
Forex Trading Guide: Dive into the thrilling world of global currency markets! This isn’t your grandpa’s investing; we’re talking about trading trillions of dollars daily, fueled by economic shifts, political drama, and the ever-evolving dance of supply and demand. Get ready to unravel the secrets behind currency pairs, master technical and fundamental analysis, and learn strategies to navigate this high-stakes arena. Whether you’re a complete newbie or looking to sharpen your skills, this guide is your passport to forex success.
We’ll cover everything from understanding basic concepts like currency pairs and leverage to mastering advanced techniques like technical analysis and risk management. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to build a solid trading plan, choose the right platform, and, most importantly, protect your capital. Think of this as your ultimate cheat sheet for conquering the forex market – one trade at a time.
Introduction to Forex Trading

Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the global marketplace where currencies are bought and sold. It’s a decentralized, over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning there’s no central exchange. This massive market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across various global financial centers. Key participants include banks, corporations, governments, and individual traders, all seeking to profit from currency fluctuations.
Currency Pairs and Notation
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another. These exchanges are represented by currency pairs, using a standardized three-letter code. The first currency in the pair is the base currency, while the second is the quote currency. For example, EUR/USD represents the Euro (EUR) against the US dollar (USD). A quote of 1.1000 means that 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.1000 US dollars. Understanding this notation is fundamental to interpreting forex quotes and analyzing price movements.
Factors Influencing Forex Exchange Rates
Numerous factors influence the ever-shifting dynamics of forex exchange rates. Economic indicators, such as interest rates, inflation, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, play a crucial role. Government policies, including monetary and fiscal measures, also significantly impact currency values. Geopolitical events, like wars or political instability, can trigger sudden and substantial shifts in exchange rates. Market sentiment and speculation, driven by news and trader psychology, also contribute to price volatility. Finally, supply and demand forces, reflecting the relative scarcity and desirability of different currencies, are the underlying drivers of forex market movements. For example, strong economic growth in a country typically leads to increased demand for its currency, pushing its value higher against other currencies.
Types of Forex Trading Accounts
Choosing the right forex trading account is crucial for both beginners and experienced traders. Different account types cater to various trading styles and capital levels.
| Account Type | Leverage | Minimum Deposit | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demo Account | Variable, often similar to standard accounts | $0 | Practice trading with virtual funds; ideal for beginners. |
| Standard Account | High (e.g., 1:100, 1:500) | Varies by broker, often several hundred dollars | Suitable for experienced traders with larger capital. Offers higher leverage and potential profits, but also higher risk. |
| Mini Account | High (e.g., 1:100, 1:500) | Lower than standard accounts (e.g., $100 – $500) | A good starting point for traders with limited capital who want to experience real market conditions. |
| Micro Account | High (e.g., 1:100, 1:500) | Very low (e.g., $50 or less) | Best for beginners with very limited capital. Allows exposure to forex trading with minimal financial commitment. |
Fundamental Analysis in Forex
Understanding the forces that drive currency values is crucial for successful forex trading. Fundamental analysis dives deep into the economic and political factors influencing these movements, offering a longer-term perspective compared to technical analysis. By analyzing these underlying factors, traders can anticipate potential shifts in currency pairs and make informed trading decisions.
Economic Indicators and Currency Values
Economic indicators paint a picture of a nation’s economic health, directly impacting its currency’s value. A strong economy generally supports a strong currency. For example, a high Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate suggests a thriving economy, attracting foreign investment and increasing demand for the country’s currency. Conversely, a low GDP growth rate or a recession can weaken a currency. Inflation, representing the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, also plays a significant role. High inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to a currency devaluation. Interest rates, set by a country’s central bank, influence investment flows. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency, while lower rates can have the opposite effect. The interplay of GDP, inflation, and interest rates creates a complex but predictable dynamic influencing currency values.
Political Events and Global News
Geopolitical events and global news headlines can trigger sudden and significant shifts in the forex market. Unexpected political changes, such as elections, regime shifts, or major policy announcements, can create volatility. For instance, a surprise policy change regarding trade tariffs could significantly impact the value of the currencies involved. Similarly, global crises, such as wars or pandemics, can drastically alter market sentiment and cause substantial currency fluctuations. News affecting investor confidence, like unexpected corporate earnings reports or major shifts in global markets, also play a crucial role in forex price movements. Traders must constantly monitor global news and political developments to anticipate potential market reactions.
