices, making it a dynamic and sometimes unpredictable market. Think of it as a giant scale constantly balancing various economic forces. These include: global economic news (like interest rate announcements or employment data), political events (elections, policy changes), market sentiment (overall optimism or pessimism), and even natural disasters. Understanding these influences is key to making informed trading decisions. For instance, positive economic news about a country usually boosts its currency’s value relative to others.
Forex Order Types
Before you jump in and start trading, you need to understand the different types of orders you can place. Choosing the right order type is vital for managing your risk and achieving your trading goals. There are several types, but we’ll focus on the two most common: market orders and limit orders.
Market Orders vs. Limit Orders
| Feature | Market Order | Limit Order |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Executed immediately at the best available market price. | Executed only when the price reaches your specified level. |
| Price | Price is determined by the market at the time of order placement. | You set the price at which you want to buy or sell. |
| Speed | Fast execution, but price may not be ideal. | Slower execution, but you control the price. |
| Risk | Higher risk of slippage (price difference between expected and executed price). | Lower risk of slippage, but order may not be filled. |
Essential Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
Forex trading can seem daunting, but mastering a few core strategies can pave the way for consistent profitability. Remember, success in forex trading requires discipline, patience, and a well-defined strategy. Don’t jump into the market without a plan – treat it like any other serious investment.
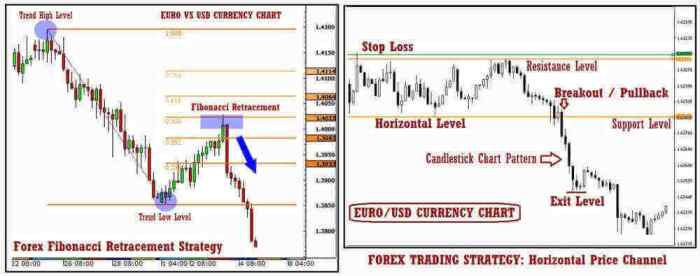
Trend Following
Trend following, also known as momentum trading, involves identifying and capitalizing on established price trends. This strategy leverages the simple observation that prices tend to move in a particular direction for a period of time. The longer a trend persists, the greater the potential profit.
Advantages of trend following include its relative simplicity and the potential for significant gains during strong trends. Disadvantages include the risk of missing out on short-term opportunities and the possibility of substantial losses if the trend reverses unexpectedly. False breakouts can also lead to unnecessary trades.
Investigate the pros of accepting forex trading signal in your business strategies.
Range Trading
Range trading focuses on profiting from price fluctuations within a defined range. This strategy works best in sideways markets, where the price oscillates between support and resistance levels without exhibiting a clear trend.
Advantages include lower risk compared to trend following, as stop-loss orders can be set relatively close to the entry price. Disadvantages include limited profit potential compared to trend following and the potential for losses if the price breaks out of the established range. Precise identification of support and resistance levels is crucial.
Obtain access to forex trading alerts to private resources that are additional.
Scalping
Scalping involves taking many small profits from quick price movements. This high-frequency trading strategy requires rapid decision-making and a deep understanding of market dynamics. Traders aim for small gains on each trade, relying on volume to generate overall profit.
Advantages include the potential for quick profits and the ability to react to short-term market fluctuations. Disadvantages include the high stress levels associated with rapid trading, high transaction costs, and the risk of significant losses if even a few trades go against the trader. This strategy demands speed, precision, and exceptional market knowledge.
Step-by-Step Guide: Implementing a Trend Following Strategy
We’ll Artikel a simplified trend-following strategy using moving averages.
- Identify the Trend: Use a longer-term moving average (e.g., 200-period) to establish the overall trend. A price consistently above the 200-period MA suggests an uptrend, while a price consistently below suggests a downtrend.
- Confirm the Trend: Use a shorter-term moving average (e.g., 50-period) as confirmation. In an uptrend, the 50-period MA should be above the 200-period MA. In a downtrend, the opposite is true.
- Enter the Trade: Enter a long position (buy) when the price crosses above the 50-period MA during an uptrend, or a short position (sell) when the price crosses below the 50-period MA during a downtrend.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Place a stop-loss order to limit potential losses and a take-profit order to secure profits. These levels should be based on your risk tolerance and the perceived strength of the trend.