Fundamental Analysis Techniques
Various techniques exist within fundamental analysis. One approach focuses on comparing a nation’s economic indicators against its peers. For example, comparing the inflation rate of the US against that of the Eurozone provides insights into the relative value of the USD and EUR. Another approach involves examining a country’s balance of payments, which tracks its international transactions. A consistent trade deficit (more imports than exports) can put downward pressure on a currency. Finally, some analysts employ sentiment analysis, gauging market confidence through news articles, surveys, and other qualitative data. The choice of technique often depends on the trader’s experience, risk tolerance, and trading style.
Hypothetical Scenario: Impact of a Major Economic Event
Let’s imagine a scenario where the US Federal Reserve unexpectedly announces a significant interest rate hike. This event would likely lead to increased demand for the US dollar (USD). Investors seeking higher returns would flock to USD-denominated assets, pushing up the value of the USD against other currencies, such as the Euro (EUR). For example, the EUR/USD exchange rate (the value of one Euro in US dollars) could fall, perhaps from 1.10 to 1.08, reflecting the increased strength of the dollar. This scenario highlights how a single economic event can significantly impact currency pairs, demonstrating the importance of fundamental analysis in forex trading.
Technical Analysis in Forex
Technical analysis is the art of predicting future price movements based on past market data. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on economic indicators and news events, technical analysis uses charts and indicators to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential trading opportunities. It’s a powerful tool, but remember, no method guarantees success in the volatile world of forex.
Candlestick Charts and Interpretation
Candlestick charts are a visual representation of price movements over a specific period. Each candle represents a timeframe (e.g., 1 hour, 1 day), showing the opening, closing, high, and low prices. The body of the candle indicates the range between the opening and closing prices. A green (or white) candle signifies a closing price higher than the opening price (bullish), while a red (or black) candle shows a closing price lower than the opening price (bearish). The wicks, or shadows, extending above and below the body, represent the high and low prices for that period. By analyzing the patterns formed by these candles, traders can identify potential trend reversals, continuations, and support/resistance levels. For example, a long green candle with a small wick suggests strong buying pressure, while a series of small candles with indecisive wicks may signal uncertainty or a potential breakout.
Common Technical Indicators
Technical indicators provide quantitative data to supplement visual analysis of candlestick charts. They help confirm trends, identify potential overbought or oversold conditions, and generate buy/sell signals.
Here are three commonly used indicators:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, highlighting the underlying trend. A simple moving average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific number of periods, while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. A crossover of a short-term moving average above a long-term moving average is often seen as a bullish signal, while the opposite suggests a bearish trend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. Readings above 70 are generally considered overbought, suggesting a potential price correction, while readings below 30 indicate oversold conditions, potentially signaling a price rebound. However, it’s crucial to remember that RSI can remain in overbought or oversold territory for extended periods.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): The MACD is a momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. It consists of a MACD line (difference between two EMAs) and a signal line (EMA of the MACD line). Crossovers of the MACD line above the signal line are considered bullish signals, while crossovers below are bearish. Divergences between the MACD and the price action can also provide valuable insights into potential trend reversals.
Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are recurring formations on price charts that often precede specific price movements. Recognizing these patterns can provide clues about potential future price direction.
Some common chart patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: This pattern resembles a head with two shoulders on either side. A neckline connects the lows of the two shoulders. A break below the neckline is often considered a bearish signal.
- Triangles: Triangles are characterized by converging trendlines. Symmetrical triangles suggest continuation of the existing trend, while ascending triangles are bullish and descending triangles are bearish. Breakouts from triangles often lead to significant price movements.
- Flags: Flags are characterized by a sharp price move followed by a period of consolidation, represented by a rectangular or pennant-shaped pattern. A breakout from the flag often continues in the direction of the initial price move.
Using Technical Analysis to Identify Trading Opportunities
A step-by-step guide to using technical analysis for identifying potential trading opportunities involves a combination of chart pattern recognition and indicator confirmation.
- Identify the Trend: Determine the overall trend using moving averages or other trend-following indicators. Are we in an uptrend, downtrend, or sideways market?
- Look for Chart Patterns: Identify potential chart patterns such as head and shoulders, triangles, or flags. These patterns can provide insights into potential trend reversals or continuations.
- Confirm with Indicators: Use indicators like RSI and MACD to confirm the signals suggested by chart patterns. For example, a bullish chart pattern confirmed by an RSI reading below 30 and a bullish MACD crossover might suggest a strong buying opportunity.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Always protect your capital by setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Take-profit orders help you lock in profits once your target price is reached. The placement of these orders should be based on your risk tolerance and the identified support and resistance levels.
- Monitor and Manage Trades: Continuously monitor your trades and be prepared to adjust your strategy based on market conditions. Trailing stop-losses can help protect profits as the price moves in your favor.
Forex Trading Strategies: Forex Trading Guide
Choosing the right forex trading strategy is crucial for success. Your strategy dictates your timeframe, risk tolerance, and ultimately, your profitability. Different strategies suit different traders, depending on their experience, available time, and risk appetite. Let’s explore some popular approaches.
Scalping
Scalping involves making numerous trades throughout the day, profiting from small price fluctuations. Traders aim for quick profits, often holding positions for mere seconds or minutes. This high-frequency approach requires intense focus, rapid execution, and a low tolerance for risk. Successful scalpers rely heavily on technical analysis, charting patterns, and precise entry/exit points. A successful scalping strategy might involve identifying a short-term trend using moving averages and taking advantage of minor price movements, aiming for pips (the smallest price increment in forex) rather than significant percentage gains. The risk is high due to the frequent trades and potential for rapid losses if market conditions change unexpectedly. However, the reward can be substantial if executed correctly, leading to high frequency of small wins.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within a single trading day. Unlike scalping, day traders typically hold positions for hours, aiming to profit from larger price swings. Technical analysis plays a significant role, with traders using indicators like RSI, MACD, and moving averages to identify potential trading opportunities. A successful day trading strategy might involve identifying a support or resistance level and placing a trade based on the anticipated price breakout. The risk is lower than scalping, but still significant, as overnight market movements are avoided, minimizing potential overnight gaps. The reward is potentially higher than scalping but still lower than swing trading on a per-trade basis.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks, aiming to capitalize on medium-term price trends. This approach requires less time commitment than day trading or scalping but necessitates a more thorough understanding of fundamental and technical analysis. Traders often use chart patterns, support and resistance levels, and indicators to identify potential entry and exit points. A successful swing trading strategy might involve identifying a trend reversal pattern, such as a head and shoulders pattern, and placing a trade based on the anticipated price movement. The risk is generally lower than scalping and day trading, allowing for more time to react to market changes. However, the reward potential is higher per trade, though the frequency of trades is much lower.
Risk Management Techniques
Effective risk management is paramount in forex trading, regardless of the chosen strategy. Two essential tools are stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Stop-loss orders automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
Take-profit orders automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, securing profits.
Using these orders helps to manage risk and protect capital. Proper position sizing is also crucial; never risk more than a small percentage of your trading capital on any single trade.
Comparison of Forex Trading Strategies
| Strategy | Timeframe | Risk | Reward |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalping | Seconds to minutes | High | Low per trade, high frequency |
| Day Trading | Hours | Medium | Medium |
| Swing Trading | Days to weeks | Low | High per trade, low frequency |
Forex Trading Platforms and Tools
Choosing the right forex trading platform is crucial for success. Your platform is your command center, impacting everything from order execution speed to the quality of your analysis. Understanding the features and functionalities of different platforms is key to optimizing your trading experience.
MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader: A Comparison
These three platforms dominate the forex market, each offering a unique set of features. MT4, a veteran in the field, is known for its simplicity and wide availability. MT5, its successor, boasts enhanced charting capabilities and more advanced order types. cTrader stands out with its speed and sophisticated algorithmic trading capabilities. The choice depends heavily on your individual trading style and needs.