- Monitor and Manage the Trade: Regularly monitor the trade and adjust your stop-loss or take-profit orders as needed. Consider trailing your stop-loss to lock in profits as the trend progresses.
Using Technical Indicators with Trend Following
Moving averages are just one tool. Other indicators can enhance this strategy. For instance, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can help identify overbought or oversold conditions, providing potential entry or exit signals. A high RSI value (above 70) might suggest a potential pullback in an uptrend, while a low RSI value (below 30) might indicate a potential bounce in a downtrend. Remember, these are just supplementary tools, not guarantees. Always combine multiple indicators and consider overall market context.
Risk Management in Forex Trading

Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Success isn’t just about finding profitable strategies; it’s about safeguarding your capital and ensuring longevity in the market. Effective risk management isn’t about avoiding losses entirely – it’s about controlling them, ensuring that any setbacks don’t wipe out your trading account. This section explores crucial risk management techniques essential for beginners.
Position Sizing in Forex Trading
Position sizing is the cornerstone of effective risk management. It dictates how much capital you allocate to each trade, directly impacting your potential profit and loss. Failing to properly size your positions can lead to devastating losses, even with a winning strategy. A crucial aspect of position sizing is determining your risk tolerance – how much of your trading capital are you comfortable losing on a single trade? A common guideline is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total capital per trade. For example, with a $10,000 account, risking 1% equates to a maximum loss of $100 per trade. This approach limits potential damage and allows for consistent trading even during periods of drawdown. Calculating the appropriate position size involves understanding your stop-loss order (discussed below) and the pip value of your currency pair.
Common Forex Trading Mistakes Beginners Make
Beginners often fall prey to several pitfalls that significantly hinder their trading success and amplify risk. Overtrading, driven by impatience and a desire for quick profits, is a common mistake. This leads to emotional decisions and poor risk management. Another prevalent error is neglecting to use stop-loss orders, leaving trades open to unlimited losses. Ignoring market analysis and relying solely on gut feeling or tips from others also contributes to poor risk management. Finally, failing to adapt strategies to changing market conditions and neglecting proper money management are common mistakes that can lead to significant losses. For example, a beginner might enter multiple trades simultaneously without considering their overall risk exposure, leading to a rapid depletion of capital if several trades go against their predictions.
Effective Risk Management Techniques
Several techniques can significantly enhance your risk management. Using stop-loss orders is paramount; these automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. Take-profit orders, conversely, automatically close a trade when it reaches a predetermined profit target, securing gains. Diversification across multiple currency pairs and trading strategies can reduce the impact of losses in any single trade. Regularly reviewing your trading journal, documenting trades, and analyzing both successes and failures, is crucial for identifying patterns and improving your risk management approach. Backtesting strategies on historical data before using them with real money is another effective technique to assess their viability and potential risks. Finally, maintaining a trading plan, outlining your risk tolerance, position sizing strategy, and trading rules, helps enforce discipline and consistency.
Risk Management Tools and Applications
| Tool | Application | Example | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stop-Loss Order | Limits potential losses on a trade. | Setting a stop-loss at 50 pips below your entry price. | Prevents significant drawdowns. |
| Take-Profit Order | Secures profits when a trade reaches a target price. | Setting a take-profit at 100 pips above your entry price. | Locks in gains and prevents profit erosion. |
| Position Sizing Calculator | Determines the appropriate lot size based on risk tolerance and stop-loss. | Using a calculator to determine a lot size that risks 1% of capital per trade. | Ensures consistent risk per trade. |
| Trading Journal | Tracks trades, analyzes performance, and identifies areas for improvement. | Recording entry/exit prices, reasons for trades, and resulting profits/losses. | Improves decision-making and risk management over time. |
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading: Forex Trading Strategies For Beginners
Understanding the forces that drive currency movements is crucial for successful forex trading. Fundamental analysis helps you do just that, by examining the economic factors influencing a currency’s value. Instead of focusing solely on price charts, fundamental analysis delves into the economic health and political stability of countries, allowing you to anticipate potential shifts in exchange rates.