Charting Tools: The Visual Heart of Forex Trading
Charting tools are indispensable for technical analysis. They allow you to visualize price movements, identify trends, and spot potential trading opportunities. Features like different chart types (candlestick, bar, line), technical indicators (moving averages, RSI, MACD), and drawing tools (trend lines, Fibonacci retracements) are crucial for effective analysis. A good platform will offer a wide array of customizable charting options to suit diverse trading strategies. For example, a trader using a moving average crossover strategy would heavily rely on the platform’s ability to easily display and adjust multiple moving averages on their charts.
Economic Calendars: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Economic calendars provide a schedule of upcoming economic news releases, such as Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) reports, inflation data, and interest rate decisions. These events can significantly impact currency prices, creating volatility that savvy traders can exploit. A reliable economic calendar integrated into your trading platform offers crucial information on the potential impact of these events, allowing you to anticipate market movements and adjust your trading strategies accordingly. For instance, a trader anticipating a significant interest rate hike might adjust their positions to profit from the expected currency appreciation.
News Feeds: Real-Time Market Intelligence
Real-time news feeds provide up-to-the-minute information on global events and their impact on the forex market. Major political events, geopolitical tensions, and unexpected economic announcements can all cause significant price swings. Access to reliable news feeds directly within your trading platform allows for immediate reaction to market-moving events. For example, a sudden geopolitical crisis reported in a news feed could trigger a trader to close a position to limit potential losses.
Choosing the Right Forex Trading Platform: A Practical Guide
Selecting the appropriate platform requires careful consideration of your individual needs and trading style. Begin by assessing your technical skills and trading experience. Beginners might prefer a user-friendly platform like MT4, while experienced traders might favor the advanced features of MT5 or cTrader. Consider the platform’s charting tools, the availability of automated trading systems (Expert Advisors or EAs), the quality of its news and economic calendar feeds, and the speed of order execution. Furthermore, check the platform’s reputation, reliability, and customer support. Ultimately, the best platform is the one that best suits your trading strategy and helps you achieve your financial goals. Demo accounts are invaluable tools for testing different platforms before committing to a live account.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, is inherently risky. Ignoring risk management is akin to sailing a ship without a compass – you might get lucky, but the odds are stacked against you. Successful forex traders understand that consistent profitability relies not just on making winning trades, but on meticulously managing potential losses. This section delves into the crucial aspects of safeguarding your capital and navigating the volatile forex market.
The Importance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is paramount in forex trading. It’s not about avoiding losses entirely—that’s impossible. Instead, it’s about controlling the size and frequency of those losses, ensuring they don’t wipe out your trading account. A robust risk management plan allows you to participate in the market confidently, knowing you have a safety net in place. Without it, even a single bad trade can be devastating. Consider it your financial airbag – protecting you from the inevitable bumps in the road.
Risk Management Strategies
Several strategies contribute to a comprehensive risk management plan. These strategies work best when implemented in conjunction with each other, creating a layered defense against potential losses.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how much capital you allocate to each individual trade. It’s a cornerstone of risk management, directly impacting the potential loss on any given trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on a single trade. For example, with a $10,000 account, a 1% risk would limit your potential loss to $100 per trade. This ensures that even a series of losing trades won’t severely deplete your account. Calculating position size requires understanding your stop-loss order (discussed below) and the pip value of your trading instrument.
Diversification
Diversification, the practice of spreading your investments across different currency pairs or asset classes, reduces overall portfolio risk. Instead of concentrating your capital in a single currency pair, you diversify across several, hedging against potential losses in any one area. For instance, instead of solely trading EUR/USD, you might include GBP/USD and USD/JPY in your portfolio. This reduces the impact of a downturn in a specific pair on your overall performance.
Leverage and its Impact
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. While it allows you to control larger positions with smaller capital, it also amplifies the risk. A high leverage ratio (e.g., 1:500) can lead to significant losses if the market moves against you. Understanding your leverage and using it responsibly is crucial. For example, a 1:100 leverage means that for every $1 you have in your account, you can control $100 worth of currency. A small market movement against you can quickly erase your capital with high leverage. Therefore, it is advisable to use lower leverage to minimize risks.