The Role of Economic News and Events
Economic news and global events are the lifeblood of fundamental analysis. Significant announcements, such as interest rate decisions by central banks, inflation reports, employment data, and geopolitical shifts, can dramatically impact currency values. For instance, unexpectedly high inflation might weaken a currency as investors seek assets in stronger economies. Conversely, positive economic news, such as strong employment figures, can boost investor confidence and strengthen the related currency. These events create volatility, providing opportunities for savvy traders to profit from anticipated market reactions.
Interpreting Key Economic Indicators
Several key economic indicators are closely watched by forex traders. Understanding these indicators and their implications is essential.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures a country’s overall economic output. A strong GDP growth rate usually strengthens the country’s currency.
- Inflation Rate: This measures the rate at which prices are rising. High inflation typically weakens a currency as it erodes purchasing power.
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates to control inflation and economic growth. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency.
- Unemployment Rate: A low unemployment rate indicates a strong economy, usually supporting a stronger currency.
- Trade Balance: This reflects the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) generally strengthens the currency.
For example, if the US Federal Reserve unexpectedly raises interest rates, the US dollar (USD) is likely to appreciate against other currencies because higher interest rates attract foreign investment seeking higher returns. Conversely, a surprise announcement of lower-than-expected GDP growth in Japan might cause the Japanese yen (JPY) to depreciate.
Using Fundamental Analysis to Predict Currency Movements
Fundamental analysis doesn’t offer guaranteed predictions, but it provides a framework for informed decision-making. By carefully analyzing economic indicators and news events, traders can form reasoned expectations about future currency movements.
For example, if you anticipate that the European Central Bank (ECB) will raise interest rates, you might consider buying the Euro (EUR) against a currency with a lower expected interest rate, anticipating the EUR’s appreciation. However, remember that unforeseen events can always impact market sentiment and lead to unexpected price movements.
Steps to Perform Fundamental Analysis
Before initiating a trade based on fundamental analysis, a structured approach is recommended.
- Identify Key Economic Indicators: Determine which indicators are most relevant to the currency pairs you’re interested in trading.
- Gather Data: Collect data from reliable sources such as central banks, financial news websites, and economic forecasting agencies.
- Analyze the Data: Interpret the data, considering the historical context and potential market reactions.
- Assess Market Sentiment: Gauge investor sentiment through news articles, analyst reports, and social media.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Based on your analysis, define your entry and exit points, stop-loss orders, and risk tolerance.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitor economic news and adjust your strategy as needed.
Remember, fundamental analysis is just one piece of the puzzle. Combining it with technical analysis and effective risk management can significantly improve your forex trading success.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Unlocking the secrets of the forex market often involves deciphering its price movements. Technical analysis provides a framework for doing just that, focusing on historical price and volume data to predict future trends. Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines economic factors, technical analysis uses charts and indicators to identify patterns and potential trading opportunities. This approach, while not foolproof, can be a powerful tool in a trader’s arsenal when used correctly and in conjunction with other forms of analysis.
Common Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on price and volume data, designed to simplify complex price action and highlight potential buy or sell signals. Understanding these indicators is crucial for interpreting charts and making informed trading decisions. Misinterpreting these signals, however, can lead to losses.
- Moving Averages: These smooth out price fluctuations, revealing underlying trends. A simple moving average (SMA) averages the closing prices over a specified period, while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. A bullish crossover occurs when a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer-term moving average, suggesting a potential uptrend. Conversely, a bearish crossover signals a potential downtrend. For example, a 50-day SMA crossing above a 200-day SMA is often considered a strong bullish signal.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This momentum indicator measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. RSI values above 70 are generally considered overbought, suggesting a potential price correction, while values below 30 indicate oversold conditions, hinting at a possible price reversal. However, RSI can also generate false signals, especially in strong trends.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): This trend-following momentum indicator uses moving averages to identify changes in momentum. The MACD line is calculated by subtracting a 26-period EMA from a 12-period EMA. A signal line (a 9-period EMA of the MACD line) helps to identify potential buy or sell signals. A bullish crossover occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, while a bearish crossover signals the opposite.
Chart Patterns in Technical Analysis
Chart patterns are recurring formations in price charts that can suggest future price movements. Recognizing these patterns can provide valuable insights into potential trading opportunities. It’s important to remember that these patterns are not guaranteed predictors of future price action and should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis.
- Head and Shoulders: This reversal pattern suggests a potential shift from an uptrend to a downtrend. It’s characterized by three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being the highest, followed by lower peaks (the shoulders) on either side. A neckline connects the lows of the two shoulders. A break below the neckline often confirms the pattern and signals a potential sell opportunity.
- Triangles: These patterns typically indicate periods of consolidation before a breakout. Symmetrical triangles, ascending triangles, and descending triangles all have unique characteristics and implications for future price movements. A breakout above a triangle’s resistance line often signals a continuation of the uptrend, while a breakout below the support line suggests a continuation of the downtrend.
- Double Tops/Bottoms: These patterns are similar to head and shoulders but simpler. A double top suggests a potential reversal from an uptrend, while a double bottom indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend. A break below the neckline of a double top or above the neckline of a double bottom often confirms the pattern.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis focuses on price charts, fundamental analysis considers economic and political factors influencing asset prices. Combining both approaches can provide a more comprehensive view of the market. For example, a strong fundamental outlook for a currency, supported by positive economic data, could be reinforced by a bullish technical pattern, increasing the confidence in a long position. Conversely, a bearish technical pattern in conjunction with negative economic news could strengthen the case for a short position.
Candlestick Chart Elements
Candlestick charts provide a visual representation of price action over a specific period. Each candlestick represents a single period (e.g., one day, one hour). The body of the candlestick represents the price range between the open and close, while the wicks (shadows) extend from the body to show the high and low prices for that period. A green (or white) candlestick indicates a closing price higher than the opening price (bullish), while a red (or black) candlestick signifies a closing price lower than the opening price (bearish). The length of the body and wicks provides additional information about the strength of the price movement. Long bodies suggest strong price action, while short bodies indicate indecision or consolidation. Long upper wicks suggest selling pressure, while long lower wicks indicate buying pressure. Analyzing the patterns and relationships between consecutive candlesticks provides valuable insights into price trends and potential turning points. For instance, a series of long green candlesticks with short upper wicks would suggest a strong uptrend with relatively little selling pressure.
Demo Accounts and Practice
Before you risk your hard-earned cash in the volatile world of forex, mastering the ropes in a risk-free environment is crucial. This is where demo accounts shine – they’re your virtual forex playground, allowing you to experiment with strategies, refine your trading skills, and develop a feel for the market without the fear of financial loss. Think of it as your forex training wheels before hitting the open road.
Demo accounts provide a realistic simulation of the forex market, mirroring the actual trading conditions, including price movements, spreads, and order execution. This hands-on experience is invaluable for beginners, enabling them to understand market dynamics and test different trading strategies without the pressure of real-money consequences. By practicing on a demo account, you can identify your strengths and weaknesses, develop a robust trading plan, and build the confidence needed to transition to live trading.
Setting Up and Using a Demo Account
Most forex brokers offer free demo accounts. The process is typically straightforward and involves registering with the broker, providing some basic information, and choosing a demo account type. Once you’ve completed the registration, you’ll receive access to a virtual trading platform identical to the one used for live trading. You’ll be given a virtual sum of money (usually $10,000 or more) to practice with. Then, you can start placing trades, analyzing charts, and experimenting with different strategies. Remember to treat your demo account as if it were real money; this helps build discipline and consistency in your trading approach. Regularly review your trades, analyze your successes and failures, and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Tips for Effective Practice and Simulated Trading, Forex trading strategies for beginners
Effective practice on a demo account goes beyond simply placing random trades. It’s about developing a structured approach to learning and refining your skills. One crucial aspect is establishing a trading plan. This plan should Artikel your trading strategy, risk management rules, and entry/exit criteria. Sticking to your plan during simulated trading is vital, as it helps reinforce discipline and consistency, essential elements for long-term success in forex trading. Backtesting your strategies on historical data before implementing them on your demo account is also highly recommended. This helps you evaluate the potential performance of your strategy and identify any weaknesses before risking real capital. Finally, keep a trading journal to record your trades, including your reasoning, results, and lessons learned. This journal will become an invaluable resource as you progress in your forex trading journey.