Managing Risk in Different Market Conditions
Risk management adapts to changing market conditions. During periods of high volatility, reducing position size and increasing stop-loss levels is prudent. Conversely, during calmer periods, you might slightly increase your position size while maintaining tight stop losses. For example, during times of geopolitical uncertainty, which often leads to heightened volatility, traders might reduce their position size to 0.5% of their account balance to mitigate the impact of sudden, sharp price movements. Conversely, during periods of low volatility, traders may increase their position size, but only within the confines of their pre-defined risk tolerance. Always adapt your strategy to the current market sentiment and conditions.
Understanding Leverage and Margin
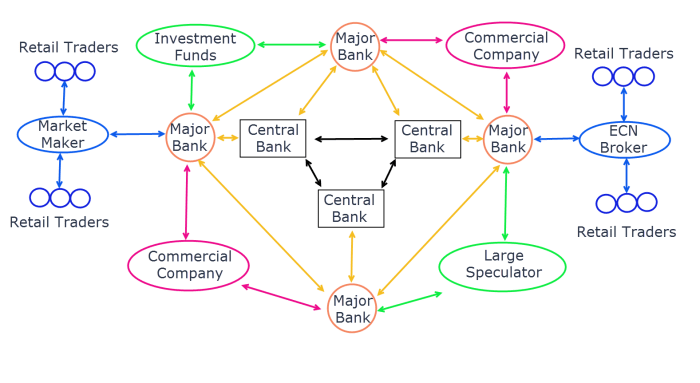
Forex trading offers the exciting possibility of substantial profits, but it also carries significant risks. A key element influencing both potential gains and losses is the use of leverage and margin. Understanding these concepts is crucial for responsible and successful trading.
Leverage in forex trading essentially allows you to control a larger position in the market than your actual capital would normally permit. This is achieved by borrowing funds from your broker. Think of it like using a lever to lift a heavy object – you’re amplifying your trading power. However, this amplification works both ways, magnifying both profits and losses.
Leverage Explained
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 1:100 or 50:1. A 1:100 leverage ratio means that for every $1 you have in your account, you can control $100 worth of currency. This allows you to participate in larger trades, potentially increasing your profit margins. However, the same leverage magnifies your losses proportionally. For example, with 1:100 leverage, a 1% move against your trade would wipe out 100% of your initial capital.
Margin Requirements
Margin is the amount of money you need to deposit in your trading account to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as collateral for the borrowed funds. The margin requirement is determined by your broker and the specific trade you’re undertaking. The broker holds this margin as security, ensuring that you can cover potential losses. If your trade moves against you and your account balance falls below a certain level (the margin call level), the broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit more funds to maintain your position. Failure to meet a margin call can lead to your position being liquidated, meaning the broker closes your trade to limit their risk.
Risks of High Leverage Trading
While leverage can boost profits, it significantly increases the risk of substantial losses. High leverage magnifies the impact of even small market movements. A seemingly small price fluctuation can quickly lead to substantial losses, potentially exceeding your initial investment. This is why proper risk management is paramount when using leverage. Many traders, especially beginners, are attracted to high leverage because it seems to promise quick riches, but it’s a double-edged sword.
Leverage Examples
Let’s illustrate with examples. Suppose you have $1000 in your trading account and use a 1:100 leverage.
Example 1: Profitable Trade
You buy 100,000 units of EUR/USD at 1.1000. The price rises to 1.1050 (a 0.5% increase). Your profit is 100,000 * (1.1050 – 1.1000) = $500. This represents a 50% return on your initial investment, significantly amplified by the leverage.
Example 2: Unprofitable Trade
You buy 100,000 units of EUR/USD at 1.1000. The price falls to 1.0950 (a 0.5% decrease). Your loss is 100,000 * (1.1000 – 1.0950) = $500. This represents a 50% loss on your initial investment.
These examples clearly demonstrate the double-edged sword of leverage. While it can exponentially increase profits, it can just as easily lead to significant losses, potentially wiping out your entire account balance. Therefore, responsible leverage usage and careful risk management are crucial.