Key Features of a Demo Account
A comprehensive understanding of the features offered by a demo account is essential for maximizing its learning potential. Here’s a list of key features you should expect:
- Realistic Market Conditions: Demo accounts replicate real-time market price fluctuations, spreads, and order execution, providing a realistic trading environment.
- Access to Trading Platform: You’ll gain access to the same trading platform used for live trading, allowing you to familiarize yourself with its tools and functionalities.
- Virtual Funds: Brokers typically provide a virtual sum of money (e.g., $10,000) to practice with, allowing you to experience trading without financial risk.
- Charting and Analysis Tools: Full access to charting tools and technical indicators, enabling you to analyze market trends and develop your trading strategies.
- Order Placement and Management: The ability to place and manage various order types (market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, etc.), mirroring real-world trading.
- Unlimited Practice: Demo accounts usually have no time limits, allowing you to practice as much as needed to develop your skills and confidence.
Choosing a Forex Broker
Picking the right forex broker is crucial for a successful trading journey. A bad broker can lead to frustrating experiences, including slippage, requotes, and even potential scams. Choosing wisely means understanding the different types of brokers and what factors contribute to their reliability.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Forex Broker
Selecting a forex broker involves careful consideration of several key aspects. These factors directly impact your trading experience, security, and overall profitability. Ignoring these points can lead to significant problems down the line.
- Regulation and Licensing: Ensure your broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority. This provides a layer of protection against fraudulent activities. Look for brokers regulated by bodies like the FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), or the CFTC/NFA (USA).
- Spreads and Commissions: These are the costs associated with trading. Compare spreads across different brokers; tighter spreads mean lower trading costs. Consider whether the broker charges commissions in addition to spreads.
- Trading Platform: A user-friendly and reliable trading platform is essential. Many brokers offer MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5), popular platforms known for their charting tools and functionalities. Consider ease of use, charting capabilities, and order execution speed.
- Account Types and Minimum Deposits: Brokers offer various account types catering to different trading styles and capital levels. Choose an account type that aligns with your trading goals and risk tolerance. Compare minimum deposit requirements.
- Customer Support: Reliable and responsive customer support is crucial, especially when dealing with issues or questions. Check the availability of support channels (phone, email, live chat) and their responsiveness.
- Leverage and Margin Requirements: Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. Understand the leverage offered and the margin requirements. High leverage can be risky for beginners.
- Educational Resources: Many brokers provide educational resources like webinars, tutorials, and market analysis. Access to such resources can be beneficial, especially for beginners.
Different Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers can be categorized into several types, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision.
| Broker Type | Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Maker | Acts as a counterparty to your trades. | Often offers tighter spreads and faster execution. | Potential for conflicts of interest. |
| ECN/STP Broker | Routes your orders to a network of liquidity providers. | Generally offers better pricing and transparency. | May have higher spreads and commissions. |
| Dealing Desk Broker | Intermediates trades, potentially influencing pricing. | Can offer personalized service. | Less transparency and potential for manipulation. |
| No Dealing Desk (NDD) Broker | Passes orders directly to the market without intervention. | Transparency and better pricing. | May require higher minimum deposits. |
Checklist for Evaluating Broker Reliability and Trustworthiness
Before committing to a forex broker, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence. This checklist helps assess the broker’s reliability and trustworthiness.
- Regulation Check: Verify the broker’s regulatory status with the relevant financial authority.
- Client Reviews and Testimonials: Read independent reviews and testimonials from other traders to gauge their experiences.
- Security Measures: Assess the broker’s security measures, including data encryption and account protection protocols.
- Transparency in Fees and Charges: Ensure the broker is transparent about all fees and charges associated with trading.
- Withdrawal Process: Check the broker’s withdrawal policies and the ease of withdrawing funds.
- Account Security Features: Verify the availability of two-factor authentication and other security features.
Outcome Summary
So, you’ve taken the first steps into the dynamic world of forex trading. Remember, consistent learning, disciplined risk management, and practice are your allies. While the potential for profit is enticing, forex trading demands respect and careful consideration. Don’t rush into live trading without thorough preparation. Use the knowledge gained here to build a solid foundation, and remember, consistent learning and adaptation are crucial for long-term success in this ever-evolving market. Happy trading!