Common Forex Trading Mistakes
So, you’ve learned the basics of forex trading – fundamental and technical analysis, risk management, leverage, the works. You’re ready to conquer the markets, right? Hold your horses! Even seasoned traders make mistakes. Beginners, however, often stumble into pitfalls that can quickly wipe out their accounts. Understanding these common errors and how to avoid them is crucial for long-term success. This section will highlight some of the most frequent missteps and offer strategies to navigate them effectively.
Many beginners dive headfirst into forex trading without a solid understanding of the market’s complexities. This lack of preparation, coupled with emotional trading and poor risk management, often leads to significant losses. Understanding these common mistakes and implementing preventative measures is essential for sustainable profitability.
Ignoring Risk Management
Ignoring proper risk management is arguably the biggest mistake novice traders make. This involves failing to set stop-loss orders, over-leveraging positions, or not having a well-defined trading plan that includes position sizing. The consequences can range from small losses to the complete depletion of your trading account. A proper risk management strategy should always limit potential losses to a manageable percentage of your overall capital, typically no more than 1-2% per trade. This ensures that even a series of losing trades won’t cripple your account.
Overtrading
Overtrading, or making too many trades too frequently, is another common pitfall. The allure of quick profits often leads beginners to jump into multiple trades simultaneously, without sufficient analysis or understanding of the market’s current conditions. This can lead to emotional decision-making, increased stress, and ultimately, significant losses. A well-defined trading plan with clear entry and exit strategies, along with patience and discipline, can help mitigate the risk of overtrading.
Emotional Trading
Letting emotions dictate trading decisions is a recipe for disaster. Fear and greed are powerful forces that can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive actions. Fear can cause traders to prematurely close profitable positions, while greed can lead to holding onto losing trades for too long, hoping for a reversal. Developing a disciplined approach, sticking to your trading plan, and practicing mindfulness can help you overcome emotional trading.
Lack of a Trading Plan, Forex trading guide
Trading without a well-defined plan is like sailing a ship without a map. A trading plan should Artikel your trading goals, risk tolerance, preferred strategies, and entry/exit rules. Without a plan, you’re essentially gambling, and the odds are stacked against you. Creating a detailed trading plan, and consistently adhering to it, will significantly increase your chances of success.
Ignoring Market Conditions
The forex market is dynamic and constantly changing. Ignoring significant geopolitical events, economic data releases, or shifts in market sentiment can severely impact your trades. Staying informed about current market conditions and adapting your strategies accordingly is crucial for success. Following reputable financial news sources and understanding the impact of global events on currency pairs is essential.
Tips for Successful Forex Trading
Developing a successful forex trading strategy requires a combination of knowledge, discipline, and consistent effort. Here are some key tips to guide you:
- Thorough Research and Education: Before risking any capital, invest time in learning about forex trading, different trading strategies, and risk management techniques.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining your trading goals, risk tolerance, and preferred strategies. This plan should act as your roadmap.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Use a demo account to test your strategies and gain experience without risking real money. This allows you to learn from mistakes without financial consequences.
- Manage Risk Effectively: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade. Never risk more than a small percentage of your capital on any single trade (1-2%).
- Be Patient and Disciplined: Avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions. Stick to your trading plan and avoid overtrading.
- Continuously Learn and Adapt: The forex market is constantly evolving. Stay updated on market trends and adapt your strategies accordingly.
- Keep a Trading Journal: Record your trades, including your rationale, entry and exit points, and the results. This will help you analyze your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Mentorship or Guidance: Consider seeking guidance from experienced traders or joining a forex trading community.
Developing a Trading Plan

A solid forex trading plan is your roadmap to success. It’s not just a wish list; it’s a detailed strategy that Artikels your goals, approach, and risk management techniques. Without a plan, you’re essentially gambling, increasing the likelihood of significant losses. A well-defined plan provides structure, discipline, and a framework for consistent decision-making, even during volatile market conditions.
Key Components of a Forex Trading Plan
A comprehensive forex trading plan encompasses several crucial elements. These components work together to create a cohesive strategy that guides your trading activities and helps you achieve your financial objectives. Ignoring any of these aspects can significantly increase your risk.
- Trading Goals: Clearly define your short-term and long-term financial objectives. Are you aiming for a specific profit target, or focusing on capital preservation? Quantifiable goals are essential.
- Trading Style: Determine your preferred trading approach – scalping, day trading, swing trading, or position trading. Each style requires a different level of time commitment and risk tolerance.
- Market Analysis: Specify the methods you’ll use to analyze the market, such as fundamental analysis (examining economic indicators and news events) or technical analysis (using charts and indicators to identify trading opportunities).
- Risk Management: Artikel your risk tolerance and strategies for managing losses. This includes setting stop-loss orders, determining position sizing, and defining your maximum acceptable drawdown.
- Trading Strategy: Detail your specific entry and exit rules for each trade. This should include clear criteria for identifying potential trades and managing your positions.
- Trading Journal: Maintain a detailed record of your trades, including entry and exit points, profits and losses, and reasons for your decisions. This helps you track your performance and identify areas for improvement.
Creating a Personalized Forex Trading Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing your plan involves a methodical process. Take your time and ensure each component aligns with your personality, resources, and risk tolerance. Rushing this process often leads to poorly conceived strategies.
- Define Your Goals: Set realistic and measurable financial goals. For example, aim for a 10% return on your investment within a year, or a specific monthly profit target.
- Choose Your Trading Style: Select a trading style that suits your lifestyle and risk tolerance. Scalping requires constant monitoring, while swing trading allows for more flexibility.
- Develop Your Market Analysis Method: Decide whether to focus on fundamental or technical analysis, or a combination of both. Learn the techniques and indicators relevant to your chosen method.
- Establish Your Risk Management Rules: Determine your maximum acceptable loss per trade and overall account drawdown. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Artikel Your Trading Strategy: Define your entry and exit signals, including specific price levels, indicators, and chart patterns.
- Backtest Your Strategy: Test your strategy on historical data to evaluate its effectiveness and identify potential weaknesses.
- Implement and Monitor: Begin trading with a small amount of capital and closely monitor your results. Adjust your plan as needed based on your performance and market conditions.
Examples of Successful Trading Plans
While specific plans vary greatly depending on individual circumstances, successful plans consistently incorporate robust risk management and a well-defined trading strategy. One example might be a day trader focusing on currency pairs with high liquidity, using technical indicators to identify short-term trends and setting tight stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Another example could be a swing trader employing fundamental analysis to identify long-term trends in emerging market currencies, holding positions for several weeks or months and using trailing stop-losses to protect profits. The key is consistency and discipline in adhering to the plan’s guidelines.
Forex Trading Plan Template
This template provides a framework for creating your personalized trading plan. Remember to fill in the details specific to your trading style and risk tolerance.
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Trading Goals | (e.g., 10% annual return, $500 monthly profit) |
| Trading Style | (e.g., Day trading, Swing trading) |
| Market Analysis Method | (e.g., Technical analysis using RSI and MACD) |
| Risk Management | (e.g., 2% risk per trade, maximum 10% drawdown) |
| Trading Strategy | (e.g., Buy EUR/USD when RSI crosses below 30 and MACD shows a bullish crossover) |
| Entry Rules | (Specific price levels, indicators, chart patterns) |
| Exit Rules | (Specific price levels, indicators, chart patterns, time-based exits) |
| Position Sizing | (e.g., 1% of account equity per trade) |
| Stop-Loss Order | (e.g., Place stop-loss orders at a predetermined price level) |
| Take-Profit Order | (e.g., Place take-profit orders at a predetermined price level) |
| Trading Journal | (Record of all trades, including entry/exit points, profits/losses, reasons for trades) |
Last Word
So, there you have it – your comprehensive guide to navigating the dynamic world of forex trading. Remember, consistent learning, disciplined risk management, and a well-defined trading plan are your keys to success. The forex market offers incredible opportunities, but it also presents significant risks. By understanding these risks and employing the strategies Artikeld here, you can significantly improve your chances of achieving your financial goals. Now, go forth and trade wisely!
Notice forex trading signal for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Explore the different advantages of forex trading seminar that can change the way you view this issue.




